Abstract
Backgrounds and aims
Mowing and P-fertilization enhance legume seedling establishment, assisting in successful restoration of degraded grasslands. Legume establishment may influence soil chemical compounds and soil microbial assemblage to facilitate legume productivity. We aim to better understand these complex plant-soil-microbial interactions to improve grassland productivity following overgrazing.
Methods
We conducted a 3-years Medicago falcata reseeding experiment was in semi-arid meadows, assessing responses of aboveground plant biomass, soil chemical compounds, and soil microbial community composition. Reseeded plots were mowed and/or P-fertilized.
Results
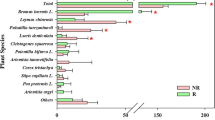
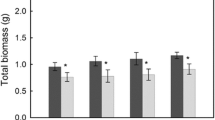
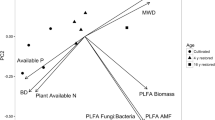
Application of both management practices increased grassland biomass compared with all other combinations. Soil chemical diversity predicted fungal alpha diversity, and fungal alpha diversity positively correlated with aboveground biomass. Our results indicate reseeded alfalfa directly altered bulk soil chemical compounds with subsequent alterations in grassland microbial communities. Soils contained chemical compounds with antifungal properties that indirectly improved grassland productivity via antagonism to pathogenic fungi. Furthermore, we found three specific compounds (5-methyltridecane, pentatriacontane, and N-tridecane) reduced microbial diversity.
Conclusions
Here we demonstrate soil chemical compounds play an important role in shaping beneficial microbial communities to improve grassland biomass. These results may help direct beneficial soil microbial community composition through improved grassland management practices.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen RC, Tu Y-K, Nevarez MJ, Bobbs AS, Friesen JW, Lorsch JR, McCauley JA, Voet JG, Hamlett NV (2013) The mercury resistance (mer) operon in a marine gliding flavobacterium, Tenacibaculum discolor 9A5. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 83:135–148. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2012.01460.x
Bastian M, Heymann S, Jacomy M (2009) Gephi: an open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. Icwsm 8:361–362
Bauer JT, Kleczewski NM, Bever JD, Clay K, Reynolds HL (2012) Nitrogen-fixing bacteria, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, and the productivity and structure of prairie grassland communities. Oecologia 170:1089–1098. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-012-2363-3
Bi B., Han F. (2018) GC-MS analysis of root exudates of alfalfa in different cropping years on the loess plateau. Acta Agrestia Sin 3: 611–617 (in China)
Borer ET, Seabloom EW, Gruner DS, Harpole WS, Hillebrand H, Lind EM, Adler PB, Alberti J, Anderson TM, Bakker JD, Biederman L, Blumenthal D, Brown CS, Brudvig LA, Buckley YM, Cadotte M, Chu C, Cleland EE, Crawley MJ, Daleo P, Damschen EI, Davies KF, DeCrappeo NM, Du G, Firn J, Hautier Y, Heckman RW, Hector A, HilleRisLambers J, Iribarne O, Klein JA, Knops JMH, La Pierre KJ, Leakey ADB, Li W, MacDougall AS, McCulley RL, Melbourne BA, Mitchell CE, Moore JL, Mortensen B, O'Halloran LR, Orrock JL, Pascual J, Prober SM, Pyke DA, Risch AC, Schuetz M, Smith MD, Stevens CJ, Sullivan LL, Williams RJ, Wragg PD, Wright JP, Yang LH (2014) Herbivores and nutrients control grassland plant diversity via light limitation. Nature 508 (7497):517–520
Broeckling CD, Broz AK, Bergelson J, Manter DK, Vivanco JM (2008) Root exudates regulate soil fungal community composition and diversity. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:738–744
Caporaso JG, Lauber CL, Walters WA, Berg-Lyons D, Lozupone CA, Turnbaugh PJ, Fierer N, Knight R (2011) Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108:4516–4522. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1000080107
Chaparro JM, Sheflin AM, Manter DK, Vivanco JM (2012) Manipulating the soil microbiome to increase soil health and plant fertility. Biol Fertil Soils 48:489–499. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-012-0691-4
Chaparro JM, Badri DV, Vivanco JM (2013) Rhizosphere microbiome assemblage is affected by plant development. ISME J 8:790–803. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2013.196
Chen, W. (2010). Study on the spatial distribution pattern of plants on the different degradation and desertification sequence in Hulunbuir steppe. Beijing Forestry University (in China)
Chen D, Li J, Lan Z, Hu S, Bai Y (2016) Soil acidification exerts a greater control on soil respiration than soil nitrogen availability in grasslands subjected to long-term nitrogen enrichment. Funct Ecol 30:658–669. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.12525
Chlebicki A (2009) Fungi on higher plants of the upper limit of the alpine zone: new species from Tian Shan. Mycotaxon 110:443–450
Cleland EE, Chiariello NR, Loarie SR, Mooney HA, Field CB (2006) Diverse responses of phenology to global changes in a grassland ecosystem. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103:13740–13744. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0600815103
Crème A, Rumpel C, Gastal F, de la Luz Mora Gil M, Chabbi A (2016) Effects of grasses and a legume grown in monoculture or mixture on soil organic matter and phosphorus forms. Plant Soil 402:117–128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2740-x
Davidson AD, Ponce E, Lightfoot DC, Fredrickson EL, Brown JH, Cruzado J, Brantley SL, Sierra-Corona R, List R, Toledo D, Ceballos G (2010) Rapid response of a grassland ecosystem to an experimental manipulation of a keystone rodent and domestic livestock. Ecology 91:3189–3200. https://doi.org/10.1890/09-1277.1
Deng Y, Jiang Y-H, Yang Y, He Z, Luo F, Zhou J (2012) Molecular ecological network analyses. BMC Bioinformatics 13:113. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-13-113
Divito GA, Sadras VO (2014) How do phosphorus, potassium and Sulphur affect plant growth and biological nitrogen fixation in crop and pasture legumes? A meta-analysis. Field Crop Res 156:161–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2013.11.004
Edgar RC (2013) UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods 10:996–998. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2604
Elsaesser M, Engel S, Breunig J, Thumm U (2014) Increasing protein yields from grassland by reseeding of legumes. Grassland Sci Eur 19:880–883
Fahrbach M, Krauss M, Preiss A, Kohler H-PE, Hollender J (2010) Anaerobic testosterone degradation in Steroidobacter denitrificans – identification of transformation products. Environ Pollut 158:2572–2581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2010.05.017
Garbeva P, Van Elsas J, Van Veen J (2008) Rhizosphere microbial community and its response to plant species and soil history. Plant Soil 302:19–32
Giese M, Brueck H, Gao YZ, Lin S, Steffens M, Kögel-Knabner I, Glindemann T, Susenbeth A, Taube F, Butterbach-Bahl K (2013) N balance and cycling of Inner Mongolia typical steppe: a comprehensive case study of grazing effects. Ecol Monogr 83:195–219
Gilbert J, Gowing D, Wallace H (2009) Available soil phosphorus in semi-natural grasslands: assessment methods and community tolerances. Biol Conserv 142:1074–1083. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2009.01.018
Graham PH, Vance CP (2003) Legumes: importance and constraints to greater use. Plant Physiol 131:872–877
Grandy AS, Strickland MS, Lauber CL, Bradford MA, Fierer N (2009) The influence of microbial communities, management, and soil texture on soil organic matter chemistry. Geoderma 150:278–286
Guimerà R, Nunes Amaral LA (2005) Functional cartography of complex metabolic networks. Nature 433:895–900. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03288
Guozheng H, Hongyan L, Yi Y, Zhaoliang S (2016) The role of legumes in plant community succession of degraded grasslands in northern China. Land Degrad Dev 27:366–372. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.2382
Han X, Sistla SA, Zhang YH, Lü XT, Han XG (2014) Hierarchical responses of plant stoichiometry to nitrogen deposition and mowing in a temperate steppe. Plant Soil 382:175–187
Janardan Y, Sant P, Verma JP (2010) Effect of rhizobium and PGPR combinations on nodulation plant growth, yield and nutrients uptake by mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) under organic farming system. Environ Ecol 28:2568–2571
Jourand P et al (2004) Methylobacterium nodulans sp. nov., for a group of aerobic, facultatively methylotrophic, legume root-nodule-forming and nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:2269–2273. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.02902-0
Kõljalg U, Nilsson RH, Abarenkov K, Tedersoo L, Taylor AFS, Bahram M, Bates ST, Bruns TD, Bengtsson-Palme J, Callaghan TM, Douglas B, Drenkhan T, Eberhardt U, Dueñas M, Grebenc T, Griffith GW, Hartmann M, Kirk PM, Kohout P, Larsson E, Lindahl BD, Lücking R, Martín MP, Matheny PB, Nguyen NH, Niskanen T, Oja J, Peay KG, Peintner U, Peterson M, Põldmaa K, Saag L, Saar I, Schüßler A, Scott JA, Senés C, Smith ME, Suija A, Taylor DL, Telleria MT, Weiss M, Larsson K-H (2013) Towards a unified paradigm for sequence-based identification of fungi. Mol Ecol 22:5271–5277. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.12481
Kowalchuk GA, Stephen JR (2001) Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacteria: A Model for Molecular Microbial Ecology. Annu Rev Microbiol 55:485–529. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.micro.55.1.485
Kozich JJ, Westcott SL, Baxter NT, Highlander SK, Schloss PD (2013) Development of a dual-index sequencing strategy and curation pipeline for analyzing amplicon sequence data on the MiSeq Illumina sequencing platform. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:5112–5120. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.01043-13
Lareen A, Burton F, Schäfer P (2016) Plant root-microbe communication in shaping root microbiomes. Plant Mol Biol 90:575–587. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-015-0417-8
Li B, Yang Y, Ma L, Ju F, Guo F, Tiedje JM, Zhang T (2015a) Metagenomic and network analysis reveal wide distribution and co-occurrence of environmental antibiotic resistance genes. ISME J 9:2490–2502. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2015.59
Li Q, Song Y, Li G, Yu P, Wang P, Zhou D (2015b) Grass-legume mixtures impact soil N, species recruitment, and productivity in temperate steppe grassland. Plant Soil 394:271–285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2525-2
Liebeke M, Brözel VS, Hecker M, Lalk M (2009) Chemical characterization of soil extract as growth media for the ecophysiological study of bacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 83:161–173
Magoč T, Salzberg SL (2011) FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 27:2957–2963
Marinari S, Masciandaro G, Ceccanti B, Grego S (2007) Evolution of soil organic matter changes using pyrolysis and metabolic indices: A comparison between organic and mineral fertilization. Bioresour Technol 98:2495–2502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2006.09.001
Mason NWH, de Bello F, Doležal J, Lepš J (2011) Niche overlap reveals the effects of competition, disturbance and contrasting assembly processes in experimental grassland communities. J Ecol 99:788–796. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2745.2011.01801.x
Mcivor JG (1984) Phosphorus requirements and responses of tropical pasture species: native and introduced grasses, and introduced legumes. Aust J Exp Agric 24:370–378
Mortenson MC, Schuman GE, Ingram LJ (2004) Carbon sequestration in rangelands Interseeded with yellow-flowering alfalfa ( Medicago sativa ssp. falcata ). Environ Manag 33:S475–S481
Mwafulirwa L, Baggs EM, Russell J, George T, Morley N, Sim A, de la Fuente CC, Paterson E (2016) Barley genotype influences stabilization of rhizodeposition-derived C and soil organic matter mineralization. Soil Biol Biochem 95:60–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2015.12.011
Newbold T, Hudson LN, Hill SLL, Contu S, Lysenko I, Senior RA, Börger L, Bennett DJ, Choimes A, Collen B, Day J, De Palma A, Díaz S, Echeverria-Londoño S, Edgar MJ, Feldman A, Garon M, Harrison MLK, Alhusseini T, Ingram DJ, Itescu Y, Kattge J, Kemp V, Kirkpatrick L, Kleyer M, Correia DLP, Martin CD, Meiri S, Novosolov M, Pan Y, Phillips HRP, Purves DW, Robinson A, Simpson J, Tuck SL, Weiher E, White HJ, Ewers RM, Mace GM, Scharlemann JPW, Purvis A (2015) Global effects of land use on local terrestrial biodiversity. Nature 520:45–50. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14324
Newman MEJ (2006) Modularity and community structure in networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103:8577–8582. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0601602103
Nierop KGJ, Pulleman MM, Marinissen JCY (2001) Management induced organic matter differentiation in grassland and arable soil: a study using pyrolysis techniques. Soil Biol Biochem 33:755–764. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-0717(00)00223-6
Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Kindt R, Legendre P, Minchin PR, O’hara R, Simpson GL, Solymos P, Stevens MHH, Wagner H (2011) Vegan: community ecology package. R package version: 117–118
Olesen JM, Bascompte J, Dupont YL, Jordano P (2007) The modularity of pollination networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104:19891–19896. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0706375104
Pearce C, Veasey L, Tillotson M, Darveaux B, Lawrence M, Sica V, Oberlies N (2013) Mevalocidin: a fungus metabolite with herbicide activity and potential for use in organic farming. Planta Med 79:PL21
Philippot L, Raaijmakers JM, Lemanceau P, van der Putten WH (2013) Going back to the roots: the microbial ecology of the rhizosphere. Nat Rev Microbiol 11:789–799. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro3109
Raaijmakers JM, Paulitz TC, Steinberg C, Alabouvette C, Moënne-Loccoz Y (2009) The rhizosphere: a playground and battlefield for soilborne pathogens and beneficial microorganisms. Plant Soil 321:341–361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-008-9568-6
Raza W, Yuan J, Wu YC, Rajer FU, Huang Q, Qirong S (2015) Biocontrol traits of two Paenibacillus polymyxa strains SQR-21 and WR-2 in response to fusaric acid, a phytotoxin produced by Fusarium species. Plant Pathol 64:1041–1052. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppa.12354
Rodríguez H, Fraga R (1999) Phosphate solubilizing bacteria and their role in plant growth promotion. Biotechnol Adv 17:319–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0734-9750(99)00014-2
Sarib S, J I, A Z, Diyana I N (2012) Bioactivities of jatropha curcas linn latex. 4th Regional Conference on Natural Resources in the Tropics (NTrop4):112–117
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ, Sahl JW, Stres B, Thallinger GG, Van Horn DJ, Weber CF (2009) Introducing mothur: Open-Source, Platform-Independent, Community-Supported Software for Describing and Comparing Microbial Communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7537–7541. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.01541-09
Schwarczinger I, Vajna L, Bruckart W (2000) Sclerostagonospora salsolae, comb. nov. Mycotaxon 76:345–348
Shen Z, Ruan Y, Chao X, Zhang J, Li R, Shen Q (2015) Rhizosphere microbial community manipulated by 2 years of consecutive biofertilizer application associated with banana Fusarium wilt disease suppression. Biol Fertil Soils 51:553–562
Sica VP, Figueroa M, Raja HA, El-Elimat T, Darveaux BA, Pearce CJ, Oberlies NH (2016) Optimizing production and evaluating biosynthesis in situ of a herbicidal compound, mevalocidin, from Coniolariella sp. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 43:1149–1157
Socher SA, Prati D, Boch S, Müller J, Klaus VH, Hölzel N, Fischer M (2012) Direct and productivity-mediated indirect effects of fertilization, mowing and grazing on grassland species richness. J Ecol 100:1391–1399. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2745.2012.02020.x
Song Y, Zhu C, Raza W, Wang D, Huang Q, Guo S, Ling N, Shen Q (2016) Coupling of the chemical niche and microbiome in the rhizosphere: implications from watermelon grafting. Front Agric Sci Eng 3:249–262
Tajick MA, Seid Mohammad Khani H, Babaeizad V (2014) Identification of biological secondary metabolites in three Penicillium species, P. goditanum, P. moldavicum, and P. corylophilum. Prog Biol Sci 4:53–61
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naïve Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5261–5267. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.00062-07
Zhang B-H et al (2016) Modestobacter lacusdianchii sp. nov., a phosphate-solubilizing Actinobacterium with ability to promote Microcystis growth. PLoS One 11:e0161069. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0161069
Zhang Y, Lu W, Zhang H, Zhou J, Shen Y (2018a) Grassland management practices in Chinese steppes impact productivity, diversity and the relationship. Front Agric Sci Eng 5:57–63. https://doi.org/10.15302/j-fase-2017192
Zhang F, Huo Y, Cobb AB, Luo G, Zhou J, Yang G, Wilson GW, Zhang Y (2018b) Trichoderma biofertilizer links to altered soil chemistry, altered microbial communities, and improved grassland biomass. Front Microbiol 9:848
Zhao W, Chen S-P, Lin G-H (2008) Compensatory growth responses to clipping defoliation in Leymus chinensis (Poaceae) under nutrient addition and water deficiency conditions. Plant Ecol 196:85–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11258-007-9336-3
Zhou J, Deng Y, Luo F, He Z, Tu Q, Zhi X (2010) Functional molecular ecological networks. Mbio 1. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00169-10
Zhou J, Deng Y, Luo F, He Z, Yang Y (2011) Phylogenetic molecular ecological network of soil microbial communities in response to elevated CO2. MBio 2:e00122-11. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00122-11
Zhou J, Zhang Y, Wilson GWT, Cobb AB, Lu W, Guo Y (2017) Small vegetation gaps increase reseeded yellow-flowered alfalfa performance and production in native grasslands. Basic Appl Ecol 24:41–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.baae.2017.08.002
Zhou J, Wilson GWT, Cobb AB, Yang G, Zhang Y (2019) Phosphorus and mowing improve native alfalfa establishment, facilitating restoration of grassland productivity and diversity. Land Degrad Dev 30:647–657. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.3251
Acknowledgements
We thank Xiaoping Xin, director of the Hulunber Grassland Ecosystem Observation and Research Station for use of these research facilities. We also thank Dr. Xinquan Zhang and Dr. Feida Sun from Sichuan Agricultural University for their valuable advice on manuscript improvement. This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31602006), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20160735), the Nanjing Agricultural University Foundation (Y0201600442), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2015 M581815), the Postdoctoral Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (1601265C), and the earmarked fund for the China Agriculture Research System (CARS-34). This work is also supported by the Post Doctoral Fellowships Program, [project no. OKL03144 / project accession no. 1019172], from the U.S. Department of Agriculture, National Institute of Food and Agriculture.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JZ, FZ and YZ conceived the ideas and designed the methodology; JZ, FZ, YH, and XX collected the data; JZ and FZ analyzed the data; JZ, FZ, and YZ led the writing of the manuscript; GW, AC, XX, and LL revised the manuscript for intellectual content; all authors contributed to the drafts and gave final approval for publication.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ulrike Mathesius.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1083 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Zhang, F., Huo, Y. et al. Following legume establishment, microbial and chemical associations facilitate improved productivity in degraded grasslands. Plant Soil 443, 273–292 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-019-04169-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-019-04169-9