Abstract
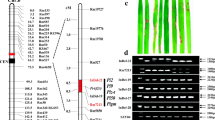
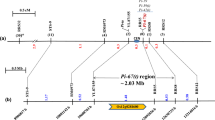
The Pik m gene in rice confers a high and stable resistance to many isolates of Magnaporthe oryzae collected from southern China. This gene locus was roughly mapped to the long arm of rice chromosome 11 with restriction fragment length polymorphic (RFLP) markers in the previous study. To effectively utilize the resistance, a linkage analysis was performed in a mapping population consisting of 659 highly susceptible plants collected from four F2 populations using the publicly available simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers. The result showed that the locus was linked to the six SSR markers and defined by RM254 and RM144 with ≈13.4 and ≈1.2 cM, respectively. To fine map this locus, additional 10 PCR-based markers were developed in a region flanked by RM254 and RM144 through bioinformatics analysis (BIA) using the reference sequence of cv. Nipponbare. The linkage analysis with these 10 markers showed that the locus was further delimited to a 0.3-cM region flanked by K34 and K10, in which three markers, K27, K28, and K33, completely co-segregated with the locus. To physically map the locus, the Pik m-linked markers were anchored to bacterial artificial chromosome clones of the reference cv. Nipponbare by BIA. A physical map spanning ≈278 kb in length was constructed by alignment of sequences of the clones anchored by BIA, in which only six candidate genes having the R gene conserved structure, protein kinase, were further identified in an 84-kb segment.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn SW (1994) International collaboration on breeding for resistance to rice blast. In: Zeigler RS, Leong SA, Teng PS (eds) Rice blast disease. CAB International, Wallingford, UK, pp 137–153
Bryan GT, Wu KS, Farrall L, Jia Y, Hershey HP, McAdams SA, Faulk KN, Donaldson GK, Tarchini R, Valent B (2000) A single amino acid difference distinguishes resistant and susceptible alleles of the rice blast resistance gene Pi-ta. Plant Cell 12:2033–2045
Chauhan S, Farman ML, Zhang HB, Leong A (2002) Genetic and physical mapping of a rice blast resistance locus, PiCO39(t), that corresponds to the avirulence gene AVR-CO39 of Magnaporthe grisea. Mol Genet Genomics 267:603–612
Chen S, Wang L, Que ZQ, Pan RQ, Pan QH (2005) Genetic and physical mapping of Pi37(t), a new gene conferring resistance to rice blast in the famous cultivar St. No. 1. Theor Appl Genet 111:1563–1570
Chen XW, Shang J, Chen D, Lei C, Zou Y, Zhai W, Liu G, Xu J, Ling Z, Cao G, Ma B, Wang Y, Zhao X, Li S, Zhu L (2006) A B-lectin receptor kinase gene conferring rice blast resistance. Plant J 46:794–804
Conoway-Bormans CA, Marchetti MA, Johnson CW, McClung AM, Park WD (2003) Molecular markers linked to the blast resistance gene Pi-z in rice for use in marker-assisted selection. Theor Appl Genet 107:1014–1020
Couch BC, Kohn LM (2002) A multilocus gene genealogy concordant with host preference indicates segregation of a new species, Magnaporthe oryzae, from M. grisea. Mycologia 94:683–693
Deng Y, Zhu X, Shen Y, He Z (2006) Genetic characterization and fine mapping of the blast resistance locus Pigm(t) tightly linked to Pi2 and Pi9 in a broad-spectrum resistant Chinese variety. Theor Appl Genet 113:705–713
Feuillet C, Travella S, Stein N, Albar L, Nublat A, Keller B (2003) Map-based isolation of the leaf rust disease resistance gene Lr10 from the hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:15253–15258
Fjellstrom R, Conaway-Bormans CA, McClung AM, Marchetti MA, Shank AR, Park WD (2004) Development of DNA markers suitable for marker assisted selection of three Pi genes conferring resistance to multiple Pyricularia grisea pathotypes. Crop Sci 44:1790–1798
Hayashi K, Hashimoto N, Daigen M, Ashikawa I (2004) Development of PCR-based SNP markers for rice blast resistance genes at the Piz locus. Theor Appl Genet 108:1212–1220
Hittalmani S, Parco A, Mew TW, Zeigler RS, Huang N (2000) Fine mapping and DNA marker-assisted pyramiding of the three major genes for blast resistance in rice. Theor Appl Genet 100:1121–1128
Horvath H, Rostoks N, Brueggeman R, Steffenson B, Wettstein DV, Kleinhofs A (2003) Genetically engineered stem rust resistance in barley using the Rpg1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:364–369
Jia YL, Bryan GT, Farrall L, Valent B (2003) Natural variation at the Pi-ta rice blast resistance locus. Phytopathology 93:1452–1459
Jia YL, Redus M, Wang Z, Rutger JN (2004) Development of a SNLP marker from the Pi-ta blast resistance gene by tri-primer PCR. Euphytica 138:97–105
Jiang J, Wang S (2002) Identification of a 118-kb DNA fragment containing the locus of blast resistance gene Pi-2(t) in rice. Mol Genet Genomics 268:249–252
Jeon JS, Chen D, Yi GH, Wang GL, Ronald PC (2003) Genetic and physical mapping of Pi5(t), a locus associated with broad-spectrum resistance to rice blast. Mol Genet Genomics 269:280–289
Kaji R, Ogawa T (1996) RFLP mapping of blast resistance gene Pi-k m in rice. Int Rice Res Note 21:47
Kiyosawa S (1989) Breakdown of blast resistance in rice in relation to general strategies of resistance gene deployment to prolong effectiveness of disease resistance in plants. In: Leonard KJ, Fry WE (eds) Plant disease epidemiology. McGraw-Hill Publishing Company, New York, pp 251–283
Lin F, Liu YG, Wang L, Liu XQ, Pan QH (2007). A high-resolution map of the rice blast resistance gene Pi15 was constructed by sequence-ready markers. Plant Breed 126:287–290
Liu G, Lu G, Zeng L, Wang GL (2002) Two broad-spectrum blast resistance genes, Pi9(t) and Pi2(t), are physically linked on rice chromosome 6. Mol Genet Genomics 267:472–480
Liu XQ, Wang L, Chen S, Lin F, Pan QH (2005) Genetic and physical mapping of Pi36(t), a novel rice blast resistance gene located on rice chromosome 8. Mol Genet Genomics 274:394–401
McCouch SR, Teytelman L, Xu Y, Lobos KB, Clare K, Walton M, Fu B, Maghirang R, Li Z, Xing Y, Zhang Q, Kono I, Yano M, Fjellstrom R, DeClerck G, Schneider D, Cartinhour S, Ware D, Stein L (2002) Development and mapping of 2240 new SSR markers for rice (Oryza sativa L.). DNA Res 9:199–207
Monosi B, Wisser RJ, Pennill L, Hulbert SH (2004) Full-genome analysis of resistance gene homologues in rice. Theor Appl Genet 109:1434–1447
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4325
Nakamura S, Asakawa S, Ohmido N, Fukui K, Shimizu N, Kawasaki S (1997) Construction of an 800-kb contig in the near-centromeric region of the rice blast resistance gene Pi-ta 2 using a highly representative rice BAC library. Mol Genet Genomics 254:611–620
Ou SH (1979) Breeding rice for resistance to blast, a critical view. In: Proceedings of the rice blast workshop. International Rice Research Institute, Manila, Philippines, pp 79–137
Ou SH (1985) Rice diseases, 2nd edn. Commonwealth Mycological Institute, Kew Surrey, UK, pp 109–201
Pan QH, Wang L, Tanisaka T, Ikehashi H (1998) Allelism of rice blast resistance genes in two Chinese native cultivars and identification of two new resistance genes. Plant Pathol 47:165–170
Pan QH, Hu ZD, Tanisaka T, Wang L (2003) Fine mapping of the blast resistance gene Pi15, linked to Pii, on rice chromosome 9. Acta Bot Sin 45:871–877
Qu S, Liu G, Zhou B, Bellizzi M, Zeng L, Dai L, Han B, Wang GL (2006) The broad-spectrum blast resistance gene Pi9 encodes a nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat protein and is a member of a multigene family in rice. Genetics 172:1901–1914
Sharma TR, Madhav MS, Singh BK, Shanker P, Jana TK, Dalal V, Pandit A, Singh A, Gaikwd K, Upreti HC, Singh NK (2005) High-resolution aping, cloning and molecular characterization of the Pi-k h gene of rice, which confers resistance to Magnaporthe grisea. Mol Genet Genomics 274:569–578
Shuler GD (1998) Electronic PCR: bridging the gap between genome mapping and genome sequencing. Trends Biotechnol 16:456–459
Sun X, Yang Z, Wang S, Zhang Q (2003) Identification of a 47-kb DNA fragment containing Xa4, a locus for bacterial blight resistance in rice. Theor Appl Genet 106:683–687
Sun X, Cao Y, Yang Z, Xu C, Li X, Wang S, Zhang Q (2004) Xa26, a gene conferring resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in rice, encodes an LRR receptor kinase-like protein. Plant J 37:517–527
Temnykh S, DeClerck G, Lukashova A, Lipovich L, Cartinhour S, McCouch S (2001) Computational and experimental analysis of microsatellites in rice (Oryza satival L.): frequency, length variation, transposon associations, and genetic marker potential. Genome Res 11:1441–1452
Wang CT, Tan MP, Xu X, Wen GS, Zhang DP, Lin XH (2003) Localizing the bacterial blight resistance gene, Xa22(t), to a 100-kilobase bacterial artificial chromosome. Phytopathology 93:1258–1262
Wang ZX, Yano M, Yamanouchi U, Lwamoto M, Monna L, Hayasaka H, Katayose Y, Sasaki T (1999) The Pib gene for rice blast resistance belongs to the nucleotide binding and leucine-rich repeat class of plant disease resistance genes. Plant J 19:55–64
Wu KS, Tanksely SD (1993) PFGE analysis of the rice genome estimation of fragment sizes, organization of repetitive sequences and relationships between genetic and physical distances. Plant Mol Biol 24:243–254
Xing ZY, Que GS, Li C (1991) Chapter V. Early japonica rice. In: Lin SC, Min SK (eds) Rice varieties and their cenealogy in China. Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers, Shanghai, China, pp 106–138
Yang Z, Sun X, Wang S, Zhang Q (2003) Genetic and physical mapping of a new gene for bacterial blight resistance in rice. Theor Appl Genet 106:1467–1472
Yi G, Lee SK, Hong YK, Cho YC, Nam MH, Kim SC, Han SS, Wang GL, Hahn TR, Ronald PC, Jeon JS (2004) Use of Pi5(t) markers in marker-assisted selection to screen for cultivars with resistance to Magnaporthe grisea. Theor Appl Genet 109:978–985
Zhou B, Qu S, Liu G, Dolan M, Sakai H, Lu G, Bellizzi M, Wang GL (2006) The eight amino-acid differences within three leucine-rich repeats between Pi2 and Piz-t resistance proteins determine the resistance specificity to Magnaporthe grisea. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 19:1216–1228
Zhu M, Wang L, Pan Q (2004) Identification and characterization of a new blast resistance gene located on rice chromosome 1 through linkage and differential analyses. Phytopathology 94:515–519
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Profs. ZH Wang at Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, ZH Zhao at Hunan Academy of Agricultural Sciences, XB Zheng at Nanjing Agricultural University, and XL Guo at Jilin Academy of Agricultural Sciences for providing the fungal isolates used in this study. The research was supported by grants from the National Basic Research Program of China (2006CB/1002006), the Innovation Research Team Project from the Ministry of Education of China (IRT0448), the Guangdong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (039254).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, LY., Wang, L., Jing, JX. et al. The Pik m gene, conferring stable resistance to isolates of Magnaporthe oryzae, was finely mapped in a crossover-cold region on rice chromosome 11. Mol Breeding 20, 179–188 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-007-9118-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-007-9118-6