Abstract
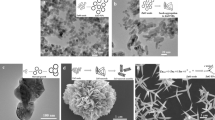
The specific role of size scale, surface capping, and aspect ratio of zinc oxide (ZnO) particles on toxicity toward prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells was investigated. ZnO nano and microparticles of controlled size and morphology were synthesized by wet chemical methods. Cytotoxicity toward mammalian cells was studied using a human osteoblast cancer cell line and antibacterial activity using Gram-negative bacteria (Escherichia coli) as well as using Gram-positive bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus). Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was conducted to characterize any visual features of the biocidal action of ZnO. We observed that antibacterial activity increased with reduction in particle size. Toxicity toward the human cancer cell line was considerably higher than previously observed by other researchers on the corresponding primary cells, suggesting selective toxicity of the ZnO to cancer cells. Surface capping was also found to profoundly influence the toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles toward the cancer cell line, with the toxicity of starch-capped ZnO being the lowest. Our results are found to be consistent with a membrane-related mechanism for nanoparticle toxicity toward microbes.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
O. Yamamoto, Int. J. Inorg. Mater. 3, 643 (2001)
J. Sawai, E. Kawada, F. Kanou, H. Igarashi, A. Hashimoto, T. Kokugan, M. Shimizu, J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 29, 627 (1996)
J. Sawai, H. Kojima, H. Igarashi, A. Hashimoto, S. Shoji, A. Takehara, T. Sawaki, T. Kokugan, M. Shimizu, J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 30, 1034 (1997)
J. Sawai, S. Shouji, H. Igarashi, A. Hashimoto, T. Kokugan, M. Shimizu, H. Kojima, J. Ferment. Bioeng. 86, 521 (1998)
Z. Yang, C. Xie, Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 47, 132 (2006)
L. Zhang, Y. Ding, M.J.W. Povey, D.W. York, J. Nanopart. Res. 9, 479 (2007)
R. Brayner, R. Ferrari-Iliou, N. Brivois, S. Djediat, M.F. Bendetti, F. Fievet, Nano Lett. 6, 866 (2006)
L.K. Adams, D.Y. Lyon, P.J. Alvarez, Water Res. 40, 3527 (2006)
K.M. Reddy, K. Feris, J. Bell, D.G. Wingett, C. Hanley, A. Punnoose, Appl. Phy. Lett. 90, 213902 (2007)
H.A. Jeng, J. Swanson, J. Enviorn. Sci. Health 41, 2699 (2006)
G. Colon, B.C. Ward, T.J. Webster, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 78, 595 (2006)
C. Sheng, F. Liu, Powder Technol. 145, 20 (2004)
W. Changle, O. Xueliang, C. Jianguo, W. Hongshui, T. Fatang, L. Shitao, Mater. Lett. 60, 1828 (2006)
M.K. Calbretta, A. Kumar, A.M. Mcdermott, C. Cai, Biomacromolecules 8, 1807 (2007)
R.B. Greenwald, H. Zhao, J. Xi, A. Martinez, J. Med. Chem. 46, 5021 (2003)
S. Pal, Y.K. Tak, J.M. Song, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 73, 1712 (2007)
P. Liu-Snynder, M.P. Logan, R. Shi, D.T. Smith, R.B. Borgens, J. Exp. Biol. 210, 1455 (2007)
L.B. Owen-Szcaub, Clin. Cancer Res. 7, 1108 (2001)
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India for financial support through the Nanoscience and Nanotechnology (NS & NT) initiative monitored by Professor C.N.R. Rao. We are thankful to Sajin P. Ravi for SEM analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nair, S., Sasidharan, A., Divya Rani, V.V. et al. Role of size scale of ZnO nanoparticles and microparticles on toxicity toward bacteria and osteoblast cancer cells. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 20 (Suppl 1), 235–241 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-008-3548-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-008-3548-5