Abstract
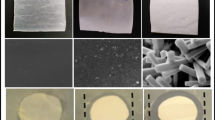
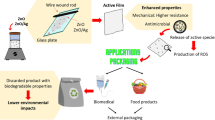
Antimicrobial surfaces can play a key role in many fields, like biomedical applications and food packaging, where it is fundamental to prevent clinical infections, foodborne diseases, or quality loss of food and beverages. Materials used for such kind of applications should be biocompatible or avoid harmful effects on human health. Additionally, since a wide variety of tools and components operating in contact with human tissues or foodstuff are made of plastic-based materials, it is important to investigate antibacterial surfaces applied in conjunction with eco-friendly bio-based plastics. For all these reasons, here we propose the use of novel composites made of nanostructured aluminum-doped zinc oxide antimicrobial coatings on polylactide films. Their surface topography is inspected at sub- and supra-micron length scales, and its influence on wettability and antibacterial activity is investigated, together with FTIR analysis for identification of molecular vibrations. Their strong antimicrobial performance is assessed against four different bacterial strains, and their safety is evaluated on two different human cell lines. The results here presented identify AZO-coated PLA films as very appealing eco-friendly antibacterial systems for food packaging and biomedical applications.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auras R, Harte B, Selke S (2004) An overview of polylactides as packaging materials. Macromol Biosci 4:835–864. https://doi.org/10.1002/mabi.200400043
Tawakkal ISMA, Cran MJ, Miltz J, Bigger SW (2014) A review of poly(lactic acid)-based materials for antimicrobial packaging. J Food Sci 79:R1477–R1490. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.12534
He X, Hwang H-M (2016) Nanotechnology in food science: Functionality, applicability, and safety assessment. J Food Drug Anal 24:671–681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfda.2016.06.001
Garcia CV, Shin GH, Kim JT (2018) Metal oxide-based nanocomposites in food packaging: applications, migration, and regulations. Trends Food Sci Technol 82:21–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2018.09.021
Gold K, Slay B, Knackstedt M, Gaharwar AK (2018) Antimicrobial activity of metal and metal-oxide based nanoparticles. Adv Ther 1:1700033. https://doi.org/10.1002/adtp.201700033
Raghunath A, Perumal E (2017) Metal oxide nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents: a promise for the future. Int J Antimicrob Agents 49:137–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2016.11.011
Khezerlou A, Alizadeh-Sani M, Azizi-Lalabadi M, Ehsani A (2018) Nanoparticles and their antimicrobial properties against pathogens including bacteria, fungi, parasites and viruses. Microb Pathog 123:505–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2018.08.008
Nair S, Sasidharan A, DivyaRani VV, Menon D, Nair S, Manzoor K, Raina S (2009) Role of size scale of ZnO nanoparticles and microparticles on toxicity toward bacteria and osteoblast cancer cells. J Mater Sci Mater Med 20:S235–S241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-008-3548-5
Kumar R, Umar A, Kumar G, SinghNalwa H (2017) Antimicrobial properties of ZnO nanomaterials: a review. Ceram Int 43:3940–3961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.12.062
Sruthi S, Ashtami J, Mohanan PV (2018) Biomedical application and hidden toxicity of Zinc oxide nanoparticles. Mater Today Chem 10:175–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtchem.2018.09.008
Valerini D, Tammaro L, Di Benedetto F, Vigliotta G, Capodieci L, Terzi R, Rizzo A (2018) Aluminum-doped zinc oxide coatings on polylactic acid films for antimicrobial food packaging. Thin Solid Films 645:187–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2017.10.038
Saxena V, Chandra P, Pandey LM (2018) Design and characterization of novel Al-doped ZnO nanoassembly as an effective nanoantibiotic. Appl Nanosci 8:1925–1941. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-018-0863-0
Chidhambaram N (2019) Augmented antibacterial efficacies of the aluminium doped ZnO nanoparticles against four pathogenic bacteria. Mater Res Express 6:075061. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab1804
Denes E, Barrière G, Poli E, Lévêque G (2018) Alumina biocompatibility. J Longterm Eff Med 28:9–13. https://doi.org/10.1615/JLongTermEffMedImplants.2018025635
Commission Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 of 14 January 2011 on plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with food
Murariu M, Doumbia A, Bonnaud L, Dechief AL, Paint Y, Ferreira M, Campagne C, Devaux E, Dubois P (2011) High-performance polylactide/ZnO nanocomposites designed for films and fibers with special end-use properties. Biomacromol 12:1762–1771. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm2001445
Pantani R, Gorrasi G, Vigliotta G, Murariu M, Dubois P (2013) PLA-ZnO nanocomposite films: water vapor barrier properties and specific end-use characteristics. Eur Polym J 49:3471–3482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2013.08.005
Martucciello S, Paolella G, Muzashvili T, Skhirtladze A, Pizza C, Caputo I, Piacente S (2018) Steroids from Helleborus caucasicus reduce cancer cell viability inducing apoptosis and GRP78 down-regulation. Chem Biol Interact 279:43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2017.11.002
Varshosaz J, Hassanzadeh F, SadeghiAliabadi H, Nayebsadrian M, Banitalebi M, Rostami M (2014) Synthesis and characterization of folate-targeted dextran/retinoic acid micelles for doxorubicin delivery in acute leukemia. Biomed Res Int 2014:525684. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/525684
Copinet A, Bertrand C, Govindin S, Coma V, Couturier Y (2004) Effects of ultraviolet light (315 nm), temperature and relative humidity on the degradation of polylactic acid plastic films. Chemosphere 55:763–773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2003.11.038
Ho K-LG, Pometto AL III (1999) Effects of electron-beam irradiation and ultraviolet light (365 nm) on polylactic acid plastic films. J Environ Polym Degrad 7:93–100. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021860301487
Saravanakumar K, Ravichandran K (2012) Synthesis of heavily doped nanocrystalline ZnO: Al powders using a simple soft chemical method. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 23:1462–1469. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-011-0612-6
Djelloul A, Aida MS, Bougdira J (2010) Photoluminescence, FTIR and X-ray diffraction studies on undoped and Al-doped ZnO thin films grown on polycrystalline α-alumina substrates by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. J Lumin 130:2113–2117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2010.06.002
Wan C, Tan H, Jin S, Yang H, Tang M, He J (2008) Highly conductive Al-doped tetra-needle-like ZnO whiskers prepared by a solid state method. Mater Sci Eng B 150:203–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2008.05.009
Vasconcelos DCL, Nunes EHM, Vasconcelos WL (2012) AES and FTIR characterization of sol–gel alumina films. J Non-Cryst Solids 358:1374–1379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2012.03.017
Ström G, Fredriksson M, Stenius P (1987) Contact angles, work of adhesion, and interfacial tensions at a dissolving Hydrocarbon surface. J Colloid Interface Sci 119:352–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9797(87)90280-3
Hsueh Y-H, Ke W-J, Hsieh C-T, Lin K-S, Tzou D-Y, Chiang C-L (2015) ZnO nanoparticles affect bacillus subtilis cell growth and biofilm formation. PLoS ONE 10:e0128457. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0128457
Cao F, Zhang L, Wang H, You Y, Wang Y, Gao N, Ren J, Qu X (2019) Defect-rich adhesive nanozymes as efficient antibiotics for enhanced bacterial inhibition. Angew Chem Int Ed 58:16236–16242. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201908289
Reddy KM, Feris K, Bell J, Wingett DG, Hanley C, Punnoose A (2007) Selective toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles to prokaryotic and eukaryotic systems. Appl Phys Lett 90:213902. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2742324
Siddiqi KS, Rahman AU, Husen TA (2018) Properties of zinc oxide nanoparticles and their activity against microbes. Nanoscale Res Lett 13:141. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-018-2532-3
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Valerini, D., Tammaro, L., Villani, F. et al. Antibacterial Al-doped ZnO coatings on PLA films. J Mater Sci 55, 4830–4847 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-019-04311-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-019-04311-z