Abstract
Purpose
To assess the long-term outcome of patients with subretinal neovascular membrane (SRNVM) secondary to type 2 idiopathic juxtafoveolar telangiectasia (IJT) receiving intravitreal anti-VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) injections.
Methods
A total of 14 eyes of 12 patients treated with intravitreal anti-VEGF for SRNVM related to type 2 IJT were retrospectively assessed.
Results
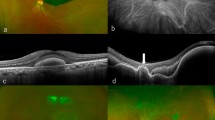
Nine men and 3 women with a mean age of 66 years (SD 12, range 47–87 years) were diagnosed with IJT-related SRNVM. On average, 6.8 injections (SD 5.5, range 3–18) were given per eye. Ten eyes were treated with ranibizumab, 3 eyes with bevacizumab and 1 eye received both substances. The median follow-up after the last injection was 31 months (IQR: 18, 48). In 6 eyes, BCVA improved by 1–4 lines (mean Δ +2.0 lines), 1 eye remained stable and 7 eyes showed decline of vision by 1–5 lines (mean Δ −2.1 lines). The baseline central foveal thickness was significantly reduced from a mean of 323 (SD 87) to 266 µm (SD 71 µm) at the last follow-up visit (p = 0.001).
Conclusions
SRNVM development is a severe complication of type 2 IJT. Since the establishment of intravitreal anti-VEGF treatment laser coagulation and PDT have lost significance. Intravitreal anti-VEGF therapy seems to be safe and effective for the treatment of IJT-related SRNVM. Frequently multiple intravitreal injections are necessary for stabilisation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gass JD, Blodi BA (1993) Idiopathic juxtafoveolar retinal telangiectasis. Update of classification and follow-up study. Ophthalmology 100:136–146
Engelbrecht NE, Aaberg TM, Sung J, Lewis ML (2002) Neovascular membranes associated with idiopathic juxtafoveolar telangiectasis. Arch Ophthalmol 120(3):320–324
Charbel Issa P, Gillies MC, Chew EY et al (2013) Macular telangiectasia type 2. Prog Retin Eye Res 34:49–77
Chhablani J, Mithal K, Rao H, Narayanan R (2014) Diagnosis of subretinal neovascularization associated with idiopathic juxtafoveal retinal telangiectasia: fluorescein angiography versus spectra-domain optical coherence tomography. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 252:549–553
Toygar O, Guess MG, Youssef DS, Miller DM (2016) Long-term outcomes of intravitreal bevacizumab therapy for subretinal neovascularization secondary to idiopathic macular telangiectasia type 2. Retina 36(11):2150–2157
Mandal S, Venkatesh P, Abbas Z, Vohra R, Garg S (2007) Intravitreal bevacizumab (Avastin) for subretinal neovascularization secondary to type 2A idiopathic juxtafoveal telangiectasia. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 245(12):1825–1829
Potter MJ, Szabo SM, Chan EY, Morris AHC (2002) Photodynamic therapy of a subretinal neovascular membrane in type 2A idiopathic juxtafoveolar retinal telangiectasis. Am J Ophthalmol 133(1):149–151
Smithen LM, Spaide RF (2004) Photodynamic therapy and intravitreal triamcinolone for a subretinal neovascularization in bilateral idiopathic juxtafoveal telangiectasis. Am J Ophthalmol 138(5):884–885
Park DW, Schatz H, McDonald HR, Johnson RN (1997) Grid laser photocoagulation for macular edema in bilateral juxtafoveal telangiectasis. Ophthalmology 10:1838–1846
Shukla D, Singh J, Kolluru CM, Kim R, Namperumalsamy P (2004) Transpupillary thermotherapy for subfoveal neovascularization secondary to group 2A idiopathic juxtafoveolar telangiectasis. Am J Ophthalmol 138(1):147–149
Berger AS, McCuen BW II, Brown GC, Brownlow RL (2004) Surgical Removal of subfoveal neovascular membrane in type 2A idiopathic juxtafoveolar retinal telangiectasis. Am J Ophthalmol 137:812–819
Stuart A, Ford JA, Duckworth S, Jones C, Pereira A (2015) Anti-VEGF therapies in the treatment of choroidal neovascularisation secondary to on-age-related macular degeneration: a systematic review. BMJ Open 5:e00776
Jorge R, Costa RA, Calucci D, Scott IU (2007) Intravitreal bevacizumab (Avastin) associated with the regression of subretinal neovascularization in idiopathic juxtafoveolar retinal telangiectasis. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 245(7):1045–1048
Konstantinidis L, Mantel I, Zografos L, Ambresin A (2009) Intravitreal ranibizumab as primary treatment for neovascular membrane associated with idiopathic juxtafoveal retinal telangiectasia. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 247:1567–1569
Mavrakanas N, Mendrinos E, Pournaras CJ, Salzmann J (2009) Intravitreal ranibizumab and bevacizumab for bilateral subretinal neovascularization secondary to idiopathic juxtafoveal telangiectasia type 2A. Acta Ophthalmol 87(8):930–932
Narayanan R, Chhablani J, Sinha M et al (2012) Efficacy of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy in subretinal neovascularization secondary to macular telangiectasia type 2. Retina 32(10):2001–2005
Roller AB, Folk JC, Patel NM et al (2011) Intravitreal bevacizumab for treatment of proliferative and nonproliferative type 2 idiopathic macular telangiectasia. Retina 31(9):1848–1855
Rishi P, Shroff D, Rishi E (2008) Combined photodynamic therapy and intravitreal ranibizumab as primary treatment for subretinal neovascular membrane (SRNVM) associated with type 2 idiopathic macular telangiectasia. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 246(4):619–621
Charbel Issa P, Finger RP, Kruse K, Baumuller S, Scholl HPN, Holz FG (2011) Monthly ranibizumab for nonproliferative macular telangiectasia type 2: a 12-month prospective study. Am J Ophthalmol 151(5):876–886
Do DV, Bressler SB, Cassard SD et al (2014) Ranibizumab for macular telangiectasia type 2 in the absence of subretinal neovascularization. Retina 34(10):2063–2071
Kupitz EH, Heeren TFC, Holz FG, Charbel Issa P (2015) Poor long-term outcome of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy in nonproliferative macular telangiectasia type 2. Retina 35(12):2619–2626
Kovach JL, Rosenfeld PJ (2009) Bevacizumab (avastin) therapy for idiopathic macular telangiectasia type II. Retina 29(1):27–32
Gamulescu M-A, Walter A, Sachs H, Helbig H (2008) Bevacizumab in the treatment of idiopathic macular telangiectasia. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 246(8):1189–1193
Meyer-ter-Vehn T, Herzog S, Schargus M, Gobel W, Guthoff R (2013) Long-term course in type 2 idiopathic macular telangiectasia. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 251(11):2513–2520
Veloso CE, Vianna RN, Pelayes DE, Nehemy MB (2013) Intravitreal bevacizumab for type 2 idiopathic macular telangiectasia. Ophthalmic Res 49(4):205–208
Kupitz EH, Heeren TF, Holz FG, Charbel Issa P (2015) Poor long-term outcome of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy in nonproliferative macular telangiectasia type 2. Retina 35:2619–2626
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
Data collection was conducted in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barth, T., Zeman, F., Helbig, H. et al. Intravitreal anti-VEGF treatment for subretinal neovascularisation secondary to type 2 idiopathic juxtafoveolar telangiectasia. Int Ophthalmol 38, 191–198 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-017-0447-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-017-0447-0