Abstract
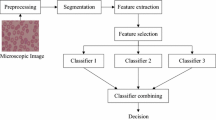
Web-enabled e-healthcare system or computer assisted disease diagnosis has a potential to improve the quality and service of conventional healthcare delivery approach. The article describes the design and development of a web-based distributed healthcare management system for medical information and quantitative evaluation of microscopic images using machine learning approach for malaria. In the proposed study, all the health-care centres are connected in a distributed computer network. Each peripheral centre manages its’ own health-care service independently and communicates with the central server for remote assistance. The proposed methodology for automated evaluation of parasites includes pre-processing of blood smear microscopic images followed by erythrocytes segmentation. To differentiate between different parasites; a total of 138 quantitative features characterising colour, morphology, and texture are extracted from segmented erythrocytes. An integrated pattern classification framework is designed where four feature selection methods viz. Correlation-based Feature Selection (CFS), Chi-square, Information Gain, and RELIEF are employed with three different classifiers i.e. Naive Bayes’, C4.5, and Instance-Based Learning (IB1) individually. Optimal features subset with the best classifier is selected for achieving maximum diagnostic precision. It is seen that the proposed method achieved with 99.2% sensitivity and 99.6% specificity by combining CFS and C4.5 in comparison with other methods. Moreover, the web-based tool is entirely designed using open standards like Java for a web application, ImageJ for image processing, and WEKA for data mining considering its feasibility in rural places with minimal health care facilities.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Malaria Report (2011). World Malaria Report. ISBN: 978924156440 3
Arya, S.C., and Agarwal, N., Laboratory tests for malaria: A diagnostic conundrum? SAMJ: S Afr Med J. 103(10):701–701, 2013.
Harchut, K., Standley, C., Dobson, A., Klaassen, B., Rambaud-Althaus, C., Althaus, F., and Nowak, K., Over-diagnosis of malaria by microscopy in the Kilombero Valley, southern Tanzania: An evaluation of the utility and cost-effectiveness of rapid diagnostic tests. Malar J. 12(1):1, 2013.
Fançony, C., Sebastião, Y.V., Pires, J.E., Gamboa, D., and Nery, S.V., Performance of microscopy and RDTs in the context of a malaria prevalence survey in Angola: A comparison using PCR as the gold standard. Malar J. 12(1):1, 2013.
Bhattacharya, D., Bhuyan, B., Pradhan, P., and Nayak, D., Transmission blocking of year round resistant malaria in Koraput (India) by OMARIA-A new antimalarial Phytotherapy. Br J Pharm Res. 3(1):54, 2013.
Reyburn, H., Mbakilwa, H., Mwangi, R., Mwerinde, O., Olomi, R., Drakeley, C., and Whitty, C.J., Rapid diagnostic tests compared with malaria microscopy for guiding outpatient treatment of febrile illness in Tanzania: Randomised trial. BMJ. 334(7590):403, 2007.
Ansah, E.K., Narh-Bana, S., Epokor, M., Akanpigbiam, S., Quartey, A.A., Gyapong, J., and Whitty, C.J., Rapid testing for malaria in settings where microscopy is available and peripheral clinics where only presumptive treatment is available: A randomised controlled trial in Ghana. BMJ. 340:c930, 2010.
Ross, N.E., Pritchard, C.J., Rubin, D.M., and Duse, A.G., Automated image processing method for the diagnosis and classification of malaria on thin blood smears. Med Biol Eng Comput. 44(5):427–436, 2006.
Sio, S.W., Sun, W., Kumar, S., Bin, W.Z., Tan, S.S., Ong, S.H., Kikuchi, H., Oshima, Y., and Tan, K.S., MalariaCount: An image analysis-based program for the accurate determination of parasitemia. J Microbiol Methods. 68(1):11–18, 2007.
Díaz, G., González, F.A., and Romero, E., A semi-automatic method for quantification and classification of erythrocytes infected with malaria parasites in microscopic images. J Biomed Inform. 42(2):296–307, 2009.
Tek, F.B., Dempster, A.G., and Kale, I., Computer vision for microscopy diagnosis of malaria. Malar J. 8(1):153, 2009.
Yang, L., Tuzel, O., Chen, W., Meer, P., Salaru, G., Goodell, L.A., and Foran, D.J., Pathminer: A web-based tool for computer-assisted diagnostics in pathology. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed. 13(3):291–299, 2009.
Somasekar, J., Reddy, A. R. M., and Reddy, L. S., An Efficient Algorithm for Automatic Malaria Detection in Microscopic Blood Images. In: Global Trends in Information Systems and Software Applications. Springer, pp 431–440, 2012.
Song, J., Yu, G., Wang, D., and Nie, T., Offline web client: approach, design and implementation based on web system. In: Web Information Systems–WISE. Springer, pp 308–314, 2006.
Hejtmánek, L., and Matyska, L., Distributed Data Storage with Strong Offline Access Support. In: International Multi-Conference on Computing in the Global Information Technology. IEEE, pp 16–16, 2007.
Colajanni, M., Lancellotti, R., and Philip, S. Y., Distributed architectures for Web content adaptation and delivery. In: Web content delivery. Springer, pp 285–304, 2005.
Kart, F., Miao, G., and Moser, L. E., and Melliar-Smith, P., A distributed e-healthcare system based on the service oriented architecture. In: IEEE International Conference on Services Computing. IEEE, pp 652–659, 2007.
Patra, D., Ray, S., Mukhopadhyay, J., Majumdar, B., and Majumdar, A., Achieving e-health care in a distributed EHR system. In: International Conference on e-Health Networking, Applications and Services (Healthcom 2009). IEEE, pp 101–107, 2009.
Matsopoulos, G.K., Kouloulias, V., Asvestas, P., Mouravliansky, N., Delibasis, K., and Demetriades, D., MITIS: A WWW-based medical system for managing and processing gynecological–obstetrical–radiological data. Comput Methods Prog Biomed. 76(1):53–71, 2004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2004.03.001.
Abràmoff, M.D., Magalhães, P.J., and Ram, S.J., Image processing with ImageJ. Biophoton Int. 11(7):36–43, 2004.
Witten, I. H., Frank, E., Trigg, L. E., Hall, M. A., Holmes, G., and Cunningham, S. J., Weka: Practical machine learning tools and techniques with Java implementations. (Working paper 99/11). Hamilton New Zealand: University of Waikato, Department of Computer Science, 1999. http://hdl.handle.net/10289/1040
Lam, E. Y., Combining gray world and retinex theory for automatic white balance in digital photography. In: Proceedings of the Ninth International Symposium on Consumer Electronics. IEEE, pp 134–139, 2005.
Das, D., Maiti, A., and Chakraborty, C., Automated system for characterization and classification of malaria-infected stages using light microscopic images of thin blood smears. J Microsc. 257(3):238–252, 2015.
Das, D.K., Ghosh, M., Pal, M., Maiti, A.K., and Chakraborty, C., Machine learning approach for automated screening of malaria parasite using light microscopic images. Micron. 45:97–106, 2013.
Yang, Q., A Hybrid Median Filter for Enhancing Dim Small Point Targets and Its Fast Implementation. In: International Conference on Multimedia and Signal Processing. IEEE, pp 239–242, 2011.
Gonzalez, R. C., Woods, R. E., and Eddins, S. L., Digital image processing using MATLAB. 2nd edition, Pearson-Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, 2009.
Otsu, N., A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. Automatica. 11(285–296):23–27, 1975.
Hu, M.-K., Visual pattern recognition by moment invariants. IRE Trans Inf Theory. 8(2):179–187, 1962.
Ojala, T., Pietikainen, M., and Maenpaa, T., Multiresolution gray-scale and rotation invariant texture classification with local binary patterns. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 24(7):971–987, 2002.
Haralick, R.M., Shanmugam, K., and Dinstein, I.H., Textural features for image classification. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern. 3(6):610–621, 1973.
Smith Jr., T., Lange, G., and Marks, W., Fractal methods and results in cellular morphology—Dimensions, lacunarity and multifractals. J Neurosci Methods. 69(2):123–136, 1996.
Pietikäinen, M., Hadid, A., Zhao, G., Ahonen, T., Computer Vision Using Local Binary Patterns, Computational Imaging and Vision. 40. Springer-Verlag, London, 2011.
Witten, I. H., and Frank, E., Data Mining: Practical machine learning tools and techniques. Morgan Kaufmann, San francisco, 560, 2005. http://hdl.handle.net/2014/35171
Fayyad, UM., Irani, K. B., Multi-interval discretization of continuous-valued attributes for classification learning. Machine Learning, Chambery, 1022-1027, 1993.
Grünwald, P. D., The minimum description length principle. (Adaptive Computation and Machine Learning) MIT Press, Cambridge, 2007.
Rissanen, J., Modeling by shortest data description. Automatica. 14(5):465–471, 1978.
Hall, M. A., Correlation-based feature selection for machine learning. PhD thesis, The University of Waikato: 1999.
Hall, M. A., and Smith, L. A., Feature Selection for Machine Learning: Comparing a Correlation-Based Filter Approach to the Wrapper. In: FLAIRS Conference. pp 235–239, 1999.
Liu, H., and Setiono, R., Chi2: Feature selection and discretization of numeric attributes. In: IEEE International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence. IEEE Computer Society, pp 388–388, 1995.
Kira, K., and Rendell, L. A., A practical approach to feature selection. In: Proceedings of the ninth international workshop on Machine learning. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc., pp 249–256, 1992.
Quinlan, J. R., C4. 5: Programs for Machine Learning. Morgan Kaufmann Pub Inc., San Francisco, USA, 1993.
Quinlan, J.R., Induction of decision trees. Mach Learn. 1(1):81–106, 1986.
Aha, D.W., Kibler, D., and Albert, M.K., Instance-based learning algorithms. Mach Learn. 6(1):37–66, 1991.
Kahate, A., Cryptography and network security, 2nd edn. Tata McGraw Hill Education Private Limited, New Delhi, 2008.
StressStimulus, A Load Testing Tool for Web Applications and Mobile. http://www.stresstimulus.com/.
Raviraja, S., and Osman, S., A Novel Technique For Malaria Diagnosis Using Invariant Moments And By Image Compression. In: International Conference on Biomedical Engineering. Springer, pp 730–733, 2008.
Rouse, D. M., and Hemami, S. S., Analyzing the role of visual structure in the recognition of natural image content with multi-scale SSIM. In: Electronic Imaging 2008. International Society for Optics and Photonics, pp 680615–680615-680614, 2008.
Wang, Z., Bovik, A.C., Sheikh, H.R., and Simoncelli, E.P., Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans Image Process. 13(4):600–612, 2004.
Halim, Silvia & Bretschneider, Timo & li, Yikun & Preiser, Peter & Kuss, Claudia.. Estimating Malaria Parasitaemia from Blood Smear Images. Proc. IEEE International Conference on Control, Automation, Robotics and Vision. 1-6. 2006 doi:10.1109/ICARCV.2006.345381
Makkapati, Vishnu & Rao, Raghuveer. Segmentation of malaria parasites in peripheral blood smear images. ICASSP, IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing - Proceedings. 1361-1364. 2009 doi:10.1109/ICASSP.2009.4959845.
Tek FB, Dempster AG, Kale I Parasite detection and identification for automated thin blood film malaria diagnosis, Computer Vision and Image Understanding 114: 21-32, 2010.
Anggraini D, Nugroho AS, Pratama C, Rozi IE, Iskandar A A, et al. Automated status identification of microscopic images obtained from malaria thin blood smears. In: Electrical Engineering and Informatics (ICEEI), 2011 International Conference on, IEEE. 1-6, 2011, doi:10.1109/ICEEI.2011.6021762
Kaewkamnerd et al. An Automatic Device for Detection and Classification of Malaria Parasite Species in Thick Blood Film. BMC Bioinformatics 13. Suppl 17 (2012): S18. PMC 2017. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-13-S17-S18
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Dept. of Pathology, Midnapur Medical College and Hospital for providing the pathological images and clinical know-how. The first author acknowledges the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research for providing financial support to carry out this research work under the award no. 09/81(1223)/2014/EMR-I dt. 12-08-2014. Authors also acknowledge to Dept. of Information Technology, Govt. of India for financial assistance (Ref. No. IIT/SRIC/SMST/DPR/2009-10/15) to carry out the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Patient Facing Systems
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maity, M., Dhane, D., Mungle, T. et al. Web-Enabled Distributed Health-Care Framework for Automated Malaria Parasite Classification: an E-Health Approach. J Med Syst 41, 192 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-017-0834-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-017-0834-0