Abstract
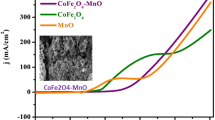
For the first time, a porous CoSe2/C microsphere interwoven by ultrathin CoSe2 and carbon nanosheets is synthesized by a simple solvothermal method. Compared with bare CoSe2, the CoSe2/C hybrid exhibits much better performance for hydrogen evolution reaction (HER): The hybrid demonstrates a Tafel mechanism rather than the Heyrovsky mechanism of CoSe2; it has a low onset potential (− 189 mV vs RHE) and an ultra-low Tafel slope (34 mV dec−1); current density increases by more than 2.5 times at equipotential; the hybrid also exhibits remarkable long-term stability even after 1000 cycles. At root, the superior HER performance of CoSe2/C stems from its unique porous microsphere intertwined by ultrathin CoSe2 nanosheets and conductive carbon nanosheets, which not only facilitate the electron transfer and ion diffusion, but also produce abundant electrocatalytic active sites for HER. This facile and scalable synthetic method can be extended to synthesize nonprecious transition-metal-based catalysts with unique nanoarchitecture and outstanding HER performance.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yin X, Sun G, Song A, Wang L, Wang Y, Dong H, Shao G (2017) A novel structure of Ni-(MoS2/GO) composite coatings deposited on Ni foam under supergravity field as efficient hydrogen evolution reaction catalysts in alkaline solution. Electrochim Acta 249:52–63
Kumar S, Sahoo PK, Satpati AK (2017) Electrochemical and SECM investigation of MoS2/GO and MoS2/rGO nanocomposite materials for HER electrocatalysis. ACS Omega 2:7532–7545
Ji X, Liu B, Ren X, Shi X, Asiri AM, Sun X (2018) P-doped Ag nanoparticles embedded in N-doped carbon nanoflake: an efficient electrocatalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:4499–4503
Theerthagiri J, Sudha R, Premnath K, Arunachalam P, Madhavan J, Al-Mayouf AM (2017) Growth of iron diselenide nanorods on graphene oxide nanosheets as advanced electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. Int J Hydrogen Energy 42:13020–13030
Wang M, Ye C, Liu H, Xu M, Bao S (2018) Nanosized metal phosphides embedded in nitrogen-doped porous carbon nanofibers for enhanced hydrogen evolution at all pH values. Angew Chem Int Ed 57:1963–1967
Jing S, Zhang L, Luo L, Lu J, Yin S, Shen PK, Tsiakaras P (2018) N-doped porous molybdenum carbide nanobelts as efficient catalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Appl Catal B 224:533–540
Murthy AP, Theerthagiri J, Madhavan J, Murugan K (2017) Enhancement of hydrogen evolution activities of low-cost transition metal electrocatalysts in near-neutral strongly buffered aerobic media. Electrochem Commun 83:6–10
Liu J, Liu Y, Xu D, Zhu Y, Peng W, Li Y, Zhang F, Fan X (2019) Hierarchical “nanoroll” like MoS2/Ti3C2Tx hybrid with high electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution activity. Appl Catal B 241:89–94
Park S, Chung DY, Ko D, Sung Y, Piao Y (2016) Three-dimensional carbon foam/N-doped graphene@MoS2 hybrid nanostructures as effective electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J Mater Chem A 4:12720–12725
Guo Y, Guo D, Ye F, Wang K, Shi Z, Chen X, Zhao C (2018) Self-supported NiSe2 nanowire arrays on carbon fiber paper as efficient and stable electrode for hydrogen evolution reaction. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:11884–11891
Liang J, Yang Y, Zhang J, Wu J, Dong P, Yuan J, Zhang G, Lou J (2015) Metal diselenide nanoparticles as highly active and stable electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Nanoscale 7:14813–14816
Yin Y, Zhang Y, Gao T, Yao T, Zhang X, Han J, Wang X, Zhang Z, Xu P, Zhang P, Cao X, Song B, Jin S (2017) Synergistic phase and disorder engineering in 1T-MoSe2 nanosheets for enhanced hydrogen-evolution reaction. Adv Mater 29:1700311
Yu P, Wang F, Shifa TA, Zhan X, Lou X, Xia F, He J (2019) Earth abundant materials beyond transition metal dichalcogenides: a focus on electrocatalyzing hydrogen evolution reaction. Nano Energy 58:244–276
Zhai L, Mak CH, Qian J, Lin S, Lau SP (2019) Self-reconstruction mechanism in NiSe2 nanoparticles/carbon fiber paper bifunctional electrocatalysts for water splitting. Electrochim Acta 305:37–46
Tao Y, Wang X, Yue S, Li F, Huang H, Lu X (2019) Molybdenum carbide nanoparticles supported on nitrogen-doped carbon as efficient electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. J Electroanal Chem 842:89–97
Tan C, Luo Z, Chaturvedi A, Cai Y, Du Y, Gong Y, Huang Y, Lai Z, Zhang X, Zheng L, Qi X, Goh MH, Wang J, Han S, Wu XJ, Gu L, Kloc C, Zhang H (2018) Preparation of high-percentage 1T-phase transition metal dichalcogenide nanodots for electrochemical hydrogen evolution. Adv Mater 30:1705509
Wang X, Zheng B, Yu B, Wang B, Hou W, Zhang W, Chen Y (2018) In situ synthesis of hierarchical MoSe2–CoSe2 nanotubes as an efficient electrocatalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction in both acidic and alkaline media. J Mater Chem A 6:7842–7850
Yu B, Qi F, Zheng B, Hou W, Zhang W, Li Y, Chen Y (2018) Self-assembled pearl-bracelet-like CoSe2–SnSe2/CNT hollow architecture as highly efficient electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. J Mater Chem A 6:1655–1662
Li J, Liu P, Qu Y, Liao T, Xiang B (2018) WSe2/rGO hybrid structure: a stable and efficient catalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. Int J Hydrogen Energy 43:2601–2609
Song D, Wang H, Wang X, Yu B, Chen Y (2017) NiSe2 nanoparticles embedded in carbon nanowires as highly efficient and stable electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. Electrochim Acta 254:230–237
Hu J, Huang B, Zhang C, Wang Z, An Y, Zhou D, Lin H, Leung MKH, Yang S (2017) Engineering stepped edge surface structures of MoS2 sheet stacks to accelerate the hydrogen evolution reaction. Energy Environ Sci 10:593–603
Shang X, Hu W, Li X, Dong B, Liu Y, Han G, Chai Y, Liu C (2017) Oriented stacking along vertical (002) planes of MoS2: a novel assembling style to enhance activity for hydrogen evolution. Electrochim Acta 224:25–31
Mazánek V, Mayorga-Martinez CC, Bouša D, Sofer Z, Pumera M (2018) WSe2 nanoparticles with enhanced hydrogen evolution reaction prepared by bipolar electrochemistry: application in competitive magneto-immunoassay. Nanoscale 10:23149–23156
Wang Y, Zhao S, Wang Y, Laleyan DA, Wu Y, Ouyang B, Ou P, Song J, Mi Z (2018) Wafer-scale synthesis of monolayer WSe2: a multi-functional photocatalyst for efficient overall pure water splitting. Nano Energy 51:54–60
Hasani A, Nguyen TP, Tekalgne M, Van Le Q, Choi KS, Lee TH, Jung Park T, Jang HW, Kim SY (2018) The role of metal dopants in WS2 nanoflowers in enhancing the hydrogen evolution reaction. Appl Catal A 567:73–79
Wu Z, Fang B, Bonakdarpour A, Sun A, Wilkinson DP, Wang D (2012) WS2 nanosheets as a highly efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. Appl Catal B 125:59–66
Wang H, Wang X, Yang D, Zheng B, Chen Y (2018) Co0.85Se hollow nanospheres anchored on N-doped graphene nanosheets as highly efficient, nonprecious electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction in both acid and alkaline media. J Power Sources 400:232–241
Wang B, Wang X, Zheng B, Yu B, Qi F, Zhang W, Li Y, Chen Y (2017) NiSe2 nanoparticles embedded in CNT networks: scalable synthesis and superior electrocatalytic activity for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Electrochem Commun 83:51–55
Ashassi-Sorkhabi H, Rezaei-Moghadam B, Asghari E, Bagheri R, Hosseinpour Z (2017) Fabrication of bridge like Pt@MWCNTs/CoS2 electrocatalyst on conductive polymer matrix for electrochemical hydrogen evolution. Chem Eng J 308:275–288
Li Y, Wang H, Xie L, Liang Y, Hong G, Dai H (2011) MoS2 nanoparticles grown on graphene: an advanced catalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J Am Chem Soc 133:7296–7299
McCarthy CL, Downes CA, Schueller EC, Abuyen K, Brutchey RL (2016) Method for the solution deposition of phase-pure CoSe2 as an efficient hydrogen evolution reaction electrocatalyst. ACS Energy Lett 1:607–611
Wan S, Jin W, Guo X, Mao J, Zheng L, Zhao J, Zhang J, Liu H, Tang C (2018) Self-templating construction of porous CoSe2 nanosheet arrays as efficient bifunctional electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:15374–15382
Zhang M, Hu A, Liu Z, Xu Y, Fan B, Tang Q, Zhang S, Deng W, Chen X (2018) Synergistic effect of three-dimensional cobalt diselenide/carbon nanotube arrays composites for enhanced hydrogen evolution reaction. Electrochim Acta 285:254–261
Li H, Qian X, Zhu C, Jiang X, Shao L, Hou L (2017) Template synthesis of CoSe2/Co3Se4 nanotubes: tuning of their crystal structures for photovoltaics and hydrogen evolution in alkaline medium. J Mater Chem A 5:4513–4526
Zhou W, Lu J, Zhou K, Yang L, Ke Y, Tang Z, Chen S (2016) CoSe2 nanoparticles embedded defective carbon nanotubes derived from MOFs as efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. Nano Energy 28:143–150
Zhao S, Jin R, Abroshan H, Zeng C, Zhang H, House SD, Gottlieb E, Kim HJ, Yang JC, Jin R (2017) Gold nanoclusters promote electrocatalytic water oxidation at the nanocluster/CoSe2 interface. J Am Chem Soc 139:1077–1080
Kwak IH, Im HS, Jang DM, Kim YW, Park K, Lim YR, Cha EH, Park J (2016) CoSe2 and NiSe2 nanocrystals as superior bifunctional catalysts for electrochemical and photoelectrochemical water splitting. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:5327–5334
Wu X, Han S, He D, Yu C, Lei C, Liu W, Zheng G, Zhang X, Lei L (2018) Metal organic framework derived Fe-doped CoSe2 incorporated in nitrogen-doped carbon hybrid for efficient hydrogen evolution. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:8672–8678
Zhang H, Yang B, Wu X, Li Z, Lei L, Zhang X (2015) Polymorphic CoSe2 with mixed orthorhombic and cubic phases for highly efficient hydrogen evolution reaction. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:1772–1779
Zhou Y, Xiao H, Zhang S, Li Y, Wang S, Wang Z, An C, Zhang J (2017) Interlayer expanded lamellar CoSe2 on carbon paper as highly efficient and stable overall water splitting electrodes. Electrochim Acta 241:106–115
Tong J, Li W, Wei B, Bo L, Li Q, Li Y, Li T, Zhang Q (2018) Facile preparing composite of CoSe2 wrapping N-doped mesoporous carbon with highly electrocatalytic activity for hydrogen evolution reaction. Int J Hydrogen Energy 43:17021–17029
Kim JK, Park GD, Kim JH, Park S, Kang YC (2017) Rational design and synthesis of extremely efficient macroporous CoSe2-CNT composite microspheres for hydrogen evolution reaction. Small 13:1700068
Yang Y, Zhang W, Xiao Y, Shi Z, Cao X, Tang Y, Gao Q (2019) CoNiSe2 heteronanorods decorated with layered-double-hydroxides for efficient hydrogen evolution. Appl Catal B 242:132–139
Lee C, Chen W, Billo T, Lin Y, Fu F, Samireddi S, Lee C, Hwang J, Chen K, Chen L (2016) Beaded stream-like CoSe2 nanoneedle array for efficient hydrogen evolution electrocatalysis. J Mater Chem A 4:4553–4561
Brug GJ, Van Den Eeden AL, Sluyters-Rehbach M, Sluyters JH (1984) Analysis of electrode impedances complicated by the presence of a constant phase element. J Electroanal Chem Interfacial Electrochem 176:275–295
Lin D, Lasia A (2017) Electrochemical impedance study of the kinetics of hydrogen evolution at a rough palladium electrode in acidic solution. J Electroanal Chem 785:190–195
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 21773024, 51372033) and National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2015AA034202).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yue, H., Yang, D., Yu, B. et al. Porous interwoven CoSe2/C microsphere: a highly efficient and stable nonprecious electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. J Mater Sci 54, 14123–14133 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-019-03881-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-019-03881-2