Abstract
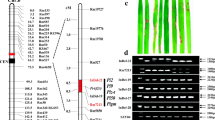
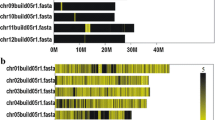
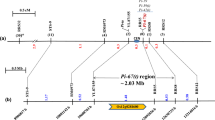
In order to understand the molecular mechanisms involved in the gene-for-gene type of pathogen resistance, high-resolution genetic and physical mapping of resistance loci is required to facilitate map-based cloning of resistance genes. Here, we report the molecular mapping and cloning of a dominant gene (Pi-k h) present in the rice line Tetep, which is associated with resistance to rice blast disease caused by Magnaporthe grisea. This gene is effective against M. grisea populations prevalent in the Northwestern Himalayan region of India. Using 178 sequence tagged microsatellite, sequence-tagged site, expressed sequence tag and simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers to genotype a population of 208 F2 individuals, we mapped the Pi-k h gene between two SSR markers (TRS26 and TRS33) which are 0.7 and 0.5 cM away, respectively, and can be used in marker-assisted-selection for blast-resistant rice cultivars. We used the markers to identify the homologous region in the genomic sequence of Oryza sativa cv. Nipponbare, and a physical map consisting of two overlapping bacterial artificial chromosome and P1 artificial chromosome clones was assembled, spanning a region of 143,537 bp on the long arm of chromosome 11. Using bioinformatic analyses, we then identified a candidate blast-resistance gene in the region, and cloned the homologous sequence from Tetep. The putative Pi-k h gene cloned from Tetep is 1.5 kbp long with a single ORF, and belongs to the nucleotide binding site-leucine rich repeat class of disease resistance genes. Structural and expression analysis of the Pi-k h gene revealed that its expression is pathogen inducible.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn SW (1994) International collaboration on breeding for resistance to rice blast. In: Zeigler RS, Leong SA, Teng PS (eds) Rice blast disease. CAB International, Wallingford, pp 137–153
Ahn SN, Kim YK, Hong HC, Han SS, Kwon SJ, Choi HC, Moon H, McCouch SR (2000) Molecular mapping of new gene for resistance to rice blast (Pyricularia grisea). Euphytica 116:17–22
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programmes. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Bonierbale MW, Plaisted RL, Tanksley SD (1988) Marker conservation between the tomato and potato species. Genetics 120:1095–1103
Bonman JM, Dedios TIV, Khin MM (1986) Physiologic specialization of Pyricularia oryzae in the Phillippines. Plant Dis 70:767–769
Bryan GT, Wu KS, Farrall L, Jia Y, Hershey HP, McAdams SA, Faulk KN, Donaldson GK, Tarchini R, Valent B (2000) A single amino acid difference distinguishes resistant and susceptible alleles of the rice blast-resistance gene Pi-ta . Plant Cell 12:2033–2045
Chauhan RS, Farman ML, Zhang HB, Leong SA (2002) Genetic and physical mapping of a rice blast-resistance locus, Pi-Co39(t), that corresponds the avirulence gene AVR1-CO39 of Magnaporthe grisea. Mol Genet Genomics 267:603–612
Chen M et al (2002) An integrated physical and genetic map of rice genome. Plant Cell 14:537–545
Chen DH, Dela Vina M, Inukai T, Mackill DJ, Ronald PC, Nelson RJ (1999) Molecular mapping of the blast-resistance gene, Pi44(t), in a line derived from a durably resistant rice cultivar. Theor Appl Genet 98:1046–1053
Craig NL (1996) Transposon Tn 7. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 204:27–48
Dangl JL, Jones JDG (2001) Plant pathogens and integrated defense responses to infection. Nature 411:826–833
Ellis JG, Lawrence GJ, Luck JE, Dodds PN (1999) Identification of regions in alleles of the flax rust resistance gene L that determine differences in gene-for-gene specificity. Plant Cell 11:495–506
Ewing B, Green P (1988) Base calling of automated sequence tracer using Phred I. Accuracy assessment. Genome Res 8:175–185
Fjellstrom R, Conaway-Bormans CA, McClung AM, Marchetti MA, Shank AR, Park WD (2004) Development of DNA markers suitable for marker assisted selection of three Pi genes conferring resistance to multiple Pyricularia grisea pathotypes. Crop Sci 44:1790–1798
Gu K, Tian D, Yang F, Wu L, Sreekala C, Wang D, Wang GL, Yin Z (2004) High-resolution genetic mapping of Xa27(t), a new bacterial blight resistance gene in rice, Oryza sativa L. Theor Appl Genet 108:800–807
Harushirma Y et al (1998) A high density genetic linkage map of 2,275 markers using a single F2 population. Genetics 148:479–494
Hayashi K, Hashimoto N, Daigen M and Ashikawa I (2004) Development of PCR based SNP markers for rice blast. Theor Appl Genet 108:1212–1220
Inukai T, Nelson RJ, Zeigler RS, Sarkarung S, Mackill DJ, Bonman JM, Takamura I, Kinoshita T (1994) Allelism of blast-resistance genes in near isogenic lines of rice. Phytopathology 84:1278–1283
Jiang J, Wang S (2002) Identification of 118-kb DNA fragment containing the locus of blast-resistance gene Pi-2(t) in rice. Mol Genet Genomics 268:249–252
Jones JDG (1996) Plant disease resistance genes: structure, function and evolution. Curr Opin Biotechnol 7:155–160
Kilian A, Kundan AD, Kleinhofs A, Yano M, Kumata N, Stephenson B, Sasaki J (1995) Rice-barley synteny and its application to saturation mapping of the barley RP91 region. Nucleic Acids Res 23:2729–2733
Kinoshita T (1998) Linkage mapping using mutant genes in rice. Rice Genet Newslett 15:13–74
Kiyosawa S (1971) Gene analysis of blast-resistance in exotic varieties of rice. Jpn Agric Res Quart 6:1–8
Kiyosawa S (1981) Gene analysis for blast-resistance. Oryza 18:196–203
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distance from recombination values. Ann Eugen 1:172–175
Lander ESP, Green J, Abhrahamson A, Barlow MJ (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Mackill DJ, Bonman JM (1992) Inheritance of blast-resistance in near-isogenic lines of rice. Phytopathology 82:746–749
McCouch SR (2002) Development and mapping of 2240 new SSR markers for rice (Oryza sativaL). DNA Res 9:193–207
McCouch SR, Nelson RJ, Thome J, Zeigler RS (1994) Mapping of blast-resistance genes in rice. In: Zeigler RS, Leong SA, Teng PS (eds) Rice blast disease. CAB International, Wallingford, pp 167–187
Nasu S, Suzuki J, Ohta R, Hasegawa K, Yui R, Kitazawa N, Monna L and Minobe Y (2002) Search for and analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in rice (Oryza sativa, O. rufipogon) and establishment of SNP markers. DNA Res 9:163–171
Rathour R, Singh BM, Sharma TR, Chauhan RS (2004) Population structure of Magnaporthe grisea from North-western Himalayas and its implications for blast-resistance breeding of rice. J Phytopathol 152:304–312
Saji S, Umehara Y, Antonio BA, Yamane H, Tanoue H, Baba T, Aoki H, Ishige N, Wu J, Koike K, Matsumato T, Sasaki T (2001) A physical map with yeast artificial chromosome clones covering 63% of 12 rice chromosomes. Genome 44:32–37
Sallaud C, Lorieux M, Roumen E, Tharreau D, Berruyer R, Svestasrani P, Garsmeur O, Ghesquiere A, Notteghem JL (2003) Identification of five new blast-resistance genes in highly resistant blast resistant cultivar IR- 64 using a QTL mapping strategy. Theor Appl Genet 106:794–803
Sharma TR, Chauhan RS, Singh BM, Paul R, Sagar V, Rathore R (2002) RAPD and pathotype analysis of Magnaporthe grisea population from North-western Himalayan region of India. J Phytopathol 150:649–656
Sharma TR, Jana TK, Shankar P, Singh BK, Plaha P, Gaikwad K, Singh NK (2003) Development of molecular markers for blast-resistance genes in Oryza sativa. Abstracts of the second international congress on plant physiology, New Delhi, p 484
Sharma TR, Shanker P, Singh BK, Jana TK, Madhav MS, Gaikwad G, Singh NK, Plaha P, Rathour R (2005) Molecular mapping of rice blast resistance gene Pi-k h in rice variety Tetep. J Pl Biochem Biotech 14:127–133
Sun X, Yang Z, Wang S, Zhang Q (2003) Identification of 47-kb DNA fragment containing Xa4, a locus for bacterial blight resistance in rice. Theor Appl Genet 106:683–687
Wang C (1999) Fine and physical mapping of bacterial blight resistance genes Xa 22 (t) and Xa 24(t) in rice (in Chinese). PhD thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China
Wang Z, Yamanouchi U (1999) The Pib gene of blast-resistance belongs to nucleotide binding and leucine rich repeat class of plant disease resistance genes. Plant J 19:55–64
Wang XZ, Yamanouchi U, Katayose Y, Sasaki T, Yano M (2001) Expression of the Pi b rice blast-resistance gene family is up-regulated by environmental conditions favoring infection and by chemical signals that trigger secondary plant defenses. Plant Mol Biol 47:653–661
Ward ER, Uknes SJ, Williams SC, Dincher SS, Widerhold DL, Alexander DC (1991) Coordinate gene activity in response to agents that induce systemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell 3:1085–1094
Yoshimura S, Yamanouchi U, Katayose Y, Toki S, Wang ZX, Kono I, Kurata N, Yano M, Iwata N, Sasaki T (1998) Expression of Xa1, a bacterial blight resistance gene in rice, is induced by bacterial inoculation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:1663–1668
Yu J et al (2002) A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica). Science 296:79–92
Yu ZH, Mackill DJ, Bonman JM, Tanksley SD (1991) Tagging of blast-resistance in rice via linkage to RFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 81:471–476
Yu Z, Mackill DJ, Bonman JM, McCouch S, Guiderdoni E, Notteghem JL, Tanksley SD (1996) Molecular mapping of genes for resistance to rice blast (Pyricularia grisea Sacc.). Theor Appl Genet 93:859–863
Zeigler RS, Leong SA, Teng PS (1994) Rice blast disease. CAB International, Wallingford
Acknowledgements
Financial assistance received from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research and the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India by TRS is gratefully acknowledged. We are thankful to Prof. K.R. Koundal, Project Director of National Research Centre on Plant Biotechnology and the incharges Phytotron Facility, Indian Agricultural Research Institute for providing facilities for phenotyping the mapping population and to R. Rathour, for providing pathogen culture. We are thankful to NCBI, FGENESH and RGP for making their databases and genome analysis tools publicly available.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, T.R., Madhav, M.S., Singh, B.K. et al. High-resolution mapping, cloning and molecular characterization of the Pi-k h gene of rice, which confers resistance to Magnaporthe grisea . Mol Genet Genomics 274, 569–578 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-005-0035-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-005-0035-2