Abstract
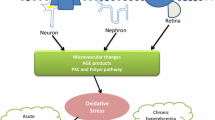
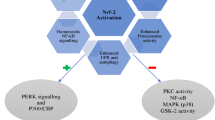
In spite of much awareness, diabetes mellitus continues to remain one of major reasons for mortality and morbidity rate all over the globe. Free radicals cause oxidative stress which is responsible for causing diabetes. The recent advancements in elucidation of ARE/keap1/Nrf2 pathway can help in better understanding of diabetes mellitus. Various clinical trials and animal studies have shown the promising effect of Nrf2 pathway in reversing diabetes by counteracting with the oxidative stress produced. The gene is known to dissociate from Keap1 on coming in contact with such stresses to show preventive and prognosis effect. The Nrf2 gene has been marked as a molecular player in dealing with wide intracellular as well as extracellular cellular interactions in different diseases. The regulation of this gene gives some transcription factor that contain antioxidant response elements (ARE) in their promoter region and thus are responsible for encoding certain proteins involved in regulation of metabolic and detoxifying enzymes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tan SM, de Haan JB (2014) Combating oxidative stress in diabetic complications with Nrf2 activators: how much is too much? Redox Rep 19(3):107–117. https://doi.org/10.1179/1351000214Y.0000000087
Dieleman JL, Baral R, Birger M, Bui AL, Bulchis A et al (2016) US spending on personal health care and public health, 1996–2013. JAMA 316(24):2627–2646. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2016.16885
Whiting DR, Guariguata L, Weil C, Shaw J (2011) IDF diabetes atlas: global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2011 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 94(3):311–321. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-016-1896-7
Schaffer SW, Jong CJ, Mozaffari M (2012) Role of oxidative stress in diabetes-mediated vascular dysfunction: unifying hypothesis of diabetes revisited. Vasc Pharmacol 57(5–6):139–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vph.2012.03.005
Sporn MB, Liby KT (2012) NRF2 and cancer: the good, the bad and the importance of context. Nat Rev Cancer 12(8):564–571. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3278
Zheng H, Whitman SA, Wu W, Wondrak GT, Wong PK et al (2011) Therapeutic potential of Nrf2 activators in streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 60(11):3055–3066. https://doi.org/10.2337/db11-0807
El-Bab MF, Zaki NS, Mojaddidi MA, Al-Barry M, El-Beshbishy HA (2013) Diabetic retinopathy is associated with oxidative stress and mitigation of gene expression of antioxidant enzymes. Int J Gen Med 6:799. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJGM.S40665
Ghosh P, Sahoo R, Vaidya A, Chorev M, Halperin JA (2015) Role of complement and complement regulatory proteins in the complications of diabetes. Endocr Rev 36(3):272–288. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2019.00459
Ayers D, Baron B, Hunter T (2015) miRNA influences in NRF2 pathway interactions within cancer models. J Nucleic Acids. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/143636
Kumagai Y, Kanda H, Shinkai Y, Toyama T (2013) The role of the Keap1/Nrf2 pathway in the cellular response to methylmercury. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/848279
Zhou S, Sun W, Zhang Z, Zheng Y (2014) The role of Nrf2-mediated pathway in cardiac remodeling and heart failure. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/260429
Wu P, Yan Y, Ma LL, Hou BY, He YY et al (2016) Effects of the Nrf2 protein modulator salvianolic acid A alone or combined with metformin on diabetes-associated macrovascular and renal injury. J Biol Chem 291(42):22288–22301. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.712703
Xu Z, Wang S, Ji H, Zhang Z, Chen J et al (2016) Broccoli sprout extract prevents diabetic cardiomyopathy via Nrf2 activation in db/db T2DM mice. Sci Rep 6:30252. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep30252
Zhang H, Liu YY, Jiang Q, Li KR, Zhao YX et al (2014) Salvianolic acid A protects RPE cells against oxidative stress through activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling. Free Radic Biol Med 69:219–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.01.025
Asmat U, Abad K, Saudi KI (2016) Diabetes mellitus and oxidative stress—a concise review. Pharm J 24(5):547–553
Lipinski B (2001) Pathophysiology of oxidative stress in diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Complications 15(4):203–210
Maritim AC, Sanders RA, Watkins JB (2003) Diabetes, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: a review. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 17(1):24–38
Pham-Huy LA, He H, Pham-Huy C (2008) Free radicals, antioxidants in disease and health. Int J Biomed Sci 4(2):89–96
Erejuwa OO (2012) Oxidative stress in diabetes mellitus: is there a role for hypoglycemic drugs and/or antioxidants. In: Oxidative stress and disease. IntechOpen, Croatia, pp 217–246
Xue M, Qian Q, Adaikalakoteswari A, Rabbani N, BabaeiJadidi R, Thornalley PJ (2008) Activation of NF-E2-related factor-2 reverses biochemical dysfunction of endothelial cells induced by hyperglycemia linked to vascular disease. Diabetes 57:2809–2817. https://doi.org/10.2337/db06-1003
Wang Y, Feng W, Xue W, Tan Y, Hein DW, Li XK et al (2009) Inactivation of GSK-3β by metallothionein prevents diabetes-related changes in cardiac energy metabolism, inflammation, nitrosative damage, and remodeling. Diabetes 58(6):1391–1402. https://doi.org/10.2337/db08-1697
Li J, Ichikawa T, Janicki JS, Cui T (2009) Targeting the Nrf2 pathway against cardiovascular disease. Expert Opin Ther Targets 13(7):785–794. https://doi.org/10.1517/14728220903025762
Pergola PE, Raskin P, Toto RD, Meyer CJ, Huff JW et al (2011) Bardoxolone methyl and kidney function in CKD with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 365(4):327–336. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1105351
Kim HJ, Vaziri ND (2010) Contribution of impaired Nrf2-Keap1 pathway to oxidative stress and inflammation in chronic renal failure. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 298(3):F662–F671. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00421.2009
He X, Kan H, Cai L, Ma Q (2009) Nrf2 is critical in defense against high glucose-induced oxidative damage in cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 46(1):47–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2008.10.007
Miao X, Bai Y, Sun W, Cui W, Xin Y et al (2012) Sulforaphane prevention of diabetes-induced aortic damage was associated with the up-regulation of Nrf2 and its down-stream antioxidants. Nutr Metab 9(1):84. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-7075-9-84
Bai Y, Cui W, Xin Y, Miao X, Barati MT et al (2013) Prevention by sulforaphane of diabetic cardiomyopathy is associated with up-regulation of Nrf2 expression and transcription activation. J Mol Cell Cardiol 57:82–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2008.10.007
Soares MA, Cohen OD, Low YC, Sartor RA, Ellison T et al (2016) Restoration of Nrf2 signaling normalizes the regenerative niche. Diabetes 65(3):633–646. https://doi.org/10.2337/db15-0453
Tan Y, Ichikawa T, Li J, Si Q, Yang H et al (2011) Diabetic downregulation of Nrf2 activity via ERK contributes to oxidative stress–induced insulin resistance in cardiac cells in vitro and in vivo. Diabetes 60(2):625–633. https://doi.org/10.2337/db10-1164
Zhong Q, Mishra M, Kowluru RA (2013) Transcription factor Nrf2-mediated antioxidant defense system in the development of diabetic retinopathy. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci 54(6):3941–3948. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.13-11598
Liu M, Grigoryev DN, Crow MT, Haas M, Yamamoto M et al (2019) Transcription factor Nrf2 is protective during ischemic and nephrotoxic acute kidney injury in mice. Kidney Int 76(3):277–285. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2009.157
Shanmugam G, Narasimhan M, Sakthivel R, Kumar R, Davidson C et al (2016) A biphasic effect of TNF-α in regulation of the Keap1/Nrf2 pathway in cardiomyocytes. Redox Biol 9:77–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2016.06.004
Deng C, Sun Z, Tong G, Yi W, Ma L, Zhao B et al (2013) α-Lipoic acid reduces infarct size and preserves cardiac function in rat myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through activation of PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 pathway. PLoS One 8(3):e58371. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0058371
Xue P, Hou Y, Chen Y, Yang B, Fu J et al (2013) Adipose deficiency of Nrf2 in ob/ob mice results in severe metabolic syndrome. Diabetes 62(3):845–854. https://doi.org/10.2337/db12-0584
Li J, Ichikawa T, Villacorta L, Janicki JS, Brower GL, Yamamoto M et al (2009) Nrf2 protects against maladaptive cardiac responses to hemodynamic stress. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29(11):1843–1850. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.189480
Oikawa K, Ishihara R, Maeda T, Yamaguchi K, Koike A et al (2009) Prognostic value of heart rate variability in patients with renal failure on hemodialysis. Int J Cardiol 131(3):370–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2007.10.033
Jiang T, Huang Z, Lin Y, Zhang Z, Fang D, Zhang DD (2010) The protective role of Nrf2 in streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 59(4):850–860. https://doi.org/10.2337/db09-1342
Sonntag KP, de Cabo R, Csiszar A, Zhang C, Ballabh P, Recchia FA et al (2011) Adaptive induction of NF-E2-related factor-2-driven. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 300:H1133–H1140. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00402.2010
Jurgens CA, Toukatly MN, Fligner CL, Udayasankar J, Subramanian SL et al (2011) β-cell loss and β-cell apoptosis in human type 2 diabetes are related to islet amyloid deposition. Am J Pathol 178(6):2632–2640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.02.036
Karakose E, Ackeifi C, Wang P, Stewart AF (2018) Advances in drug discovery for human beta cell regeneration. Diabetologia 61(8):1693–1699. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-018-4639-6
Nezu M, Suzuki N, Yamamoto M (2017) Targeting the KEAP1-NRF2 system to prevent kidney disease progression. Am J Nephrol 45(6):473–483. https://doi.org/10.1159/000475890
Takaya K, Suzuki T, Motohashi H, Onodera K, Satomi S et al (2012) Validation of the multiple sensor mechanism of the Keap1-Nrf2 system. Free Radic Biol Med 53(4):817–827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.06.023
Yu ZW, Li D, Ling WH, Jin TR (2012) Role of nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 in metabolic homeostasis and insulin action: a novel opportunity for diabetes treatment? World J Diabetes 3(1):19. https://doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v3.i1.19
Meneses MJ, Silvestre R, Sousa-Lima I, Macedo MP (2019) Paraoxonase-1 as a regulator of glucose and lipid homeostasis: impact on the onset and progression of metabolic disorders. Int J Mol Sci 20(16):4049. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20164049
Arellano-Buendía AS, Tostado-González M, García-Arroyo FE, Cristóbal-García M, Loredo-Mendoza ML et al (2016) Anti-inflammatory therapy modulates Nrf2-Keap1 in kidney from rats with diabetes. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/4693801
Li B, Liu S, Miao L, Cai L (2012) Prevention of diabetic complications by activation of Nrf2: diabetic cardiomyopathy and nephropathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/216512
Li B, Cui W, Tan Y, Luo P, Chen Q et al (2014) Zinc is essential for the transcription function of Nrf2 in human renal tubule cells in vitro and mouse kidney in vivo under the diabetic condition. J Cell Mol Med 18(5):895–906. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.12239
Saha PK, Reddy VT, Konopleva M, Andreeff M, Chan L (2010) The triterpenoid 2-cyano-3, 12-dioxooleana-1, 9-dien-28-oic-acid methyl ester has potent anti-diabetic effects in diet-induced diabetic mice and Leprdb/db mice. J Biol Chem 285(52):40581–40592. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.176545
Gerber PA, Rutter GA (2017) The role of oxidative stress and hypoxia in pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. Antioxid Redox 26(10):501–518. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2016.6755
Furusawa Y, Uruno A, Yagishita Y, Higashi C, Yamamoto M (2014) Nrf2 induces fibroblast growth factor 21 in diabetic mice. Genes Cells 19(12):864–878. https://doi.org/10.1111/gtc.12186
Puddu A, Sanguineti R, Mach F, Dallegri F, Viviani GL, Montecucco F (2013) Update on the protective molecular pathways improving pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction. Mediat Inflamm. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/750540
Cui W, Bai Y, Miao X, Luo P, Chen Q et al (2012) Prevention of diabetic nephropathy by sulforaphane: possible role of Nrf2 upregulation and activation. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/821936
Thornalley PJ, Rabbani N (2012) Dietary and synthetic activators of the antistress gene response in treatment of renal disease. J Ren Nutr 22(1):195–202. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jrn.2011.10.012
De Haan JB (2011) Nrf2 activators as attractive therapeutics for diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 60(11):2683–2684. https://doi.org/10.2337/db11-1072
Liu Y, Wang Y, Miao X, Zhou S, Tan Y et al (2014) Inhibition of JNK by compound C66 prevents pathological changes of the aorta in STZ‐induced diabetes. J Cell Mol Med 18(6):1203–1212. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.12267
Sireesh D, Dhamodharan U, Ezhilarasi K, Vijay V, Ramkumar KM (2018) Association of NF-E2 related factor 2 (Nrf2) and inflammatory cytokines in recent onset type 2 diabetes mellitus. Sci Rep 8:5126. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-22913-6
Wu KC, McDonald PR, Liu J, Klaassen CD (2014) Screening of natural compounds as activators of the keap1-nrf2 pathway. Planta Med 80(1):97. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0033-1351097
Rabbani PS, Zhou A, Borab ZM, Frezzo JA, Srivastava N et al (2017) Novel lipoproteoplex delivers Keap1 siRNA-based gene therapy to accelerate diabetic wound healing. Biomaterials 132:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.04.001
Palsamy P, Subramanian S (2011) Resveratrol protects diabetic kidney by attenuating hyperglycemia-mediated oxidative stress and renal inflammatory cytokines via Nrf2–Keap1 signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1812(7):719–731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.03.008
Larouche J, Sheoran S, Maruyama K, Martino MM (2018) Immune regulation of skin wound healing: mechanisms and novel therapeutic targets. Adv Wound Care 7(7):209–231. https://doi.org/10.1089/wound.2017.0761
Facecchia K, Fochesato LA, Ray SD, Stohs SJ, Pandey S (2011) Oxidative toxicity in neurodegenerative diseases: role of mitochondrial dysfunction and therapeutic strategies. J Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/683728
Cuadrado A, Manda G, Hassan A, Alcaraz MJ, Barbas C et al (2018) Transcription factor NRF2 as a therapeutic target for chronic diseases: a systems medicine approach. Pharmacol Rev 70(2):348–383. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.117.014753
Kitamura H, Motohashi H (2018) NRF2 addiction in cancer cells. Cancer Sci 109(4):900–911. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13537
Abbasi A, Corpeleijn E, Gansevoort RT, Gans RO, Struck J et al (2014) Circulating peroxiredoxin 4 and type 2 diabetes risk: The Prevention of Renal and Vascular Endstage Disease (PREVEND) study. Diabetologia 57(9):1842–1849. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-014-3278-9
Katoh Y, Iida K, Kang MI, Kobayashi A, Mizukami M et al (2005) Evolutionary conserved N-terminal domain of Nrf2 is essential for the Keap1-mediated degradation of the protein by proteasome. Arch Biochem Biophys 433(2):342–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2004.10.012
Bonnard C, Durand A, Peyrol S, Chanseaume E, Chauvin MA, Morio B, Vidal H, Rieusset J (2008) Mitochondrial dysfunction results from oxidative stress in the skeletal muscle of diet-induced insulin-resistant mice. J Clin Invest 118:789–800. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI32601
Bashan N, Kovsan J, Kachko I, Ovadia H, Rudich A (2009) Positive and negative regulation of insulin signaling by reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. Physiol Rev 89:27–71. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00014.2008
Tullet JM, Hertweck M, An JH, Baker J, Hwang JY, Liu S, Oliveira RP, Baumeister R, Blackwell TK (2018) Direct inhibition of the longevity-promoting factor SKN-1 by insulin-like signaling in C. elegans. Cell 132(1025):1038–1050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2008.01.030roteasome
Reisman SA, Buckley DB, Tanaka Y et al (2009) CDDO-Im protects from acetaminophen hepatotoxicity through induction of Nrf2-dependent genes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 236:109–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2008.12.024
Tsai PY, Ka SM, Chang JM et al (2011) Epigallocatechin-3-gallate prevents lupus nephritis development in mice via enhancing the Nrf2 antioxidant pathway and inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Free Radic Biol Med 51:744–754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.05.016
Maher J, Yamamoto M (2014) The rise of antioxidant signaling-the evolution and hormetic actions of Nrf2. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 244:4–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2010.01.011
Yu Z, Shao W, Chiang Y, Foltz W, Zhang Z, Ling W, Fantus IG, Jin T (2011) Oltipraz upregulates the nuclear factor (erythroidderived 2)-like 2 [corrected] (NRF2) antioxidant system and prevents insulin resistance and obesity induced by a highfat diet in C57BL/6J mice. Diabetologia 54:922–934. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-010-2001-8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TB and ES: Draft of the article; TB: Conceived the idea, Proof Reading; IK, AS and MG: Literature Review and Revision Process; AK: Figure Work; SB: Proof Read.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest in preparing the current article.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Behl, T., Kaur, I., Sehgal, A. et al. Unfolding Nrf2 in diabetes mellitus. Mol Biol Rep 48, 927–939 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-06081-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-06081-3