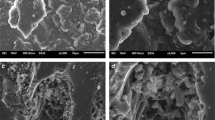
Abstract
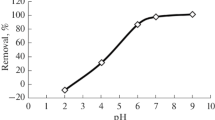
In this study, the removal of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride (a fluoroquinolone antibiotic) by using various effective adsorbents such as activated carbon, montmorillonite, modified montmorillonite (commercial name Cloisite 20A), and alumina was investigated. Adsorption experiments were performed to determine and compare the adsorption capacities of these adsorbents. The adsorption capacities of adsorbents were examined at different initial concentrations of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride. Activated carbon was found to be having the best adsorption capacity for the removal of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride. For the solution having an initial ciprofloxacin hydrochloride concentration of 4 ppm, the adsorption capacities of adsorbents were obtained as 1.86 mg g−1 for activated carbon, 1.67 mg g−1 for modified montmorillonite, 1.15 mg g−1 for alumina, and 0.60 mg g−1 for montmorillonite. And also, about 92% of the ciprofloxacin hydrochloride was removed from the water using the activated carbon. In addition, Langmuir, Freundlich, and Temkin isotherm models were employed to express the adsorption process. For all adsorbents, Freundlich isotherm model provided best fitting to the experimental data because of very high values of R2 (> 0.99). Kinetic models of pseudo-first order, pseudo-second order, Elovich, and Weber-Morris intraparticle diffusion model were utilized to evaluate the experimental adsorption data. Adsorption kinetics data were well represented by pseudo-second order kinetic model with values of R2 (> 0.999).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadzadeh, S., Asadipour, A., Pournamdari, M., Behnam, B., Rahimi, H. R., & Dolatabadi, M. (2017). Removal of ciprofloxacin from hospital wastewater using electrocoagulation technique by aluminum electrode: optimization and modelling through response surface methodology. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 109, 538–547.
Albadarin, A. B., Collins, M. N., Naushad, M., Shirazian, S., Walker, G., & Mangwandi, C. (2017). Activated lignin-chitosan extruded blends for efficient adsorption of methylene blue. Chemical Engineering Journal, 307, 264–272.
Alqadami, A. A., Naushad, M., Alothman, Z. A., & Ghfar, A. A. (2017). Novel metal–organic framework (MOF) based composite material for the sequestration of U (VI) and Th (IV) metal ions from aqueous environment. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 9, 36026–36037.
Awual, M. R., Eldesoky, G. E., Yaita, T., Naushad, M., Shiwaku, H., AlOthman, Z. A., & Suzuki, S. (2015). Schiff based ligand containing nano-composite adsorbent for optical copper (II) ions removal from aqueous solutions. Chemical Engineering Journal, 279, 639–647.
Bajpai, S., & Bhowmik, M. (2010). Adsorption of diclofenac sodium from aqueous solution using polyaniline as a potential sorbent. I. Kinetic studies. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 117, 3615–3622.
Bajpai, S. K., Bajpai, M., & Rai, N. (2012). Sorptive removal of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride from simulated wastewater using sawdust: kinetic study and effect of pH. Water SA, 38, 673–682.
Balarak, D., Mostafapour, F. K., & Joghataei, A. (2017). Kinetics and mechanism of red mud in adsorption of ciproloxacin in aqueous solution. Bioscience Biotechnology Research Communications, 10, 243–250.
Baylan, N., & Meriçboyu, A. E. (2016). Adsorption of lead and copper on bentonite and grapeseed activated carbon in single-and binary-ion systems. Separation Science and Technology, 51, 2360–2368.
Behnamfard, A., & Salarirad, M. M. (2009). Equilibrium and kinetic studies on free cyanide adsorption from aqueous solution by activated carbon. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 170, 127–133.
Carabineiro, S., Thavorn-Amornsri, T., Pereira, M., Serp, P., & Figueiredo, J. (2012). Comparison between activated carbon, carbon xerogel and carbon nanotubes for the adsorption of the antibiotic ciprofloxacin. Catalysis Today, 186, 29–34.
Chen, H., Gao, B., & Li, H. (2015). Removal of sulfamethoxazole and ciprofloxacin from aqueous solutions by graphene oxide. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 282, 201–207.
Chiban, M., Soudani, A., Sinan, F., & Persin, M. (2011). Single, binary and multi-component adsorption of some anions and heavy metals on environmentally friendly Carpobrotus edulis plant. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 82, 267–276.
De Witte, B., Van Langenhove, H., Demeestere, K., Saerens, K., De Wispelaere, P., & Dewulf, J. (2010). Ciprofloxacin ozonation in hospital wastewater treatment plant effluent: effect of pH and H2O2. Chemosphere, 78, 1142–1147.
Elsaim, M. H. (2017). Removal of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride from aqueous solution by pomegranate peel grown in Alziedab agricultural scheme-River Nile State, Sudan. Biochemistry, 5, 89–96.
Erdem, B., Özcan, A., Gök, Ö., & Özcan, A. S. (2009). Immobilization of 2, 2′-dipyridyl onto bentonite and its adsorption behavior of copper (II) ions. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 163, 418–426.
Figueiredo, J. L., Pereira, M. F., Freitas, M. M., & Órfão, J. J. (2007). Characterization of active sites on carbon catalysts. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 46, 4110–4115.
Futalan, C. M., Kan, C.-C., Dalida, M. L., Hsien, K.-J., Pascua, C., & Wan, M.-W. (2011). Comparative and competitive adsorption of copper, lead, and nickel using chitosan immobilized on bentonite. Carbohydrate Polymers, 83, 528–536.
Genç, N., & Dogan, E. C. (2015). Adsorption kinetics of the antibiotic ciprofloxacin on bentonite, activated carbon, zeolite, and pumice. Desalination and Water Treatment, 53, 785–793.
Gu, C., & Karthikeyan, K. (2005). Sorption of the antimicrobial ciprofloxacin to aluminum and iron hydrous oxides. Environmental Science & Technology, 39, 9166–9173.
Jalil, M. E. R., Baschini, M., & Sapag, K. (2015). Influence of pH and antibiotic solubility on the removal of ciprofloxacin from aqueous media using montmorillonite. Applied Clay Science, 114, 69–76.
Kumar, A., Kumar, A., Sharma, G., Naushad, M., Veses, R. C., Ghfar, A. A., Stadler, F. J., & Khan, M. R. (2017). Solar-driven photodegradation of 17-β-estradiol and ciprofloxacin from waste water and CO 2 conversion using sustainable coal-char/polymeric-gC 3 N 4/RGO metal-free nano-hybrids. New Journal of Chemistry, 41, 10208–10224.
Kumar, A., Sharma, G., Naushad, M., Ahamad, T., Veses, R. C., & Stadler, F. J. (2019). Highly visible active Ag2CrO4/Ag/BiFeO3@ RGO nano-junction for photoreduction of CO2 and photocatalytic removal of ciprofloxacin and bromate ions: The triggering effect of Ag and RGO. Chemical Engineering Journal, 370, 148–165.
Liu, X., Lu, S., Liu, Y., Meng, W., & Zheng, B. (2017). Adsorption of sulfamethoxazole (SMZ) and ciprofloxacin (CIP) by humic acid (HA): characteristics and mechanism. RSC Advances, 7, 50449–50458.
Ma, J., Yang, M., Yu, F., & Zheng, J. (2015). Water-enhanced removal of ciprofloxacin from water by porous graphene hydrogel. Scientific Reports, 5, 13578.
Mishra, P., & Patel, R. (2009). Removal of lead and zinc ions from water by low cost adsorbents. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 168, 319–325.
Mostafapour, F. K., Balarak, D., & Baniasadi, M. (2018). Removal of ciprofloxacin from of pharmaceutical wastewater by adsorption on SiO2 nanoparticle. Journal of Pharmaceutical Research International, 1-9.
Naushad, M. (2014). Surfactant assisted nano-composite cation exchanger: development, characterization and applications for the removal of toxic Pb2+ from aqueous medium. Chemical Engineering Journal, 235, 100–108.
Naushad, M., Ahamad, T., Al-Maswari, B. M., Alqadami, A. A., & Alshehri, S. M. (2017). Nickel ferrite bearing nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbon as efficient adsorbent for the removal of highly toxic metal ion from aqueous medium. Chemical Engineering Journal, 330, 1351–1360.
Parsa, J. B., Panah, T. M., & Chianeh, F. N. (2016). Removal of ciprofloxacin from aqueous solution by a continuous flow electro-coagulation process. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 33, 893–901.
Soetaredjo, F. E., Ismadji, S., Foe, K. & Woworuntu, G. L. (2018) Removal of hazardous contaminants from water or wastewater using polymer nanocomposites materials, Nanotechnology for Sustainable Water Resources (pp. 103–139).
Suciu, N. A., & Capri, E. (2009). Adsorption of chlorpyrifos, penconazole and metalaxyl from aqueous solution by modified clays. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part B, 44, 525–532.
Sun, S.-P., Guo, H.-Q., Ke, Q., Sun, J.-H., Shi, S.-H., Zhang, M.-L., & Zhou, Q. (2009). Degradation of antibiotic ciprofloxacin hydrochloride by photo-Fenton oxidation process. Environmental Engineering Science, 26, 753–759.
Sun, S. P., Hatton, T. A., & Chung, T.-S. (2011). Hyperbranched polyethyleneimine induced cross-linking of polyamide− imide nanofiltration hollow fiber membranes for effective removal of ciprofloxacin. Environmental Science & Technology, 45, 4003–4009.
Wang, C.-J., Li, Z., Jiang, W.-T., Jean, J.-S., & Liu, C.-C. (2010). Cation exchange interaction between antibiotic ciprofloxacin and montmorillonite. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 183, 309–314.
Wang, C.-J., Li, Z., & Jiang, W.-T. (2011). Adsorption of ciprofloxacin on 2: 1 dioctahedral clay minerals. Applied Clay Science, 53, 723–728.
Wang, Y., Ngo, H., & Guo, W. (2015). Preparation of a specific bamboo based activated carbon and its application for ciprofloxacin removal. Science of the Total Environment, 533, 32–39.
Wu, Q., Li, Z., Hong, H., Li, R., & Jiang, W.-T. (2013). Desorption of ciprofloxacin from clay mineral surfaces. Water Research, 47, 259–268.
Yu, F., Sun, S., Han, S., Zheng, J., & Ma, J. (2016). Adsorption removal of ciprofloxacin by multi-walled carbon nanotubes with different oxygen contents from aqueous solutions. Chemical Engineering Journal, 285, 588–595.
Zhang, C.-L., Qiao, G.-L., Zhao, F., & Wang, Y. (2011). Thermodynamic and kinetic parameters of ciprofloxacin adsorption onto modified coal fly ash from aqueous solution. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 163, 53–56.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Avcı, A., İnci, İ. & Baylan, N. A Comparative Adsorption Study with Various Adsorbents for the Removal of Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride from Water. Water Air Soil Pollut 230, 250 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4315-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4315-6