Abstract
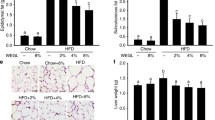
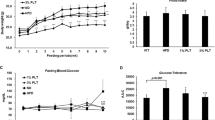
Gynostemma pentaphyllum (G. pentaphyllum) is a perennial liana herb of the Cucurbitaceae family which has both nutraceutical and pharmacological functions. The objective of the current study was to investigate the preventative effects of G. pentaphyllum and Gypenoside-IV (GP-IV, a saponin monomer in G. pentaphyllum) on metabolic symptoms in high fat diet induced obese (DIO) mice with gut microbiota dysbiosis. G. pentaphyllum water extract (GPWE, 150 mg/kg•d− 1) and GP-IV (50 mg/kg•d− 1) were orally administered to DIO mice by gavage for 10 weeks. The results showed that both GPWE and GP-IV prevented obesity development by decreasing body weight gain, reducing fat mass/body weight ratio and inhibiting adipocyte hypertrophy. GPWE and GP-IV also improved lipid profile and glucose tolerance effectively. Moreover, GPWE and GP-IV treatments partly restored gut microbiota in DIO mice. Typically, GPWE and GP-IV reduced Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes ratio, increased the abundance of certain health-promoting bacteria and reduced the abundance of microbiota that were associated with metabolic disorders. We conclude that GPWE and GP-IV can ameliorate metabolic symptoms possibly via modulating gut microbiota in DIO mice.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Zhao Y, Sedighi R, Wang P, Chen H, Zhu Y, Sang S (2015) Acid as a major bioactive component in rosemary extract ameliorates high-fat-diet-induced obesity and metabolic syndrome in mice. J Agric Food Chem 63:4843–4852. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b01246
He X, Zheng S, Sheng Y, Miao T, Zhao C (2020) Chlorogenic acid ameliorates obesity by preventing energy balance shift in high fat diet induced obese mice. J Sci Food Agric 101:631–637. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.10675
Han Y, Zhao C, He X, Sheng Y, Ma T, Sun Z, Liu X, Liu C, Fan S, Xu W (2018) Purple lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) attenuates metabolic disorders in diet induced obesity. J Funct Foods 45:462–470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2018.04.027
Liu E, Tsuboi H, Ikegami S, Kamiyama T, Ji ZS (2021) Effects of Nelumbo nucifera leaf extract on obesity. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 76:377–384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11130-020-00852-w
Garcia-Diaz DF, Jimenez P, Reyes-Farias M, Soto-Covasich J, Costa AGV (2019) A review of the potential of Chilean native berries in the treatment of obesity and its related features. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 74:277–286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11130-019-00746-6
Attawish A, Chivapat S, Phadungpat S, Bansiddhi J, Techadamrongsin Y, Mitrijit O, Chaorai B, Chavalittumrong P (2004) Chronic toxicity of Gynostemma pentaphyllum. Fitoterapia 75:539–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2004.04.010
la Cour B, Mølgaard P, Yi Z (1995) Traditional Chinese medicine in treatment of hyperlipidaemia. J Ethnopharmacol 46:125–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-8741(95)01234-5
Xia X, Xu J, Wang X, Wang H, Lin Z, Shao K, Fang L, Zhang C, Zhao Y (2020) Jiaogulan tea (Gynostemma pentaphyllum) potentiates the antidiabetic effect of white tea via the AMPK and PI3K pathways in C57BL/6 mice. Food Funct 11:4339–4355. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0FO00395F
Wang J, Yang J-L, Zhou P-P, Meng X-H, Shi Y-P (2017) Further new gypenosides from Jiaogulan (Gynostemma pentaphyllum). J Agric Food Chem 65:5926–5934. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b01477
Takemoto T, Arihara S, Nakajima T, Okuhira M (1983) Studies on the constituents of Gynostemma pentaphyllum MAKINO. II. structures of Gypenoside XV-XXI. Yakugaku Zasshi 103:1015–1023. https://doi.org/10.1248/yakushi1947.103.10_1015
Erk T, Hauser J, Williamson G, Renouf M, Steiling H, Dionisi F, Richling E (2014) Structure– and dose–absorption relationships of coffee polyphenols. BioFactors 40:103–112. https://doi.org/10.1002/biof.1101
Sun J, Yu XH, Huangpu HQ, Yao FZ (2019) Ginsenoside Rb3 protects cardiomyocytes against hypoxia/reoxygenation injury via activating the antioxidation signaling pathway of PERK/Nrf2/HMOX1. Biomed Pharmacother 109:254–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.09.002
Bu QT, Zhang WY, Chen QC, Zhang CZ, Gong XJ, Liu WC, Li W, Zheng YN (2012) Anti-diabetic effect of ginsenoside Rb-3 in alloxan-induced diabetic mice. Med Chem 8:934–941. https://doi.org/10.2174/157340612802084199
Sekirov I, Russell SL, Antunes LCM, Finlay BB (2010) Gut microbiota in health and disease. Physiol Rev 90:859–904. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00045.2009
Zhang T, Yang Y, Liang Y, Jiao X, Zhao C (2018) Beneficial effect of intestinal fermentation of natural polysaccharides. Nutrients 10:1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10081055
Leal-Díaz AM, Noriega LG, Torre-Villalvazo I, Torres N, Alemán-Escondrillas G, López-Romero P, Sánchez-Tapia M, Aguilar-López M, Furuzawa-Carballeda J, Velázquez-Villegas LA, Avila-Nava A, Ordáz G, Gutiérrez-Uribe JA, Serna-Saldivar SO, Tovar AR (2016) Aguamiel concentrate from Agave salmiana and its extracted saponins attenuated obesity and hepatic steatosis and increased Akkermansia muciniphila in C57BL6 mice. Sci Rep 6:34242. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep34242
Huang X, Chen W, Yan C, Yang R, Chen Q, Xu H, Huang Y (2019) Gypenosides improve the intestinal microbiota of non-alcoholic fatty liver in mice and alleviate its progression. Biomed Pharmacother 118:109258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109258
Lee HS, Lim SM, Jung JI, Kim SM, Lee JK, Kim YH, Cha KM, Oh TK, Moon JM, Kim TY, Kim EJ (2019) Gynostemma pentaphyllum extract ameliorates high-fat diet-induced obesity in C57BL/6 N mice by upregulating SIRT1. Nutrients 11:15. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102475
Jiang M, Wang C, Meng Q, Li F, Li K, Luo L, Sun C (2013) Cyclosporin A attenuates weight gain and improves glucose tolerance in diet-induced obese mice. Mol Cell Endocrinol 370:96–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2013.02.018
Zhang J, Wang O, Guo Y, Wang T, Wang S, Li G, Ji B, Deng Q (2016) Effect of increasing doses of linoleic and α-linolenic acids on high-fructose and high-fat diet induced metabolic syndrome in rats. J Agric Food Chem 64:762–772. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b04715
Zhu X, Zhang X, Gao X, Yi Y, Hou Y, Meng X, Jia C, Chao B, Fan W, Li X, Zhang H (2020) Effects of inulin propionate ester on obesity-related metabolic syndrome and intestinal microbial homeostasis in diet-induced obese mice. ACS Omega 5:12865–12876. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c00649
Chassaing B, Koren O, Goodrich JK, Poole AC, Srinivasan S, Ley RE, Gewirtz AT (2015) Dietary emulsifiers impact the mouse gut microbiota promoting colitis and metabolic syndrome. Nature 519:92–96. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14232
Boulange CL, Neves AL, Chilloux J, Nicholson JK, Dumas ME (2016) Impact of the gut microbiota on inflammation, obesity, and metabolic disease. Genome Med 8:42. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13073-016-0303-2
Wang JJ, Tang H, Zhang CH, Zhao YF, Derrien M, Rocher E, Vlieg J, Strissel K, Zhao LP, Obin M, Shen J (2015) Modulation of gut microbiota during probiotic-mediated attenuation of metabolic syndrome in high fat diet-fed mice. Isme J 9:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2014.99
Acknowledgements
X.Y.H. would like to thank the 2115 Talent Development Program of China Agricultural University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is not conflict of interest in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 26.2 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shu, X., Chen, R., Yang, M. et al. Gynostemma pentaphyllum and Gypenoside-IV Ameliorate Metabolic Disorder and Gut Microbiota in Diet-Induced-Obese Mice. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 77, 367–372 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11130-022-00982-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11130-022-00982-3