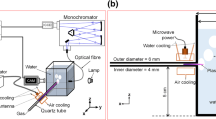
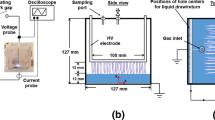
Abstract
Plasma-induced water treatment is a novel water treatment technique that has shown high efficiency and flexibility. Although the electrical conductivity of impure water varies depending on the degree of pollution, its influence on plasma treatment efficiency is not well understood. In this study, we investigate the fundamentals of a microwave plasma jet submerged in water with electrical conductivities (σw) ranging from 10 to 10,000 µS/cm. The plasma characteristics, namely composition, electron density, and temperature, and their variations as a function of σw, are derived using optical emission spectroscopy. The plasma-bubble dynamics is investigated using space- and time-resolved high-speed imaging. The results show that the plasma fills the bubble volume at relatively low flow rate (typically, < 2 L/min) and high σw (typically, > 1000 µS/cm). The influence of σw on the degradation of methylene blue, a standard water pollutant, is also assessed, and the obtained results indicate that the plasma becomes extremely inefficient at high σw. These findings are of great importance for the community of plasma-induced liquid processing, particularly wastewater treatment.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belmonte T, Hamdan A, Kosior F, Noël C, Henrion G (2014) Interaction of discharges with electrode surfaces in dielectric liquids: application to nanoparticle synthesis. J Phys D Appl Phys 47(22):224016
Hamdan A, Noël C, Ghanbaja J, Belmonte T (2014) Comparison of aluminium nanostructures created by discharges in various dielectric liquids. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 34(5):1101–1114
Hamdan A, Noël C, Ghanbaja J, Migot-Choux S, Belmonte T (2013) Synthesis of platinum embedded in amorphous carbon by micro-gap discharge in heptane. Mater Chem Phys 142(1):199–206
Yang Y, Cho YI, Fridman A (2017) Plasma discharge in liquid: water treatment and applications. CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton
Misra NN, Schlüter O, Cullen PJ (eds) (2016) Cold plasma in food and agriculture: fundamentals and applications, Academic Press
Ito M, Ohta T, Hori M (2012) Plasma agriculture. J Korean Phys Soc 60(6):937–943
Bruggeman PJ et al (2016) Plasma–liquid interactions: a review and roadmap. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 25(5):053002
Weltmann KD, Kindel E, von Woedtke T, Hähnel M, Stieber M, Brandenburg R (2010) Atmospheric-pressure plasma sources: prospective tools for plasma medicine. Pure Appl Chem 82(6):1223–1237
Maheux S et al (2015) Formation of ammonium in saline solution treated by nanosecond pulsed cold atmospheric microplasma: a route to fast inactivation of E. coli bacteria. RSC Adv 5(52):42135–42140
Schütze A, Jeong JY, Babayan SE, Park J, Selwyn GS, Hicks RF (1998) The atmospheric-pressure plasma jet: a review and comparison to other plasma sources. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 26(6):1685–1694
Bruggeman P, Schram D, González MÁ, Rego R, Kong MG, Leys C (2009) Characterization of a direct dc-excited discharge in water by optical emission spectroscopy. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 18(2):025017
Lu XP, Laroussi M (2005) Atmospheric pressure glow discharge in air using a water electrode. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 33(2):272–273
Wang H, Wandell RJ, Tachibana K, Voráč J, Locke BR (2018) The influence of liquid conductivity on electrical breakdown and hydrogen peroxide production in a nanosecond pulsed plasma discharge generated in a water-film plasma reactor. J Phys D Appl Phys 52(7):075201
Ishijima T, Hotta H, Sugai H, Sato M (2007) Multibubble plasma production and solvent decomposition in water by slot-excited microwave discharge. Appl Phys Lett 91(12):1–4
Hamdan A, Čerņevičs K, Cha MS (2017) The effect of electrical conductivity on nanosecond discharges in distilled water and in methanol with argon bubbles. J Phys D Appl Phys 50(18):185207
Kolikov VA et al (2007) Prolonged microbial resistance of water treated by a pulsed electrical discharge. Tech Phys 52(2):263–270
Kolikov VA, Kurochkin VE, Panina LK, Rutberg FG (2005) Pulse Electric discharges and the prolonged microbial resistance of water. Dokl Biol Sci 403:279–281
Lukes P et al (1999) Generation of chemically active species by electrical discharges in water. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 8:258
Liu J-L, Park H-W, Hamdan A, Cha MS (2018) In-liquid arc plasma jet and its application to phenol degradation. J Phys D Appl Phys 51:114005
Hamdan A, Liu JL, Cha MS (2018) Microwave plasma jet in water: characterization and feasibility to wastewater treatment. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 38(5):1003–1020
Malik MA (2010) Water purification by plasmas: which reactors are most energy efficient? Plasma Chem Plasma Process 30(1):21–31
Cardoso RP, Belmonte T, Keravec P, Kosior F, Henrion G (2007) Influence of impurities on the temperature of an atmospheric helium plasma in microwave resonant cavity. J Phys D Appl Phys 40:1394–1400
Bruggeman P, Brandenburg R (2013) Atmospheric pressure discharge filaments and microplasmas: physics, chemistry and diagnostics. J Phys D Appl Phys 46(46):464001
Chen C-J, Li S-Z, Zhang J, Liu D (2017) “Temporally resolved diagnosis of an atmospheric-pressure pulse- modulated argon surface wave plasma by optical emission spectroscopy. J Phys D Appl Phys 51(2):025201
Gigosos MA, Valentín C (1996) New plasma diagnosis tables of hydrogen Stark broadening including ion dynamics. J Phys B: At Mol Opt Phys 29(20):4795
Bruggeman P, Schram DC (2010) On OH production in water containing atmospheric pressure plasmas. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 19(4):045025
Bravo JA, Rincón R, Muñoz J, Sánchez A, Calzada MD (2015) Spectroscopic characterization of argon-nitrogen surface-wave discharges in dielectric tubes at atmospheric pressure. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 35(6):993–1014
Durocher-Jean A, Delnour N, Stafford L (2019) Influence of N2, O2, and H2 admixtures on the electron power balance and neutral gas heating in microwave Ar plasmas at atmospheric pressure. J Phys D Appl Phys. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361
Hamdan A, Gagnon C, Aykul M, Profili J (2019) Characterization of a microwave plasma jet (TIAGO) in-contact with water: application in degradation of methylene blue dye. Plasma Process Polym (submitted)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamdan, A., Profili, J. & Cha, M.S. Microwave Plasma Jet in Water: Effect of Water Electrical Conductivity on Plasma Characteristics. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 40, 169–185 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-019-10034-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-019-10034-5