Abstract
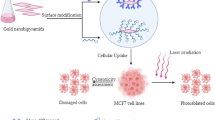
The current work demonstrated an in vitro model of diastase capped gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) and nanoplates (Au NPts) as unique contrast agents for molecular imaging and photothermal cancer therapy, respectively. The Au NPs/Au NPts were fabricated and conjugated with monoclonal antibodies of anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (anti-EGFR). Anti-EGFR-AuNPs bioconjugate was studied for molecular imaging allowing to interact with the nasopharyngeal carcinoma (CNE2 cells). Confocal immunofluorescence microscopic results revealed the increased scattering and reflectance properties of CNE2 cells after attachment and localization of Anti-EGFR-AuNPs bioconjugate on the cell surface, consequently providing the good optical contrast for the cancer cell imaging. On the other hand, Anti-EGFR-Au NPts were studied for photothermal applications using two malignant oral epithelial cell lines (HSC 3 and HOC 313 clone 8) and a nonmalignant epithelial cell line (HaCat), which revealed that the malignant cells require almost half of the laser energy to be photothermally eliminated after exposure to continuous red laser at 800 nm when compared with the nonmalignant cells. Further, the present approach may have potential for development of NPs for selective photothermal therapy and a successful diagnostics of cancer cell for bioimaging applications.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
I. H. El-Sayed, X. Huang, and M. A. El-Sayed (2005). Selective laser photo-thermal therapy of epithelial carcinoma using anti-EGFR antibody conjugated gold nanoparticles. Cancer Lett. 239, 129–135.
C. Loo, A. Lowery, N. Halas, J. West, and R. Drezek (2005). Immunotargeted nanoshells for integrated cancer imaging and therapy. Nano Lett. 5, 709–711.
R. Weissleder (2001). A clearer vision for in vivo imaging. Nat. Biotechnol. 19, 316–317.
N. W. Shi Kam, M. O’Connell, J. A. Wisdom, and H. Dai (2005). Carbon nanotubes as multifunctional biological transporters and near-infrared agents for selective cancer cell destruction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 11600–11605.
E. Hao and G. C. Schatz (2004). Electromagnetic fields around silver nanoparticles and dimers. J. Chem. Phys. 120, 357–366.
E. Hao, G. C. Schatz, and J. T. Hupp (2004). Synthesis and optical properties of anisotropic metal nanoparticles. J. Fluoresc. 14, 331–341.
F. Koenig, J. Knittel, and H. Stepp (2001). Diagnosing cancer in vivo. Science 292, 1401–1403.
K. Sokolov, J. Aaron, et al. (2003). Optical systems for in vivo molecular imaging of cancer. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2, 491–504.
K. Sokolov, M. Follen, J. Aaron, I. Pavlova, A. Malpica, R. Lotan, and R. Richards-Kortum (2003). Real-time vital optical imaging of precancer using anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibodies conjugated to gold nanoparticles. Cancer Res. 63, 1999–2004.
P. Mulvaney (1996). Surface plasmon spectroscopy of nanosized metal particles. Langmuir 12, 788–800.
W. D. Geoghegan and G. A. Ackerman (1977). Adsorption of horseradish peroxidase, ovomucoid, and antiimmunoglobulin to colloidal gold for the indirect detection of concanavalin A, wheat germ agglutinin, and goat anti-human immunoglobulin G on cell surfaces at the electron microscope level: a new method, theory, and application. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 25, 1187–1200.
D. M. Shin, J. Y. Ro, W. K. Hong, and W. N. Hittelman (1994). Dysregulation of epidermal growth factor receptor expression in premalignant lesions during head and neck tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 54, 3153–3159.
I. H. El-Sayed, X. Huang, and M. A. El-Sayed (2005). Surface plasmon resonance scattering and absorption of anti-EGFR antibody conjugated gold nanoparticles in cancer diagnostics: applications in oral cancer. Nano Lett. 5, 829–834.
J. C. Kah, C. J. Sheppard, C. G. Lee, M. C. Olivo, Application of antibody-conjugated gold nanoparticles for optical molecular imaging of epithelial carcinoma cells. in Nanobiophotonics and Biomedical Applications III (International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2006), p. 609503.
M. J. Abrams and B. A. Murrer (1993). Metal compounds in therapy and diagnosis. Science 261, 725–730.
M. Sireesh Babu, M. Badal Kumar, R. Shivendu, and D. Nandita (2015). Diastase assisted green synthesis of size controllable gold nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 5, 26727.
A. M. E. Nouri, C. Thompson, H. Cannell, M. Symes, S. Purkiss, and Z. Amirghofran (2000). Profile of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFr) expression in human malignancies: effects of exposure to EGF and its biological influence on established human tumor cell lines. Int. J. Mol. Med. 6, 495–500.
S. B. Maddinedi, B. K. Mandal, and K. K. Anna (2017). Environment friendly approach for size controllable synthesis of biocompatible Silver nanoparticles using diastase. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 49, 131–136.
A. J. Shnoudeh, I. Hamad, R. W. Abdo, L. Qadumii, A. Y. Jaber, H. S. Surchi, and S. Z. Alkelany, Synthesis, characterization, and applications of metal nanoparticles. In Biomaterials and Bionanotechnology. (Academic Press, Boca Raton, 2019), pp. 527–612.
R. S. Herbst and D. M. Shin (2002). Monoclonal antibodies to target epidermal growth factor receptor–positive tumors. Cancer 94, 1593–1611.
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to Wisdom Health care Institute, Chongqing City Management College, Chongqing for their support for this research work.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Research Involving Human and/or Animal rights
Not applicable.
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tao, K., Murakonda, G.K. & Jarubula, R. Development of Protein Capped Nano Gold for NIR Photothermal and Molecular Imaging Applications for Diagnosis of Cancer Cells: In Vitro Studies. J Clust Sci 33, 2643–2650 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-021-02179-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-021-02179-1