Abstract
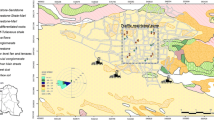
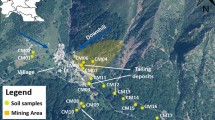
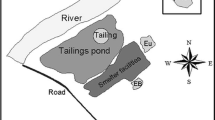
Bioaccessibility of lead (Pb) and cadmium (Cd) was conducted in soil samples collected from a dirt road that connects a former Pb and zinc (Zn) beneficiation and smelting plant in the city of Adrianópolis (Paraná state, southern Brazil). Samples were taken in three sites (beneficiation plant, slag deposit, and near Adrianópolis downtown). Samples were air-dried and sieved (< 0.074, 0.074, 0.42, 0.589, 0.84, 1.00, 1.41, 2.00, 2.83, 3.36, 4.00, and 4.76 mm) and subjected to gastric bioaccessibility tests using 0.4 M glycine. The results were analyzed using the estimated daily intake (considering adult and child targets) and target hazard quotient (THQ) considering the exposure of 100 and 1700 mg day−1. The concentration of bioaccessible Pb (0.00–2818.25 mg kg−1) was significantly higher than Cd (0.00–1.28 mg kg−1), with alarming concentrations predominantly in the finer particles near the slag deposit (< 2.83 mm) and the former beneficiation (< 0.589 mm). The bioaccessible fraction (BAFs) varied from 0 to 20.7% (Cd) and 0 to 126.7% (Pb). Considering the 100 mg day−1 scenario, Pb is a key contaminant in the slag deposit sample, while in the 1700 mg day−1 scenario, Pb is a key contaminant in the slag deposit and the beneficiation sample. The maximum soil and dust intake considering Pb and Cd bioaccessible concentration is critical in the deposit sample, where values varied from 12.8 to 1272.7 mg day−1. The Pb gastric bioaccessible fraction is higher in finer fractions, and these fractions (especially, < 0.074 and 0.074 mm) are more subjected to adhering in the skin and being ingested, which represents a risk to the population that uses this dirt road. Oral bioaccessiblity in mining contaminated areas is usually conducted with fine or particulate matter, and the study with soil fractioning is rare. In this study, soil fractioning was used to verify the portions that are more subjected to Pb and Cd gastric bioaccessibility in a metal-contaminated area. The fine and coarse fractions present several risks according to the THQ, and in the case of incidental ingestion can pose a health risk.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated during this study are demonstrated in the form of tables and/or figures.
References
Bosso, S. T., & Enzweiler, J. (2008). Bioaccessible lead in soils, slag, and mine wastes from an abandoned mining district in Brazil. Environmental Geochemical and Health, 30, 219–229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-007-9110-4
Buschle, B. N., Palmeiro, J. K., Sade, Y. B., de Melo, V. F., de Andrade, M. G., & Batista, A. H. (2010). Kinetics of lead release from soils in heavy metal mining and metallurgy area. Revista Brasileira de Ciências do Solo, 34, 1865–1874.
Caballero-Gallardo, K., Palomares-Bolaños, J., & Olivero-Verbel, J. (2022). Mercury concentrations in water, sediments, soil, and fish around ancestral Afro-descendant territories impacted by gold mining in the Cauca Department, Colombia. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 233, 393. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05779-3
Cetin, M., Pekkan, O. I., Ozturk, G. B., & Kurkcuoglu, M. A. S. (2022). Examination of the change in the vegetation around the Kirka Boron mine site by using remote sensing techniques. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 233, 254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05738-y
Chu, Z., Lin, C., Yang, K., Cheng, H., Gu, X., Wang, B., Wu, I., & Ma, J. (2022). Lability, bioaccessibility, and ecological and health risks of anthropogenic toxic heavy metals in the arid calcareous soil around a nonferrous metal smelting area. Chemosphere, 307(Part 4), 136200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.136200
Crescêncio, S. (2001). Bioacessibilidade, geoacumulação e risco ecológico de elementos potencialmente tóxicos em resíduos de mineração – Adrianópolis. Undergraduate thesis. São Carlos School of Engineering, São Paulo University
Cunha, F. G. (2003). Contaminação Humana e Ambiental por Chumbo no Vale do Ribeira, nos Estados de SP e PR, BR. Doctorate thesis. Campinas, State University of Campinas
Daitx, E. C. (1996). Origem e evolução dos depósitos sulfetados tipo Perau (Pb-Zn-Ag) com base nas jazidas Canoas e Perau (Vale do Ribeira, PR). Doctorate thesis. University of São Paulo. 453
de Andrade, M. G., de Melo, V. F., de Souza, L. C. P., Gabardo, J., & Reissmann, C. B. (2009). Heavy metals in soils of a lead mining and metallurgy area. II - forms and plant availability. Revista Brasileira de Ciências do Solo, 33, 1889–1897.
de Melo, V. F., de Andrade, M., Batista, A. H., & Favaretto, N. (2012). Lead and Zinc in water and sediments of a metal mining and metallurgy area. Química Nova, 35(1), 22–29.
Espinoza, S. E., Quiroz, I. A., Magni, C. R., & Yáñez, M. A. (2022). Long-term effects of copper mine tailings on surrounding soils and sclerophyllous vegetation in Central Chile. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 233, 288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05782-8
Ettler, V., Stepanek, D., Mihaljevic, M., Drahota, P., Jedlicka, R., Kříbek, B., Vanek, A., Penizek, V., Sracek, O., & Nyambe, I. (2020). Slagdust from Kabwe (Zambia): Contaminant mineralogy and oral bioaccessibility. Chemosphere, 260, 127642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127642
Ettler, V., Cuhlova, M., Jarosikova, A., Mihaljevic, M., Drahota, P., Kříbek, B., Vanek, A., Penizek, V., Sracek, O., Klementova, M., Engel, Z., Kamona, F., & Mapani, B. (2019). Oral bioaccessibility of metal(loid)s in dust materials from mining areas of northern Namibia. Environmental International, 124, 205–2015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.12.027
Ettler, V., Kříbek, B., Majer, V., Knési, I., & Mihaljevic, M. (2012). Differences in the bioaccessibility of metals/metalloids in soils from mining and smelting areas (Copperbelt. Zambia). Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 113, 67–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2011.08.001
Ettler, V., Johan, Z., Kříbek, B., Sebek, O., & Mihaljevic, M. (2009). Mineralogy and environmental stability of slags from the Tsumeb smelter Namibia. Applied Geochemistry, 24(1), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2008.10.003
Fleming, C., Belmer, N., Reynolds, J. K., Robba, L., Davies, P. J., & Wright, I. A. (2022). Legacy contamination of river sediments from four decades of coal mine effluent inhibits ecological recovery of a polluted world heritage area river. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 233, 15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05487-4
Goix, S., Uzu, G., Oliva, P., Barraza, F., Calas, A., Castet, S., Point, D., Masbou, J., Duprey, J. L., Huayta, C., Chincheros, J., & Gardon, J. (2016). Metal concentration and bioaccessibility in different particle sizes of dust and aerosols to refine metal exposure assessment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 317, 552–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.05.083
Guimarães, V. (2007) Resíduos de mineração e metalurgia: Efeitos poluidores em sedimentos e em espécie biomonitoa – rio Ribeira de Iguape - SP. Doctorate thesis. University of São Paulo. 106
Guimarães, V., & Sígolo, J. B. (2008). Associação de resíduos da metalurgia com sedimentos em suspensão - Rio Ribeira de Iguape. Geologia USP. Série Científica, 8(2), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.5327/Z1519-874X2008000200001
Hamel, S. C., Ellickson, K. M., & Lioy, P. J. (1999). The estimation of the bioaccessibility of heavy metals in soils using artificial biofluids by two novel methods: Mass-balance and soil recapture. Science of the Total Environment, 15(243–244), 273–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0048-9697(99)00402-7
Hazou, E., Patchali, T. E., Konzou, E., Kola, P., Zorko, B., Moyo, M. N., & Tchakpele, P. K. (2022). Radiological assessment and statistical approaches of natural radionuclides in soil samples related to phosphate ore activities in the site of Dagbati, southern region of Togo. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 233, 237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05700-y
Heiman, J. A., Tran, I. T., Behlke-Entwisle, M., Pavlowsky, R. T., & Kisson, L. T. (2022). Metal accumulation in American sycamores in a mining-contaminated river in Southeastern Missouri. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 233, 125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05586-w
Helser, J., Vassilieva, E., & Cappuyns, V. (2022). Environmental and human health risk assessment of sulfidic mine waste: Bioaccessibility, leaching and mineralogy. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 424(Part A), 127313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127313
Hund-Rinke, K., & Kördel, W. (2003). Underlying issues in bioaccessibility and bioavailability: Experimental methods. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 56, 52–62.
Ju, T., Liang, Z., Liu, W., Li, B., Huang, R., & Geng, T. (2022). Monitoring of air pollution by remote sensing in Lanzhou City from 2010 to 2019. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 233, 359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05830-3
Kasemodel, M. C., Lima, J. Z., Sakamoto, I. K., Varesche, M. B. A., Trofino, J. C., & Rodrigues, V. G. S. (2016). Soil contamination assessment for Pb, Zn and Cd in a slag disposal area using integration of geochemical and microbiological data. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188, 697–720. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5708-2
Kasemodel, M. C., Papa, T. B. R., Sígolo, J. B., & Rodrigues, V. G. S. (2019a). Assessment of the mobility, bioaccessibility, and ecological risk of Pb and Zn on a dirt road located in a former mining area – Ribeira Valley – Brazil. Environmental Monitoring Assessment, 191, 100–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7238-1
Kasemodel, M. C., Sakamoto, I. K., Varesche, M. B. A., & Rodrigues, V. G. S. (2019b). Potentially toxic metal contamination and microbial community analysis in an abandoned Pb and Zn mining waste deposit. Science of the Total Environment, 675, 367–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.223
Kříbek, B., Nyambe, I., Majer, V., Knési, I., Mihaljevic, M., Ettler, V., Vanek, A., Penízek, V., & Sracek, O. (2019). Soil contamination near the Kabwe Pb-Zn smelter in Zambia: Environmental impacts and remediation measures proposal. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 197, 159–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2018.11.018
Kříbek, B., Majer, V., Knésl, I., Keder, J., Mapani, B., Kamona, F., Mihaljevič, M., Ettler, V., Penížek, V., Vaněk, A., & Sracek, O. (2016). Contamination of soil and grass in the Tsumeb smelter area, Namibia: Modeling of contaminants dispersion and ground geochemical verification. Applied Geochemistry, 64, 75–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2015.07.006
Kummer, L., de Melo, V. F., Barros, Y. J., & de Azevedo, J. C. R. (2011). Sequential extraction of lead and zinc from soils of heavy metal mining and processing area. Revista Brasileira de Ciências do Solo, 35, 2005–2018.
Li, Y., Padoan, E., & Ajmone-Marsan, F. (2021). Soil particle size fraction and potentially toxic elements bioaccessibility: A review. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 209, 111806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111806
Liu, J., Wang, Y., Wang, Y., Li, Y., Li, H., Xu, J., & Liu, X. (2022). Novel insights into probabilistic health risk and source apportionment based on bioaccessible potentially toxic elements around an abandoned e-waste dismantling site. Science of The Total Environment, 838(Part 3), 156372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156372
Marques, J. P., da Ferreira Silva, E. A., Patinha, C., Kasemodel, M. C., & Rodrigues, V. G. S. (2019). Adsorption of lead (Pb) in weathered tropical soil (Ribeira Valley region - Brazil). Earth Sciences Research Journal, 23(4), 385–395. https://doi.org/10.15446/esrj.v23n4.77869
Ng, J. C., Juhasz, A., Smith, E., & Naidu, R. (2015). Assessing the bioavailability and bioaccessibility of metals and metalloids. Environmental Science Pollution Research, 22, 8802–8825. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1820-9
Padoan, E., Romè, C., Mehta, N., Dino, G. A., De Luca, D. A., & Ajmone-Marsan, F. (2021). Bioaccessibility of metals in soils surrounding two dismissed mining sites in Northern Italy. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 18, 1349–1360. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02938-z
Panagos, P., Van Liedekerke, M., Yigini, Y., & Montanarella, L. (2013). Contaminated sites in Europe: Review of the current situation based on data collected through a European Network. Journal of Environmental and Public Health, 2013, 158764. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/158764
Paoliello, M. M. B., De Capitani, E. M., da Cunha, F. G., Matsuo, T., de Carvalho, M. F., Sakuma, A., & Figueiredo, B. R. (2002). Exposure of children to lead and cadmium from a mining area of Brazil. Environmental Research Section A, 88, 120–128. https://doi.org/10.1006/enrs.2001.431
Pelfrêne, A., & Douay, F. (2018). Assessment of oral and lung bioaccessibility of Cd and Pb from smelter-impacted dust. Environmental Science Pollution Research, 25, 3718–3730. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0760-1
Poggio, L., Vrscaj, B., Schulin, R., Hepperle, E., & Marsan, F. A. (2009). Metals pollution and human bioaccessibility of topsoils in Grugliasco (Italy). Environmental Pollution, 157, 680–689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2008.08.009
Raimondi, I. M. (2014). Estudo e caracterização geológica e geotécnica de rejeitos de mineração (p. 199). Adrianópolis (PR): University of São Paulo.
Rodrigues, S. M., Cruz, N., Carvalho, L., Duarte, A. C., Pereira, E., Boim, A. G. F., Alleoni, L. R. F., & Römkens, P. F. A. M. (2018). Evaluation of a single extraction test to estimate the human oral bioaccessibility of potentially toxic elements in soils: Towards more robust risk assessment. Science of the Total Environment, 635, 188–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.063
Rodriguez, R. R., & Basta, N. T. (1999). An in vitro gastrointestinal method to estimate bioavailable arsenic in contaminated soils and solid media. Environmental Science and Technology, 33, 642–649.
Ruby, M. V., Davis, A., Schoof, R., Eberle, S., & Sellstone, C. M. (1996). Estimation of lead and arsenic bioavailability using a physiologically based extraction test. Environmental Science and Technology, 30, 422–430.
Ruby, M. V., Schoof, R., Brattin, W., Goldade, M., Post, G., Harnois, M., Mosby, D. E., Casteel, S. W., Berti, W., Carpenter, M., Edwards, D., Cragin, D., & Chappell, W. (1999). Advances in evaluating the oral bioavailability of inorganics in soil for use in human health risk assessment. Environmental Science and Technology, 33, 3697–3705.
Schindler, M., Santosh, M., Dotto, G., Silva, L. F. O. & Hochella, M. F. (2021) A review on Pb-bearing nanoparticles, particulate matter and colloids released from mining and smelting activities. Gondwana Research. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2021.07.011
SESA. (2008). Avaliação de risco à saúde humana por exposição aos resíduos da Plumbum no município de Adrianópolis – PR. 219
Smolders, E., Roels, L., Kuhangana, T. C., Coorevits, K., Vassilieva, E., Nemery, B., & Nkulu, C. B. L. (2019). Unprecedentedly high dust ingestion estimates for the general population in a mining district of DR Congo. Environmental Science and Technology., 53, 7851–7858. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b01973
Soltani, N., Keshavarzi, B., Moore, F., Cave, M., Sorooshian, A., Mahmoudi, R. M., Ahmadi, M. R., & Golshani, R. (2021). In vitro bioaccessibility phase portioning and health risk of potentially toxic elements in dust of an iron mining and industrial complex. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 212(1), 111972. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.111972
Samal, P., Mohanty, A. K., Khaoash, S., & Mishra, P. (2022). Hydrogeochemical evaluation, groundwater quality appraisal, and potential health risk assessment in a coal mining region of Eastern India. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 233, 324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05811-6
Souffit, D. G., Valdes, M. J., Modibo, O. B., Flore, T. S. Y., Félix, B. A. J., & Saïdou-Tokonami, S. (2022). Radon risk assessment and correlation study of indoor radon, radium-226, and radon in soil at the cobalt–nickel bearing area of Lomié, Eastern Cameroon. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 233, 196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05666-x
Tiesjema, B. & Baars, A. J. (2009) Re-evaluation of some human-toxicological maximum permissible risk levels earlier evaluated in the period 1991–2001. RIVM Report 711701092. Bilthoven, the Netherlands
Epa, U. S. (2007). Estimation of relative bioavailability of lead in soil and soil-like materials using in vivo and in vitro methods (pp. 7–77). US EPA, Washington: Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response. OSWER 9285.7-77.
US EPA. (2001). Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund: Volume III - Part A, Process for conducting probabilistic risk assessment. Office of Emergency and Remedial Response, US EPA, Washington 385:OSWER 9285.7–45
US EPA. (2022). Child-specific exposure factors handbook. National Center for Environmental Assessment, Washington, DC; EPA/600/P-00/002B. Available from: National Information Service, Springfield, VA 448:PB2003-101678
Wang, C. C., Li, M. Y., Yan, C. A., Tian, W., Deng, Z. H., Wang, Z. X., Xu, W. M., Tuo, Y. F., & Xiang, P. (2022). Refining health risk assessment of heavy metals in vegetables from high geochemical background areas: Role of bioaccessibility and cytotoxicity. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 159, 345–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2022.01.003
Wang, H., Yang, Q., Zhu, Y., Gu, Q., & Martín, J. D. (2023). Speciation, in vitro bioaccessibility and health risk of antimony in soils near an old industrial area. Science of The Total Environment, 854, 158767. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.158767
Wcisło, E., Bronder, J., Rodríguez-Valdés, E., & Gallego, J. L. R. (2022). Health risk assessment of post-mining Hg-As-contaminated soil: Implications for land remediation. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 233, 306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05712-8
Xu, C., Feng, Y., Li, H., Wu, R., Ju, J., Liu, S., Yang, Y., & Wang, B. (2022). Adsorption of heavy metal ions by iron tailings: Behavior, mechanism, evaluation and new perspectives. Journal of Cleaner Production, 344, 131065. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131065
Yan, K., Dong, Z., Wijayawardena, M. A. A., Liu, Y., Naidu, R., & Semple, K. (2017). Measurement of soil lead bioavailability and influence of soil types and properties: A review. Chemosphere, 184, 27–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.05.143
Zhang, X., Sun, L., Huang, X., & Yuan, D. (2022). Mercury sources and processes implied by other pollutants distributions in surface water and sediments of a subtropical estuary in Southern China. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 233, 315. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05800-9
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the financial support provided by the São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) for project 2014/07180-7 and the post-doctoral scholarship provided by the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kasemodel, M.C., Rodrigues, V.G.S. Soil Particle Size Fractioning and Pb and Cd Bioaccessibility on a Dirt Road Near Former Beneficiation and Smelting Plant. Water Air Soil Pollut 233, 478 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05936-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05936-8