Abstract
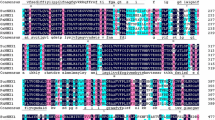
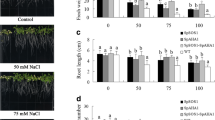
The plant Na+/H+ antiporter (NHX) plays a significant role in cellular ion homeostasis. Herein, an Na+/H+ antiporter gene, SpNHX1 from the Sesuvium portulacastrum plant, was obtained by homology-cloning method. The SpNHX1 gene contains 2113 bp with an open-reading frame encoding a polypeptide of 554 amino acid residues with an estimated molecular mass of 61.27 kDa and an isoelectric point of 7.24. The amino acid sequences of SpNHX1 shared a high similarity with Arabidopsis thaliana AtNHX1 (75.81%), AtNHX2 (77.12%) and Oryza sativa OsNHX1 (73.10%). SpNHX1 contains an amiloride-binding region (FFIYLLPPI), which is a highly-conserved domain in plant Na+/H+ antiporters. RT-PCR (reverse transcriptional PCR) analysis showed that the SpNHX1 gene had a high expression level in roots compared to other tissues under normal conditions. The qRT-PCR (quantitative real-time PCR) results indicated that NaCl treatment induced the expression of SpNHX1 gene in the roots, but its transcriptional levels were not influenced by the ABA, PEG, H2O2, heat (42 °C) or cold (4 °C) stresses. The growth of yeast cells expressing SpNHX1 was better than the non-transgenic control cells in the presence of 30 mM NaCl, 0.4 M KCl, or 0.5 mM LiCl. Furthermore, transgenic yeast cells with SpNHX1 accumulated more Na+ relative to control cells under salinity stress. These results suggested that SpNHX1 was a key determinant in the salt-stress response in Sesuvium portulacastrum.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apse MP, Aharon GS, Snedden WA et al (1999) Salt tolerance conferred by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiport in Arabidopsis. Science 285:1256–1258
Asif MA, Zafar Y, Iqbal J et al (2011) Enhanced expression of AtNHX1, in transgenic groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) improves salt and drought tolerance. Mol Biotechnol 49:250–256
Banjara M, Zhu L, Shen G et al (2012) Expression of an Arabidopsis sodium/proton antiporter gene (AtNHX1) in peanut to improve salt tolerance. Plant Biotechnol Rep 6:59–67
Barragan V, Leidi EO, Andres Z et al (2012) Ion exchangers NHX1 and NHX2 mediate active potassium uptake into vacuoles to regulate cell turgor and stomatal function in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24:1127–1142
Blumwald E, Poole RJ (1985) Na/H antiport in isolated tonoplast vesicles from storage tissue of Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 78:163–167
Brett CL, Donowitz M, Rao R (2005) Evolutionary origins of eukaryotic sodium/proton exchangers. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 288:C223–C239
Brini F, Hanin M, Mezghani I et al (2007) Over-expression of wheat Na+/H+ antiporter TNHX1 and H+-pyrophosphatase TVP1 improve salt- and drought-stress tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana plants. J Exp Bot 58:301–308
Chen M, Chen Q, Niu X et al (2007) Expression of OsNHX1 gene in maize confers salt tolerance and promotes plant growth in the field. Plant Soil Environ 53:490–498
Fan W, Deng G, Wang H et al (2015) Elevated compartmentalization of Na+ into vacuoles improves salt and cold stress tolerance in sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas). Physiol Plant 154:560–571
Fukuda A, Nakamura A, Tagin A et al (2004) Function, intracellular localization and the importance in salt tolerance of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter from rice. Plant Cell Physiol 45:146–159
Fukuda A, Nakamura A, Hara N et al (2011) Molecular and functional analyses of rice NHX-type Na+/H+ antiporter genes. Planta 233:175–188
Gaxiola RA, Rao R, Sherman A et al (1999) The Arabidopsis thaliana proton transporters, AtNhx1 and Avp1, can function in cation detoxification in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:1480–1485
Kizhakkedath P, Jegadeeson V, Venkataraman G et al (2015) A vacuolar antiporter is differentially regulated in leaves and roots of the halophytic wild rice Porteresia coarctata (Roxb.) Tateoka. Mol Biol Rep 42:1091–1105
Kronzucker HJ, Britto DT (2011) Sodium transport in plants: a critical review. New Phytol 189:54–81
Liu SP, Zheng LQ, Xue YH et al (2010) Overexpression of OsVP1 and OsNHX1 increases tolerance to drought and salinity in rice. J Plant Biol 53:444–452
Liu L, Zeng Y, Pan X et al (2012) Isolation, molecular characterization, and functional analysis of the vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter genes from the halophyte Karelinia caspica. Mol Biol Rep 39:7193–7202
Liu QL, Xu KD, Zhong M et al (2013) Cloning and characterization of a novel vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene (Dgnhx1) from chrysanthemum. PLoS One 8:e83702
Ma XL, Zhang Q, Shi HZ et al (2004) Molecular cloning and different expression of a Na+/H+ antiporter gene in Suada salsa under salt stress. Biol Plantarum 48:219–225
Messedi D, Sleimi N, Abdelly C (2001) Salt tolerance in Sesuvium portulacastrum. Plant Nutr 92:406–407
Mishra S, Alavilli H, Lee BH et al (2014) Cloning and functional characterization of a Na+/H+ antiporter gene from mungbean (VrNHX1) and its ectopic expression enhanced salt tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS One 9:e106678
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 58:651–681
Ohta M, Hayashi Y, Nakashima A et al (2002) Introduction of a Na+/H+ antiporter gene from Atriplex gmelini confers salt tolerance to rice. FEBS Lett 532(3):279–282
Pardo JM, Cubero B, Leidi EO et al (2006) Alkali cation exchangers: roles in cellular homeostasis and stress tolerance. J Exp Bot 57:1181–1199
Qiao WH, Zhao XY, Li W et al (2007) Overexpression of AeNHX1, a root-specific vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter from Agropyron elongatum, confers salt tolerance to Arabidopsis and Festuca plants. Plant Cell Rep 26:1663–1672
Quintero FJ, Blatt MR, Pardo JM (2000) Functional conservation between yeast and plant endosomal Na+/H+ antiporters. FEBS Lett 472:224–228
Rodriguez-Rosales MP, Jiang XY, Galvez FJ et al (2008) Overexpression of the tomato K+/H+ antiporter LeNHX2 confers salt tolerance by improving potassium compartmentalization. New Phytol 179:366–377
Rodriguez-Rosales MP, Galvez FJ, Huertas R et al (2009) Plant NHX cation/proton antiporters. Plant Signal Behav 4:265–276
Shi HZ, Ishitani M, Kim C et al (2000) The Arabidopsis thaliana salt tolerance gene SOS1 encodes a putative Na+/H+ antiporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:6896–6901
Shi HZ, Quintero FJ, Pardo JM et al (2002) The putative plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter SOS1 controls long-distance Na+ transport in plants. Plant Cell 14:465–477
Shi HZ, Lee BH, Wu SJ et al (2003) Overexpression of a plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter gene improves salt tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Biotechnol 21:81–85
Silva P, Geros H (2009) Regulation by salt of vacuolar H+-ATPase and H+-pyrophosphatase activities and Na+/H+ exchange. Plant Signal Behav 4(8):718–726
Slama I, Ghnaya T, Messedi D et al (2007) Cd-induced growth reduction in the halophyte Sesuvium portulacastrum is significantly improved by NaCl. J Plant Res 120:309–316
Sun Y, Wang D, Bai Y et al (2006) Studies on the overexpression of the soybean GmNHX1 in Lotus corniculatus: the reduced Na+ level is the basis of the increased salt tolerance. Chin Sci Bull 51:1306–1315
Sychrova H (2004) Yeast as a model organism to study transport and homeostasis of alkali metal cations. Physiol Res 53(Suppl 1): S91–S98
Tester M, Davenport R (2003) Na+ tolerance and Na+ transport in higher plants. Ann Bot 91:503–527
Venema K, Quintero FJ, Pardo JM, Donaire JP (2002) The Arabidopsis Na+/H+ exchanger AtNHX1 catalyzes low affinity Na+ and K+ transport in reconstituted liposomes. J Biol Chem 277:2413–2418
Wu C, Gao X, Kong X et al (2009) Molecular cloning and functional analysis of a Na+/H+ antiporter gene ThNHX1 from a halophytic plant Thellungiella halophila. Plant Mol Biol Rep 27:1–12
Wu G, Feng R, Wang S et al (2015) Co-expression of xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum ZxNHX and ZxVP1-1 confers enhanced salinity tolerance in chimeric sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.). Front Plant Sci https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00581
Xu HX, Jiang XY, Zhan KH et al (2008) Functional characterization of a wheat plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter in yeast. Arch Biochem Biophy 473:8–15
Xu YY, Zhou Y, Hong S et al (2013) Functional characterization of a wheat NHX antiporter gene TaNHX2 that encodes a K+/H+ exchanger. PLoS ONE 8:e78098
Xue Z, Zhi D, Xue G et al (2004) Enhanced salt tolerance of transgenic wheat (Tritivum aestivum L.) expressing a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene with improved grain yields in saline soils in the field and a reduced level of leaf Na+. Plant Sci 167:849–859
Yokoi S, Quintero FJ, Cubero B et al (2002) Differential expression and function of Arabidopsis thaliana NHX Na+/H+ antiporters in the salt stress response. Plant J 30:529–539
Zhang HX, Blumwald E (2001) Transgenic salt-tolerant tomato plants accumulate salt in foliage but not in fruit. Nat Biotechnol 19:765–768
Zhang H, Liu Y, Xu Y et al (2012) A newly isolated Na+/H+ antiporter gene, DmNHX1, confers salt tolerance when expressed transiently in Nicotiana benthamiana or stably in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Tiss Org 110:189–200
Zhang L, Niu Y, Huridu H et al (2014) Salicornia europaea L. Na+/H+ antiporter gene improves salt tolerance in transgenic alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Genet Mol Res 13:5350–5360
Zhou Y, Yin XC, Duan RJ et al (2015) SpAHA1 and SpSOS1 coordinate in transgenic yeast to improve salt tolerance. PLoS One 10(9):e0137447
Zorb C, Noll A, Karl S et al (2005) Molecular characterization of Na+/H+ antiporters (ZmNHX) of maize (Zea mays L.) and their expression under salt stress. J Plant Physiol 162:55–65
Acknowledgements
We thank American Journal Experts (AJE) for English language editing. This work was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (31260218, 31660253), the Fundamental Scientific Research Funds for Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences (CATAS-1630052014004) and the Scientific and Technological Foundation of Hainan Province (HNGDhs201502).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by S Renault.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Yang, C., Hu, Y. et al. The novel Na+/H+ antiporter gene SpNHX1 from Sesuvium portulacastrum confers enhanced salt tolerance to transgenic yeast. Acta Physiol Plant 40, 61 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-018-2631-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-018-2631-x