Abstract
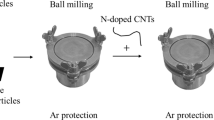
Bismuth has been deemed to be the promising anode material for sodium-ion batteries on account of large volumetric capacity (3800 mAh cm−3) and high electrical conductivity. However, huge volume change during sodiation/desodiation usually causes pulverization of electrode, leading to poor rate performance and cycling stability. Herein, one-step large-scale fabrication of bismuth@N-doped carbon (Bi@C) is proposed to construct well-behaved electrode materials for sodium-ion batteries. Surprisingly, the Bi@C anode presents superior sodium storage performance, manifesting a high specific capacity (346 mAh g−1 at 0.1 A g−1), excellent rate stability (274 mAh g−1 under ultrahigh current density of 50 A g−1) and long life span (344 mAh g−1 at 1 A g−1 after cycling over 1500 times, 0.003% loss per cycle). Such excellent performances of Bi@C are attributed to the nano-sized Bi particles (~ 15 nm) encapsulated by thin carbon layer doped with N. These structural characteristics optimize the ion transfer and increase the accessible area between electrode and electrolyte, and then give a high capacitive contribution to the capacity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Assat G, Tarascon J-M (2018) Fundamental understanding and practical challenges of anionic redox activity in Li-ion batteries. Nat Energy 3:373–386
Li M, Lu J, Chen Z, Amine K (2018) 30 years of lithium-ion batteries. Adv Mater 30:1800561
Winter M, Barnett B, Xu K (2018) Before li ion batteries. Chem Rev 118:11433–11456
Goodenough JB, Park KS (2013) The Li-ion rechargeable battery: a perspective. J Am Chem Soc 135:1167–1176
Li Z, Yin Q, Hu W et al (2019) Tin/tin antimonide alloy nanoparticles embedded in electrospun porous carbon fibers as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. J Mater Sci 54:9025–9033. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-019-03539-z
Nayak PK, Yang L, Brehm W, Adelhelm P (2018) From lithium-ion to sodium-ion batteries: advantages, challenges, and surprises. Angew Chem Int Ed 57:102–120
Hwang JY, Myung ST, Sun YK (2017) Sodium-ion batteries: present and future. Chem Soc Rev 46:3529–3614
Yang D, Li S, Cheng D et al (2021) Nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorus codoped hollow carbon microtubes derived from silver willow blossoms as a high-performance anode for sodium-ion batteries. Energy Fuels 35:2795–2804
Xie F, Zhang L, Ye C, Jaroniec M, Qiao SZ (2019) The application of hollow structured anodes for sodium-ion batteries: from simple to complex systems. Adv Mater 31:1800492
Yabuuchi N, Kubota K, Dahbi M, Komaba S (2014) Research development on sodium-ion batteries. Chem Rev 114:11636–11682
Wang L, Wang C, Li F, Cheng F, Chen J (2017) In situ synthesis of Bi nanoflakes on Ni foam for sodium-ion batteries. Chem Commun 54:38–41
Li H, Peng L, Zhu Y, Chen D, Zhang X, Yu G (2016) An advanced high-energy sodium ion full battery based on nanostructured Na2Ti3O7/VOPO4 layered materials. Energy Environ Sci 9:3399–3405
Ma C, Fan Q, Dirican M, Song Y, Zhang X, Shi J (2020) Porous carbon nanosheets derived from expanded graphite for supercapacitors and sodium-ion batteries. J Mater Sci 55:16323–16333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-05154-9
Saurel D, Orayech B, Xiao B, Carriazo D, Li X, Rojo T (2018) From charge storage mechanism to performance: a roadmap toward high specific energy sodium-ion batteries through carbon anode optimization. Adv Energy Mater 8:1703268
Xiao B, Rojo T, Li X (2019) Hard carbon as sodium-ion battery anodes: progress and challenges. Chemsuschem 12:133–144
Hou H, Banks CE, Jing M, Zhang Y, Ji X (2015) Carbon quantum dots and their derivative 3D porous carbon frameworks for sodium-ion batteries with ultralong cycle life. Adv Mater 27:7861–7866
Palomares V, Serras P, Villaluenga I, Hueso KB, Carretero-González J, Rojo T (2012) Na-ion batteries, recent advances and present challenges to become low cost energy storage systems. Energy Environ Sci 5:5884
Kubota K, Komaba S (2015) Review—practical issues and future perspective for Na-ion batteries. J Electrochem Soc 162:A2538–A2550
Zou G, Hou H, Ge P et al (2018) Metal-organic framework-derived materials for sodium energy storage. Small 14:1702648
Alvin S, Yoon D, Chandra C et al (2019) Revealing sodium ion storage mechanism in hard carbon. Carbon 145:67–81
Jin Q, Li W, Wang K et al (2019) Experimental design and theoretical calculation for sulfur-doped carbon nanofibers as a high performance sodium-ion battery anode. J Mater Chem A 7:10239–10245
Xu F, Qiu Y, Han H et al (2020) Manipulation of carbon framework from the microporous to nonporous via a mechanical-assisted treatment for structure-oriented energy storage. Carbon 159:140–148
Li X, Ni J, Savilov SV, Li L (2018) Materials based on antimony and bismuth for sodium storage. Chem Eur J 24:13719–13727
Gao H, Niu J, Zhang C, Peng Z, Zhang Z (2018) A dealloying synthetic strategy for nanoporous bismuth–antimony anodes for sodium ion batteries. ACS Nano 12:3568–3577
Liu J, Yu L, Wu C et al (2017) New nanoconfined galvanic replacement synthesis of hollow Sb@C yolk-shell spheres constituting a stable anode for high-rate Li/Na-ion batteries. Nano Lett 17:2034–2042
Ruiz O, Cochrane M, Li M et al (2018) Enhanced cycling stability of macroporous bulk antimony-based sodium-ion battery anodes enabled through active/inactive composites. Adv Energy Mater 8:1801781
Palaniselvam T, Goktas M, Anothumakkool B et al (2019) Sodium storage and electrode dynamics of tin–carbon composite electrodes from bulk precursors for sodium-ion batteries. Adv Funct Mater 29:1900790
Wang L, Voskanyan AA, Chan KY, Qin B, Li F (2019) Combustion synthesized porous bismuth/N-doped carbon nanocomposite for reversible sodiation in a sodium-ion battery. ACS Appl Energy Mater 3:565–572
Yang H, Chen LW, He F et al (2020) Optimizing the void size of yolk-shell Bi@void@C nanospheres for high-power-density sodium-ion batteries. Nano Lett 20:758–767
Cheng X, Li D, Wu Y, Xu R, Yu Y (2019) Bismuth nanospheres embedded in three-dimensional (3D) porous graphene frameworks as high performance anodes for sodium- and potassium-ion batteries. J Mater Chem A 7:4913–4921
Liang L, Xu Y, Li Y et al (2017) Facile synthesis of hierarchical fern leaf-like Sb and its application as an additive-free anode for fast reversible Na-ion storage. J Mater Chem A 5:1749–1755
Moradi M, Li Z, Qi J et al (2015) Improving the capacity of sodium ion battery using a virus-templated nanostructured composite cathode. Nano Lett 15:2917–2921
Webb SA, Baggetto L, Bridges CA, Veith GM (2014) The electrochemical reactions of pure indium with Li and Na: Anomalous electrolyte decomposition, benefits of FEC additive, phase transitions and electrode performance. J Power Sources 248:1105–1117
Yang H, Xu R, Yao Y, Ye S, Zhou X, Yu Y (2019) Multicore–shell Bi@N-doped carbon nanospheres for high power density and long cycle life sodium- and potassium-ion anodes. Adv Funct Mater 29:1809195
Chen J, Fan X, Ji X et al (2018) Intercalation of Bi nanoparticles into graphite results in an ultra-fast and ultra-stable anode material for sodium-ion batteries. Energy Environ Sci 11:1218–1225
Qiu J, Li S, Su X et al (2017) Bismuth nano-spheres encapsulated in porous carbon network for robust and fast sodium storage. Chem Eng J 320:300–307
Sottmann J, Herrmann M, Vajeeston P et al (2016) How crystallite size controls the reaction path in nonaqueous metal ion batteries: the example of sodium bismuth alloying. Chem Mater 28:2750–2756
Xu F, Zhai Y, Zhang E et al (2020) Ultrastable surface-dominated pseudocapacitive potassium storage enabled by edge-enriched n-doped porous carbon nanosheets. Angew Chem Int Ed 59:2–10
Li Z, Cheng A, Zhong W et al (2020) Facile fabrication of carbon nanosheets with hierarchically porous structure for high-performance supercapacitor. Microp Mesop Mater 306:110440
Li Z, Yu P, Zhong W et al (2021) Hydrothermal intercalation for the synthesis of novel three-dimensional hierarchically superstructured carbons composed of graphene-like ultrathin nanosheets. Carbon 176:1–10
Wang C, Wang L, Li F, Cheng F, Chen J (2017) Bulk bismuth as a high-capacity and ultralong cycle-life anode for sodium-ion batteries by coupling with glyme-based electrolytes. Adv Mater 29:1702212
Xiong P, Bai P, Li A et al (2019) Bismuth nanoparticle@carbon composite anodes for ultralong cycle life and high-rate sodium-ion batteries. Adv Mater 31:1904771
Liu S, Luo Z, Guo J, Pan A, Cai Z, Liang S (2017) Bismuth nanosheets grown on carbon fiber cloth as advanced binder-free anode for sodium-ion batteries. Electrochem Commun 81:10–13
Su D, Dou S, Wang G (2015) Bismuth: A new anode for the Na-ion battery. Nano Energy 12:88–95
Xiang J, Liu Z, Song T (2018) Bi@C nanoplates derived from (BiO)2CO3 as an enhanced electrode material for lithium/sodium-ion batteries. ChemistrySelect 3:8973–8979
Yang F, Yu F, Zhang Z, Zhang K, Lai Y, Li J (2016) Bismuth nanoparticles embedded in carbon spheres as anode materials for sodium/lithium-ion batteries. Chem Eur J 22:2333–2338
Augustyn V, Come J, Lowe MA et al (2013) High-rate electrochemical energy storage through Li+ intercalation pseudocapacitance. Nat Mater 12:518–522
Simon P, Gogotsi Y, Dunn B (2014) Where do batteries end and supercapacitors begin? Science 343:1210–1211
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Science and Technology Program of Guangdong Province of China (2019A050510012, 2020A050515007) and Guangzhou emerging industry development fund project of Guangzhou development and reform commission.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Kyle Brinkman.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Zhong, W., Cheng, D. et al. One-step large-scale fabrication of Bi@N-doped carbon for ultrahigh-rate and long-life sodium-ion battery anodes. J Mater Sci 56, 11000–11010 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-021-05978-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-021-05978-z