Abstract
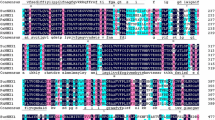
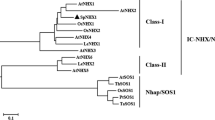
Salinity causes multifarious adverse effects to plants. Plants response to salt stress involves numerous processes that function in coordination to alleviate both cellular hyperosmolarity and ion disequilibrium. A Na+/H+ antiporter NHX1 gene has been isolated from a halophytic plant Salicornia brachiata in this study. Predicted amino acid sequence similarity, protein topology and the presence of functional domains conserved in SbNHX1 classify it as a plant vacuolar NHX gene. The SbNHX1 cDNA has an open reading frame of 1,683 bp, encoding a polypeptide of 560 amino acid residues with an estimated molecular mass 62.44 kDa. The SbNHX1 shows high amino acid similarity with other halophytic NHX gene and belongs to Class-I type NHXs. TMpred suggests that SbNHX1 contains 11 strong transmembrane (TM). Real time PCR analysis revealed that SbNHX1 transcript expresses maximum at 0.5 M. Transcript increases gradually by increasing the treatment duration at 0.5 M NaCl, however, maximum expression was observed at 48 h. The overexpression of SbNHX1 gene in tobacco plant showed NaCl tolerance. This study shows that SbNHX1 is a potential gene for salt tolerance, and can be used in future for developing salt tolerant crops.




Similar content being viewed by others

References
Blumwald E (2000) Sodium transport and salt tolerance in plants. Curr Opin Cell Biol 12:431–434
Shi H, Lee BH, Wu SJ, Zhu JK (2003) Over-expression of a plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter gene improves salt tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Biotechnol 21:81–85
Taji T, Seki M, Satou M, Sakurai T, Kobayashi M, Ishiyama K et al (2004) Comparative genomics in salt tolerance between Arabidopsis and Arabidopsis-related halophyte salt cress using Arabidopsis microarray. Plant Physiol 135:1697–1709
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681
Niu X, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM, Pardo JM (1995) Ion homeostasis in NaCl stress environments. Plant Physiol 109:735–742
Blumwald E, Aharon GS, Apse MP (2000) Sodium transport in plant cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1465:140–151
Brett CL, Donowitz M, Rao R (2005) Evolutionary origins of eukaryotic sodium/proton exchangers. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 288:223–239
Pardo JM, Cubero B, Leidi EO, Quintero FJ (2006) Alkali cation exchangers: roles in cellular homeostasis and stress tolerance. J Exp Bot 57:1181–1199
Yokoi S, Quintero FJ, Cubero B, Ruiz T, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM, Pardo JM (2002) Differential expression and function of Arabidopsis thaliana NHX Na+/H+ antiporters in the salt stress response. Plant J 30:1–12
Gaxiola RA, Rao R, Sherman A, Grifasi P, Alpier SL, Fink GR (1999) The Arabidopsis thaliana proton transporters, AtNHX1 and Avp1, can function in cation detoxification in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:1480–1485
Apse MP, Aharon GS, Snedden WA, Blumwald E (1999) Salt tolerance conferred by over expression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiport in Arabidopsis. Science 285:1256–1258
Zhang HX, Blumwald E (2001) Transgenic salt-tolerant tomato plants accumulate salt in foliage but not in fruit. Nat Biotechnol 19:765–768
Zhang HX, Hodson JN, Williams JP, Blumwald E (2001) Engineering salt-tolerant Brassica plants: characterization of yield and seed oil quality in transgenic plants with increased vacuolar sodium accumulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:12832–12836
Xue ZY, Zhi DY, Xue GP, Zhang H, Zhao YX, Xia GM (2004) Enhanced salt tolerance of transgenic wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) expressing a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene with improved grain yields in saline soils in the field and a reduced level of leaf Na+. Plant Sci 167:849–859
Rajagopal D, Agarwal P, Tyagi W, Singla-Pareek SL, Reddy MK, Sopory SK (2007) Pennisetum glaucum Na+/H+ antiporter confers high level of salinity tolerance in transgenic Brassica juncea. Mol Breed 19:137–151
Chauhan S, Forsthoefel N, Ran Y, Quigley F, Nelson DE, Bohnert HJ (2000) Na+/myo-inositol symporters and Na+/H+-antiport in Mesembryanthemum crystallinum. Plant J 24:511–522
Hamada A, Shono M, Xia T, Ohta M, Hayashi Y, Tanaka A, Hayakawa T (2001) Isolation and characterization of a Na+/H+ antiporter gene from the halophyte Atriplex gmelini. Plant Mol Biol 46:35–42
Ma XL, Zhang Q, Shi HZ, Zhu JK, Zhao YX, Ma CL, Zhang H (2004) Molecular cloning and different expression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene in Suaeda salsa under salt stress. Biol Plant 48:219–225
Xia T, Apse MP, Aharon GS, Blumwald E (2002) Identification and characterization of a NaCl-inducible vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter in Beta vulgaris. Physiol Plant 116:206–212
Zhou S, Chen X, Zhang X, Li Y (2008) Improved salt tolerance in tobacco plants by co-transformation of a betaine synthesis gene BADH and a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene SeNHX1. Biotechnol Lett 30:369–376
Jha B, Agarwal PK, Reddy PS, Lal S, Sopory SK, Reddy MK (2009) Identification of salt -induced genes from Salicornia brachiata, an extreme halophyte through expressed sequence tags analysis. Genes Genet Syst 84:111–120
Agarwal PK, Gupta K, Jha B (2010) Molecular characterization of the Salicornia brachiata SbMAPKK gene and its expression by abiotic stress. Mol Biol Rep 37:981–986
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real- time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts polyphenol oxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24:1–15
Nagata T, Iizumi S, Satoh K, Kikuchi S (2008) Comparative molecular biological analysis of membrane transport genes in organisms. Plant Mol Biol 66:565–585
Counillon L, Pouyssegur J (2000) The expanding family of eukaryotic Na+/H+ exchangers. J Biol Chem 275:1–4
Rodríguez-Rosales MP, Gálvez FJ, Huertas R, Aranda MN, Baghour M, Cagnac O, Venema K (2009) Plant NHX cation/proton antiporters. Plant Signal Behav 4:265–276
Vera-Estrella R, Barkla BJ, García-Ramírez L, Pantoja O (2005) Salt stress in Thellungiella halophila activates Na+ transport mechanisms required for salinity tolerance. Plant Physiol 139:1507–1517
Wells KM, Rao R (2001) The yeast Na+/H+ exchanger Nhx1 is an N-linked glycoprotein. Topological implications. J Biol Chem 276:3401–3407
Zahran HH, Marín-Manzano MC, Sánchez-Raya AJ, Bedmar EJ, Venema K, Rodríguez-Rosales MP (2007) Effect of salt stress on the expression of NHX-type ion transporters in Medicago intretexta and Melilotus indicus plants. Physiol Plant 131:122–130
Zörb C, Noll A, Karl S, Leib K, Yan F, Schubert S (2004) Molecular characterization of Na+/H+ antiporters (ZmNHX) of maize (Zea mays L.) and their expression under salt stress. J Plant Physiol 162:55–66
Fukuda A, Chiba K, Maeda M, Nakamura A, Maeshima M, Tanaka Y (2004) Effect of salt and osmotic stresses on the expression of genes for the vacuolar H+-pyrophosphatase, H+-ATPase subunit A, and Na+/H+ antiporter from barley. J Exp Bot 55:585–594
Fukuda A, Nakamura A, Tagiri A, Tanaka H, Miyao A, Hirochika H et al (2004) Function, intracellular localization and the importance in salt tolerance of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter from rice. Plant Cell Physiol 45:146–159
Wu CA, Yang GD, Meng QW, Zheng CC (2004) The cotton GhNHX1 gene encoding a novel putative tonoplast Na+/H+ antiporter plays an important role in salt stress. Plant Cell Physiol 45:600–607
Wang ZN, Zhang JS, Guo BH, He SJ, Tian AG, Chen SY (2002) Cloning and characterization of the Na+/H+ antiport genes from Triticum aestivum. Acta Bot Sin 44:1203–1208
Li JY, He XW, Xu L, Zhou J, Wu P, Shou HX et al (2007) Molecular and functional comparisons of the vacuolar Na+/H+ exchangers originated from glycophytic and halophytic species. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 9:132–140
Zhang GH, Su Q, An LJ, Wu S (2008) Characterization and expression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene from the monocot halophyte Aeluropus littoralis. Plant Physiol Biochem 46:117–126
Ohta M, Hayashi Y, Nakashima A, Hamada A, Tanaka A, Nakamura T et al (2002) Introduction of a Na+/H+ antiporter gene from Atriplex gmelini confers salt tolerance to rice. FEBS Lett 532:279–282
Liu P, Yang GD, Li H, Zheng CC, Wu C-A (2010) Overexpression of NHX1s in transgenic Arabidopsis enhances photoprotection capacity in high salinity and drought conditions. Acta Physiol Plant 32:81–90
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to DST, Govt. of India, New Delhi for financial support. AJ is thankful to DST for Junior Research Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jha, A., Joshi, M., Yadav, N.S. et al. Cloning and characterization of the Salicornia brachiata Na+/H+ antiporter gene SbNHX1 and its expression by abiotic stress. Mol Biol Rep 38, 1965–1973 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0318-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0318-5