Abstract
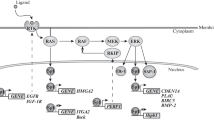
Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) are evolutionary conserved enzymes in cell signal transduction connecting cell-surface receptors to critical regulatory targets within cells and control cell survival, adaptation, and proliferation. Previous studies revealed that zinc finger proteins are involved in the regulation of the MAPK signaling pathways. Here we report the identification and characterization of a novel human zinc finger protein, ZNF436. The cDNA of ZNF436 is 3.8 kb, encoding 470 amino acids in the nucleus. The protein is highly conserved in evolution across different vertebrate species from rat to human. RT-PCR indicates that ZNF436 is expressed in all the human fetal tissues examined, with a high level in brain and heart. Overexpression of pCMV-tag2A-ZNF436 in the COS-7 cells represses the transcriptional activities of SRE and AP-1. These results suggest that ZNF436 is a member of the zinc finger transcription factor family and may act as a negative regulator in gene transcription mediated by the MAPK signaling pathways.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium
- DAPI4’:
-
6′-Diamidino-2- phenylindole hydrochloride
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MAPKKMKK or MEK:
-
MAPK kinase
- MAPKKK or MEKKA:
-
MAPKK kinase or MEK kinase
- SRE:
-
Serum response element
- AP-1:
-
Activation protein 1
References
Tjian R, Maniatis T (1994) Transcriptional activation: a complex puzzle with few easy pieces. Cell 77(1):5–8
Maldonado E, Hampsey M, Reinberg D (1999) Repression: targeting the heart of the matter. Cell 99(5):455–458
Park M, Wu X, Golden K, Axelrod JD, Bodmer R (1996) The wingless signaling pathway is directly involved in Drosophila heart development. Dev Biol 177(1):104–116
Pavletich NP, Pabo CO (1993) Crystal structure of a five-finger GLI-DNA complex: new perspectives on zinc fingers. Science 261(5129):1701–1707
Venter JC, Adams MD, Myers EW, Li PW et al (2001) The sequence of the human genome. Science 291(5507):1304–1351
Huang C, Wang Y, Li D, Li Y, Luo J, Yuan W, Ou Y, Zhu C, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Liu M Wu X (2004) Inhibition of transcriptional activities of AP-1 and c-Jun by a new zinc finger protein ZNF394. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 320(4):1298–1305
Hagen G, Muller S, Beato M, Suske G (1994) Sp1-mediated transcriptional activation is repressed by Sp3. EMBO J 13(16):3843–3851
Drummond IA, Madden SL, Rohwer-Nutter P, Bell GI, Sukhatme VP, Rauscher FJ 3rd (1992) Repression of the insulin-like growth factor II gene by the Wilms tumor suppressor WT1. Science 257(5070):674–678
Schuh R, Aicher W, Gaul U, Cote S, Preiss A, Maier D, Seifert E, Nauber U, Schroder C, Kemler R et al (1986) A conserved family of nuclear proteins containing structural elements of the finger protein encoded by Kruppel, a Drosophila segmentation gene. Cell 47(6):1025–1032
Kadonaga JT, Carner KR, Masiarz FR, Tjian R (1987) Isolation of cDNA encoding transcription factor Sp1 and functional analysis of the DNA binding domain. Cell 51(6):1079–1090
Haber DA, Buckler AJ, Glaser T, Call KM, Pelletier J, Sohn RL, Douglass EC, Housman DE (1990) An internal deletion within an 11p13 zinc finger gene contributes to the development of Wilms' tumor. Cell 61(7):1257–1269
Vortkamp A, Gessler M, Grzeschik KH (1991) GLI3 zinc-finger gene interrupted by translocations in Greig syndrome families. Nature 352(6335):539–540
Dang DT, Pevsner J, Yang VW (2000) The biology of the mammalian Kruppel-like family of transcription factors. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 32(11–12):1103–1121
Wu LC (2002) ZAS: C2H2 zinc finger proteins involved in growth and development. Gene Exp 10(4):137–152
Takeuchi A, Mishina Y, Miyaishi O, Kojima E, Hasegawa T Isobe K (2003) Heterozygosity with respect to Zfp148 causes complete loss of fetal germ cells during mouse embryogenesis. Nat Genet 33(2):172–176
Turner J, Crossley M (1999) Mammalian Kruppel-like transcription factors: more than just a pretty finger. Trends Biochem Sci 24(6):236–240
Villavicencio EH, Walterhouse DO, Iannaccone PM (2000) The sonic hedgehog-patched-gli pathway in human development and disease. Am J Hum Genet 67(5):1047–1054
Li Y, Wang Y, Zhang C, Yuan W, Wang J, Zhu C, Chen L, Huang W, Zeng W, Wu X, Liu M (2004) ZNF322, a novel human C2H2 Kruppel-like zinc-finger protein, regulates transcriptional activation in MAPK signaling pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 325(4):1383–1392
Davis RJ (1994) MAPKs: new JNK expands the group. Trends Biochem Sci 19(11):470–473
Chang L, Karin M (2001) Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades. Nature 410(6824):37–40
English J, Pearson G, Wilsbacher J, Swantek J, Karandikar M, Xu S, Cobb MH (1999) New insights into the control of MAP kinase pathways. Exp Cell Res 253(1):255–270
Davis RJ (1993) The mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathway. J Biol Chem 268(20):14553–14556
Sanchez I, Hughes RT, Mayer BJ, Yee K, Woodgett JR, Avruch J, Kyriakis JM, Zon LI (1994) Role of SAPK/ERK kinase-1 in the stress-activated pathway regulating transcription factor c-Jun. Nature 372(6508):794–798
Gupta S, Campbell D, Derijard B, Davis RJ (1995) Transcription factor ATF2 regulation by the JNK signal transduction pathway. Science 267(5196):389–393
Mavrothalassitis G, Ghysdael J (2000) Proteins of the ETS family with transcriptional repressor activity. Oncogene 19(55):6524–6532
Jeanmougin F, Thompson JD, Gouy M, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1998) Multiple sequence alignment with Clustal X. Trends Biochem Sci 23(10):403–405
Kyriakis JM, Avruch J (2001) Mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation. Physiol Rev 81(2):807–869
Keeton AB, Bortoff KD, Bennett WL, Franklin JL, Venable DY Messina JL (2003) Insulin-regulated expression of Egr-1 and Krox20: dependence on ERK1/2 and interaction with p38 and PI3-kinase pathways. Endocrinology 144(12):5402–5410
Ray A, Yu GY, Ray BK (2002) Cytokine-responsive induction of SAF-1 activity is mediated by a mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol 22(4):1027–1035
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to all members of the Center for Heart Development, College of Life Sciences in Hunan Normal University for their excellent technical assistance and encouragement. This study was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 90508004, 30470867, 30270722, 30570934, 30571048, 30570265), PCSIRT of Education Ministry of China (IRT0445), National Basic Research Program of China (2005CB522505), and the Foundation of Hunan Province (No. 04FJ2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Yongqing Li and Xiaoyan Du contributed equally to the work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Du, X., Li, F. et al. A novel zinc-finger protein ZNF436 suppresses transcriptional activities of AP-1 and SRE. Mol Biol Rep 33, 287–294 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-006-9019-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-006-9019-5