Abstract
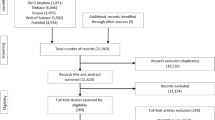
Researchers have proposed culture- and religion-based variations in experience and expression of gratitude. Accordingly, the present study developed and validated a Hindu Gratitude Scale (HGS) based on Hindu notion of rnas. The rnas are sacred obligations (duties) that every Hindu is supposed to fulfil during their lifetime. These pious obligations are practised to acknowledge, honour, and appreciate others’ contribution in one’s life. These five holy duties are Pitṛ-yajna, Bhūta-yajna, Manuṣya-yajna, Deva-yajna, and Brahma-yajna. The study started with rnas-based conceptualisation of gratitude followed by item generation using both inductive and deductive approaches. These statements were subjected to content validity and pretesting, which resulted in nineteen items. The psychometric properties of proposed HGS (with nineteen items) were analysed with the help of three studies. The first study evaluated factorial validity of the proposed HGS using exploratory factor analysis (EFA) and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) using a sample of 1032 respondents. Poor factor loading in EFA suggested removal of three statements. The EFA recommended five dimensions of the HGS—appreciation for family, ancestors, and cultural values (AFF), appreciation for family, ancestors, and cultural values (AFF), appreciation for God, appreciation for knowledge, skills, and talents, and appreciation for ecosystem. Further, CFA also suggested removal of one statement. Lastly, the EFA and CFA result suggested adequate factorial validity of a fifteen-itemed five-factored HGS. The second study examined the reliability and validity of the HGS derived from CFA with the help of a sample of 644 participants. And, in the third study, the test–retest reliability was investigated by collecting the data twice. The results revealed significant positive correlations in two sets of data, thereby concluding test–retest reliability of the HGS. The study offered a novel fifteen-item Hindu Gratitude Scale, which could be used in future studies to explore gratitude level of Hindus.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data could be procured from author upon reasonable request
References
Ajmal, A., Abid, S., Bokhari, S. Z., & Rasool, A. (2018). Role of gratitude and forgiveness in spiritual well-being of teachers. Pakistan Journal of Professional Psychology: Research and Practice, 9(2), 1–14.
Amri, M. A., Zaid, I., Md Nasser, N. A., & Abdul Khaiyom, J. H. (2022). Initial construction and validation of the islamic gratitude (I-Gratitude) scale. Iium Journal of Human Sciences, 4(2), 52–64.
Arias, M. R. M., Lloreda, M. J. H., & Lloreda, M. V. H. (2014). Psicometria. Madrid: Alianza Editorial.
Boateng, G. O., Neilands, T. B., Frongillo, E. A., Melgar-Quiñonez, H. R., & Young, S. L. (2018). Best practices for developing and validating scales for health, social, and behavioral research: A primer. Frontiers in Public Health. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2018.00149
Cronbach, L. J., & Shavelson, R. J. (2004). My current thoughts on coefficient alpha and successor procedures. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 64(3), 391–418. https://doi.org/10.1177/0013164404266386
Elosúa, M. R. (2015). The influence of gratitude in physical, psychological, and spiritual well-being. Journal of Spirituality in Mental Health, 17(2), 110–118. https://doi.org/10.1080/19349637.2015.957610
Emmons, R. A., & Crumpler, C. A. (2000). Gratitude as a human strength: Appraising the evidence. Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology, 19(1), 56–69. https://doi.org/10.1521/jscp.2000.19.1.56
Emmons, R. A., & Kneezel, T. T. (2005). Giving thanks: Spiritual and religious correlates of gratitude. Journal of Psychology and Christianity. http://transformationalchange.pbworks.com/f/Spiritual%20and%20Religious%20Correlates%20of%20Gratitude.pdf.
Emmons, R. A., & McCullough, M. E. (2003). Counting blessings versus burdens: An experimental investigation of gratitude and subjective well-being in daily life. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 84(2), 377–389. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.84.2.377
Fadiman, J., & Frager, R. A. (1976). Personality and Personal Growth. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/ncid/BA00975230
Feizi, S., Nasiri, M., Bahadori, H., Amiri, M. H., & Mirhosseini, H. (2020). The relationship between spiritual well-being and happiness among healthcare students: Application of the spiritual health questionnaire for the Iranian population. Heliyon. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05448
Fornell, C., & Larcker, D. F. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. Journal of Marketing Research, 18(1), 39. https://doi.org/10.2307/3151312
Garg, N. (2017a). Workplace spirituality and employee well-being: An empirical exploration. Journal of Human Values, 23(2), 129–147. https://doi.org/10.1177/0971685816689741
Garg, N. (2017b). Workplace spirituality and organizational performance in Indian context: Mediating effect of organizational commitment, work motivation and employee engagement. South Asian Journal of Human Resources Management, 4(2), 191–211. https://doi.org/10.1177/2322093717736134
Garg, N. (2021). Gratitude resentment and appreciation scale (GRAT-16): Analyzing psychometrics properties in the Indian context. Current Psychology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-021-02169-6
Garg, N., Jain, A., & Punia, B. (2020). Gratitude, social intelligence, and leadership among university teachers: Mediation and moderation analysis. International Journal of Organizational Analysis, 29(2), 368–388. https://doi.org/10.1108/ijoa-01-2020-2016
Garg, N., & Katiyar, N. (2021). Gratitude questionnaire (GQ-6)—Exploring psychometric properties in India. Journal of Religion and Health, 60(5), 3716–3731. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10943-021-01419-y
Garg, N., Kumari, S., & Punia, B. (2022). Resolving stress of university teacher: Exploring role of workplace spirituality and constructive workplace deviance. South Asian Journal of Business Studies, 11(3), 295–315. https://doi.org/10.1108/sajbs-04-2020-0118
George, D., & Mallery, P. (2008). SPSS for windows step by step: A simple guide and reference, 16.0 update (9th ed.). Allyn & Bacon.
Hlava, P., Elfers, J., & Offringa, R. (2014a). A transcendent view of gratitude: The transpersonal gratitude scale. International Journal of Transpersonal Studies, 33(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.24972/ijts.2014.33.1.1
Hlava, P., Elfers, J., & Offringa, R. (2014b). A transcendent view of gratitude: The transpersonal gratitude scale. International Journal of Transpersonal Studies, 33(1), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.24972/ijts.2014.33.1.1
Kessler, R. C., Barker, P. R., Colpe, L. J., Epstein, J. F., Gfroerer, J. C., Hiripi, E., Howes, M. J., Normand, S. L. T., Manderscheid, R. W., Walters, E. E., & Zaslavsky, A. M. (2003). Screening for serious mental illness in the general population. Archives of General Psychiatry, 60(2), 184. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.60.2.184
Knabb, J. J., Vazquez, V. E., & Wang, K. T. (2020). The Christian contentment scale: An Emic measure for assessing inner satisfaction within the Christian tradition. Journal of Psychology and Theology, 49(4), 324–341. https://doi.org/10.1177/0091647120968146
Knabb, J. J., Vazquez, V. E., Wang, K. T., & Pate, R. A. (2021). The Christian Gratitude Scale: An emic approach to measuring thankfulness in every season of life. Spirituality in Clinical Practice. https://doi.org/10.1037/scp0000278
Koenig, H. G., & Al Zaben, F. (2021). Psychometric validation and translation of religious and spiritual measures. Journal of Religion and Health, 60(5), 3467–3483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10943-021-01373-9
Kraus, R., Desmond, S. A., & Palmer, Z. D. (2014). Being thankful: examining the relationship between young adult religiosity and gratitude. Journal of Religion and Health, 54(4), 1331–1344. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10943-014-9923-2
Loi, N. M., & Ng, D. L. (2021). The relationship between gratitude, wellbeing, spirituality, and experiencing meaningful work. Psych, 3(2), 85–95. https://doi.org/10.3390/psych3020009
Mahipalan, M., & Sheena, S. (2019). Workplace spirituality and subjective happiness among high school teachers: Gratitude as a moderator. Explore, 15(2), 107–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.explore.2018.07.002
McCullough, M. E., Emmons, R. A., & Tsang, J. A. (2002). The grateful disposition: A conceptual and empirical topography. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 82(1), 112–127. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.82.1.112
Mills, P. J., Redwine, L., Wilson, K., Pung, M. A., Chinh, K., Greenberg, B. H., Lunde, O., Maisel, A., Raisinghani, A., Wood, A., & Chopra, D. (2015). The role of gratitude in spiritual well-being in asymptomatic heart failure patients. Spirituality in Clinical Practice, 2(1), 5–17. https://doi.org/10.1037/scp0000050
Morgan, B., Gulliford, L., & Kristjánsson, K. (2014). Gratitude in the UK: A new prototype analysis and a cross-cultural comparison. The Journal of Positive Psychology, 9(4), 281–294. https://doi.org/10.1080/17439760.2014.898321
Morgan, B., Gulliford, L., & Kristjánsson, K. (2017). A new approach to measuring moral virtues: The multi-component gratitude measure. Personality and Individual Differences, 107, 179–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2016.11.044
Navare, A., & Pandey, A. (2022). Karma yoga: Scale development and studies of the impact on positive psychological outcomes at the workplace. International Journal of Cross Cultural Management, 22(2), 271–299. https://doi.org/10.1177/14705958221111239
Osborne, J. W. (2015). What is rotating in exploratory factor analysis. Practical Assessment, Research and Evaluation, 20(2), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.7275/hb2g-m060
Paloutzian, R. F., Bufford, R. K., & Wildman, A. J. (2012). Spiritual well-being scale: Mental and physical health relationships. In M. Cobb, C. Puchalski, & B. Rumbold (Eds.), Oxford textbook of spirituality in healthcare (pp. 353–358). Oxford University Press.
Pandey, A., & Navare, A. V. (2018). Paths of yoga: Perspective for workplace spirituality. The Palgrave Handbook of Workplace Spirituality and Fulfillment. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-62163-0_4
Peterson, C., & Seligman, M. E. P. (2004). Character strengths and virtues: A handbook and classification. Oxford University Press.
Rosmarin, D., Alper, D., & Pargament, K. (2016). Religion, spirituality, and mental health. Encyclopedia of Mental Health. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-397045-9.00190-7
Rothenberg, W. A., Hussong, A. M., Langley, H. A., Egerton, G. A., Halberstadt, A. G., Coffman, J. L., Mokrova, I., & Costanzo, P. R. (2016). Grateful parents raising grateful children: Niche selection and the socialization of child gratitude. Applied Developmental Science, 21(2), 106–120. https://doi.org/10.1080/10888691.2016.1175945
Rusdi, A., Sakinah, S., Bachry, P. N., Anindhita, N. P., & Hasibuan, M. a. I. (2021). The development and validation of the Islamic gratitude scale (IGS-10). Psikis: Jurnal Psikologi Islami, 7(2), 120–142. https://doi.org/10.19109/psikis.v7i2.7872
Saxena, A., Garg, N., Punia, B., & Prasad, A. (2020). Exploring role of Indian workplace spirituality in stress management: A study of oil and gas industry. Journal of Organizational Change Management, 33(5), 779–803. https://doi.org/10.1108/jocm-11-2019-0327
Shankar, R. (2014). Celebrating silence. Van Duuren Media.
Sharma, N., Pathak, A., Lavanya, B. L., Garg, N., & Lata, K. (2022). Exploring the psychometric properties of personal optimism and self-efficacy optimism-extended (POSO-E) scale among Indian teachers. Benchmarking: An International Journal. https://doi.org/10.1108/bij-01-2022-0054
Sommers, S., & Kosmitzki, C. (1988). Emotion and social context: An American-German comparison. British Journal of Social Psychology, 27(1), 35–49. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2044-8309.1988.tb00803.x
Tudge, J. R., Freitas, L. B., & O’Brien, L. T. (2015). The virtue of gratitude: A developmental and cultural approach. Human Development, 58(4–5), 281–300. https://doi.org/10.1159/000444308
Watkins, P. C., Woodward, K., Stone, T., & Kolts, R. L. (2003). Gratitude and happiness: Development of a measure of gratitude, and relationship with subjective well-being. Social Behavior and Personality: An International Journal, 31(5), 431–451. https://doi.org/10.2224/sbp.2003.31.5.431
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the study are carried out in accordance with the ethical standards of the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Participants were duly informed of the study’s purpose, and consent was procured from all the participants.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Garg, N. Development and Validation of Hindu Gratitude Scale (HGS-15): A Rnas Perspective. J Relig Health 62, 3622–3639 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10943-023-01831-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10943-023-01831-6