Abstract
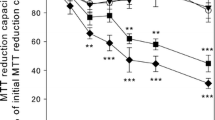
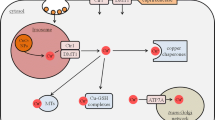
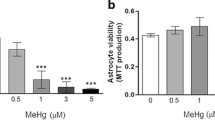
To test for the prolonged consequences of a short transient exposure of astrocytes to silver nanoparticles (AgNP), cultured primary astrocytes were incubated for 4 h in the presence of AgNP and the cell viability as well as various metabolic parameters were investigated during a subsequent incubation in AgNP-free medium. Acute exposure of astrocytes to AgNP led to a concentration-dependent increase in the specific cellular silver content to up to 46 nmol/mg protein, but did not compromise cell viability. During a subsequent incubation of the cells in AgNP-free medium, the cellular silver content of AgNP-treated astrocytes remained almost constant for up to 7 days. The cellular presence of AgNP did neither induce any delayed cell toxicity nor were alterations in cellular glucose consumption, lactate production or in the cellular ratio of glutathione to glutathione disulfide observed. However, Western blot analysis and immunocytochemical staining revealed that AgNP-treated astrocytes strongly upregulated the expression of metallothioneins. These results demonstrate that a prolonged presence of accumulated AgNP does not compromise the viability and the basal metabolism of cultured astrocytes and suggest that the upregulation of metallothioneins may help to prevent silver-mediated toxicity that could be induced by AgNP-derived silver ions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dastjerdi R, Montazer M (2010) A review on the application of inorganic nano-structured materials in the modification of textiles: focus on anti-microbial properties. Colloid Surf B 79(1):5–18
Ahamed M, AlSalhi MS, Siddiqui MKJ (2010) Silver nanoparticle applications and human health. Clin Chim Acta 411(23–24):1841–1848
Tolaymat TM, El Badawy AM, Genaidy A, Scheckel KG, Luxton TP, Suidan M (2010) An evidence-based environmental perspective of manufactured silver nanoparticle in syntheses and applications: a systematic review and critical appraisal of peer-reviewed scientific papers. Sci Total Environ 408(5):999–1006
Stensberg MC, Wei Q, McLamore ES, Porterfield DM, Wei A, Sepúlveda MS (2011) Toxicological studies on silver nanoparticles: challenges and opportunities in assessment, monitoring and imaging. Nanomedicine 6(5):879–898. doi:10.2217/nnm.11.78
Mahmoudi M, Azadmanesh K, Shokrgozar MA, Journeay WS, Laurent S (2011) Effect of nanoparticles on the cell life cycle. Chem Rev 111(5):3407–3432. doi:10.1021/cr1003166
Tang JL, Xiong L, Zhou GF, Wang S, Wang JY, Liu L, Li JG, Yuan FQ, Lu SF, Wan ZY, Chou LS, Xi TF (2010) Silver nanoparticles crossing through and distribution in the blood-brain barrier in vitro. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 10(10):6313–6317. doi:10.1166/jnn.2010.2625
Sharma HS, Patnaik R, Sharma A (2010) Diabetes aggravates nanoparticles induced breakdown of the blood-brain barrier permeability, brain edema formation, alterations in cerebral blood flow and neuronal injury. An experimental study using physiological and morphological investigations in the rat. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 10(12):7931–7945. doi:10.1166/jnn.2010.3616
Trickler WJ, Lantz SM, Murdock RC, Schrand AM, Robinson BL, Newport GD, Schlager JJ, Oldenburg SJ, Paule MG, Slikker W, Hussain SM, Ali SF (2010) Silver nanoparticle induced blood-brain barrier inflammation and increased permeability in primary rat brain microvessel endothelial cells. Toxicol Sci 118(1):160–170. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfq244
Mathiisen TM, Lehre KP, Danbolt NC, Ottersen OP (2010) The perivascular astroglial sheath provides a complete covering of the brain microvessels: an electron microscopic 3D reconstruction. Glia 58(9):1094–1103. doi:10.1002/glia.20990
Ji JH, Jung JH, Kim SS, Yoon J-U, Park JD, Choi BS, Chung YH, Kwon IH, Jeong J, Han BS, Shin JH, Sung JH, Song KS, Yu IJ (2007) Twenty-eight-day inhalation toxicity study of silver nanoparticles in Sprague–Dawley rats. Inhal Toxicol 19(10):857–871. doi:10.1080/08958370701432108
Win-Shwe TT, Fujimaki H (2011) Nanoparticles and neurotoxicity. Int J Mol Sci 12(9):6267–6280. doi:10.3390/ijms12096267
Luther EM, Koehler Y, Diendorf J, Epple M, Dringen R (2011) Accumulation of silver nanoparticles by cultured primary brain astrocytes. Nanotechnology 22(37):375101. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/22/37/375101
Greulich C, Diendorf J, Simon T, Eggeler G, Epple M, Köller M (2011) Uptake and intracellular distribution of silver nanoparticles in human mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Biomater 7(1):347–354
Hamprecht B, Löffler F (1985) Primary glial cultures as a model for studying hormone action. Method Enzymol 109:341–345
Dringen R, Kussmaul L, Hamprecht B (1998) Detoxification of exogenous hydrogen peroxide and organic hydroperoxides by cultured astroglial cells assessed by microtiter plate assay. Brain Res Prot 2(3):223–228
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193(1):265–275
Dringen R, Hamprecht B (1996) Glutathione content as an indicator for the presence of metabolic pathways of amino acids in astroglial cultures. J Neurochem 67(4):1375–1382. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.1996.67041375.x
Liddell JR, Zwingmann C, Schmidt MM, Thiessen A, Leibfritz D, Robinson SR, Dringen R (2009) Sustained hydrogen peroxide stress decreases lactate production by cultured astrocytes. J Neurosci Res 87(12):2696–2708. doi:10.1002/jnr.22093
Hohnholt MC, Geppert M, Dringen R (2011) Treatment with iron oxide nanoparticles induces ferritin synthesis but not oxidative stress in oligodendroglial cells. Acta Biomater 7(11):3946–3954. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2011.06.052
Aschner M, Conklin DR, Yao CP, Allen JW, Tan KH (1998) Induction of astrocyte metallothioneins (MTs) by zinc confers resistance against the acute cytotoxic effects of methylmercury on cell swelling, Na+ uptake, and K+ release. Brain Res 813(2):254–261. doi:10.1016/s0006-8993(98)00947-0
Aschner M, Cherian MG, Klaassen CD, Palmiter RD, Erickson JC, Bush AI (1997) Metallothioneins in brain—the role in physiology and pathology. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 142(2):229–242. doi:10.1006/taap.1996.8054
Haase A, Rott S, Mantion A, Graf P, Plendl J, Thünemann AF, Meier WP, Taubert A, Luch A, Reiser G (2012) Effects of silver nanoparticles on primary mixed neural cell cultures: uptake, oxidative stress and acute calcium responses. Toxicol Sci 126(2):457–468. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfs003
Suresh AK, Pelletier DA, Wang W, Morrell-Falvey JL, Gu B, Doktycz MJ (2012) Cytotoxicity induced by engineered silver nanocrystallites is dependent on surface coatings and cell types. Langmuir 28(5):2727–2735. doi:10.1021/la2042058
Foldbjerg R, Olesen P, Hougaard M, Dang DA, Hoffmann HJ, Autrup H (2009) PVP-coated silver nanoparticles and silver ions induce reactive oxygen species, apoptosis and necrosis in THP-1 monocytes. Toxicol Lett 190(2):156–162
Powers CM, Badireddy AR, Ryde IT, Seidler FJ, Slotkin TA (2010) Silver nanoparticles compromise neurodevelopment in PC12 Cells: critical contributions of silverion, particle size, coating, and composition. Environ Health Persp 119(1):37–44
Greulich C, Diendorf J, Gessmann J, Simon T, Habijan T, Eggeler G, Schildhauer TA, Epple M, Koller M (2011) Cell type-specific responses of peripheral blood mononuclear cells to silver nanoparticles. Acta Biomater 7(9):3505–3514. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2011.05.030
Piao MJ, Kang KA, Lee IK, Kim HS, Kim S, Choi JY, Choi J, Hyun JW (2011) Silver nanoparticles induce oxidative cell damage in human liver cells through inhibition of reduced glutathione and induction of mitochondria-involved apoptosis. Toxicol Lett 201(1):92–100. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2010.12.010
Hirrlinger J, Dringen R (2010) The cytosolic redox state of astrocytes: maintenance, regulation and functional implications for metabolite trafficking. Brain Res Rev 63(1–2):177–188
Tulpule K, Robinson SR, Bishop GM, Dringen R (2010) Uptake of ferrous iron by cultured rat astrocytes. J Neurosci Res 88(3):563–571. doi:10.1002/jnr.22217
Geppert M, Hohnholt MC, Thiel K, Nürnberger S, Grunwald I, Rezwan K, Dringen R (2011) Uptake of dimercaptosuccinate-coated magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles by cultured brain astrocytes. Nanotechnology 22(14):145101
Hoepken HH, Korten T, Robinson SR, Dringen R (2004) Iron accumulation, iron-mediated toxicity and altered levels of ferritin and transferrin receptor in cultured astrocytes during incubation with ferric ammonium citrate. J Neurochem 88(5):1194–1202
Dang TN, Bishop GM, Dringen R, Robinson SR (2011) The metabolism and toxicity of hemin in astrocytes. Glia 59(10):1540–1550. doi:10.1002/glia.21198
Kramer KK, Liu J, Choudhuri S, Klaassen CD (1996) Induction of metallothionein mRNA and protein in murine astrocyte cultures. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 136(1):94–100. doi:10.1006/taap.1996.0011
West AK, Hidalgo J, Eddins D, Levin ED, Aschner M (2008) Metallothionein in the central nervous system: roles in protection, regeneration and cognition. Neurotoxicology 29(3):489–503. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2007.12.006
Hidalgo J, Garcia A, Oliva AM, Giralt M, Gasull T, Gonzalez B, Milnerowicz H, Wood A, Bremner I (1994) Effect of zinc, copper and glucocorticoids on metallothionein levels of cultured neurons and astrocytes from rat brain. Chem Biol Interact 93(3):197–219
Miura N, Shinohara Y (2009) Cytotoxic effect and apoptosis induction by silver nanoparticles in HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 390(3):733–737. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.10.039
Kang SJ, I Ryoo, Lee YJ, Kwak M-K (2012) Role of the Nrf2-heme oxygenase-1 pathway in silver nanoparticle-mediated cytotoxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 258(1):89–98. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2011.10.011
AshaRani P, Hande MP, Valiyaveettil S (2009) Anti-proliferative activity of silver nanoparticles. BMC Cell Biol 10(1):65
Heuchel R, Radtke F, Georgiev O, Stark G, Aguet M, Schaffner W (1994) The transcription factor MTF-1 is essential for basal and heavy metal-induced metallothionein gene expression. EMBO J 13(12):2870–2875
Andrews GK (2000) Regulation of metallothionein gene expression by oxidative stress and metal ions. Biochem Pharmacol 59(1):95–104. doi:10.1016/s0006-2952(99)00301-9
Vašák M, Meloni G (2011) Chemistry and biology of mammalian metallothioneins. J Biol Inorg Chem 16(7):1067–1078. doi:10.1007/s00775-011-0799-2
Floriańczyk B (2007) Metallothioneins and its role in metal regulation, binding of reactive oxygen species, apoptosis and cell differentiation. J Pre-Clin Clin Res 1(1):016–018
Cortese-Krott MM, Münchow M, Pirev E, Heβner F, Bozkurt A, Uciechowski P, Pallua N, Kröncke K-D, Suschek CV (2009) Silver ions induce oxidative stress and intracellular zinc release in human skin fibroblasts. Free Radic Biol Med 47(11):1570–1577. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.08.023
Ohtsuji M, Katsuoka F, Kobayashi A, Aburatani H, Hayes JD, Yamamoto M (2008) Nrf1 and Nrf2 play distinct roles in activation of antioxidant response element-dependent genes. J Biol Chem 283(48):33554–33562. doi:10.1074/jbc.M804597200
Reisman SA, Aleksunes LM, Klaassen CD (2009) Oleanolic acid activates Nrf2 and protects from acetaminophen hepatotoxicity via Nrf2-dependent and Nrf2-independent processes. Biochem Pharmacol 77(7):1273–1282
Bishop GM, Dringen R, Robinson SR (2007) Zinc stimulates the production of toxic reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inhibits glutathione reductase in astrocytes. Free Rad Biol Med 42(8):1222–1230
Yao CP, Allen JW, Mutkus LA, Xu SB, Tan KH, Aschner M (2000) Foreign metallothionein-I expression by transient transfection in MT-I and MT-II null astrocytes confers increased protection against acute methylmercury cytotoxicity. Brain Res 855(1):32–38. doi:10.1016/s0006-8993(99)02211-8
Hidalgo J, Aschner M, Zatta P, Vašák M (2001) Roles of the metallothionein family of proteins in the central nervous system. Brain Res Bull 55(2):133–145. doi:10.1016/s0361-9230(01)00452-x
Tiffany-Castiglioni E, Qian Y (2001) Astroglia as metal depots: molecular mechanisms for metal accumulation, storage and release. Neurotoxicology 22(5):577–592
Dringen R, Bishop G, Koeppe M, Dang T, Robinson S (2007) The pivotal role of astrocytes in the metabolism of iron in the brain. Neurochem Res 32(11):1884–1890. doi:10.1007/s11064-007-9375-0
Acknowledgments
E.M. Luther is a member of the Ph.D. graduate school nanoToxCom at the University of Bremen and would like to thank the Hans-Böckler Stiftung for her Ph.D. fellowship. M. Epple thanks the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft for funding within the Priority Program SPP 1313 BioNanoResponses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luther, E.M., Schmidt, M.M., Diendorf, J. et al. Upregulation of Metallothioneins After Exposure of Cultured Primary Astrocytes to Silver Nanoparticles. Neurochem Res 37, 1639–1648 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-012-0767-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-012-0767-4