Abstract
Objective and design
The antinociception induced by the intraperitoneal coadministration in mice of combinations of metamizol and paracetamol was evaluated in the tail flick test and orofacial formalin test.
Methods
The antinociception of each drugs alone and the interaction of the combinations was evaluated by isobolographic analysis in the tail-flick and in the formalin orofacial assay of mice.
Results
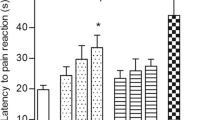
Mice pretreated with the drugs demonstrated that the antinociception of metamizol and paracetamol is dose-dependent. The potency range on the antinocifensive responses for metamizol or paracetamol was as follows: orofacial (Phase II) > orofacial (Phase I) > tail flick. In addition, the coadministration of metamizol with paracetamol induced a strong synergistic antinociception in the algesiometer assays. Both drugs showed effectiveness in inflammatory pain.
Conclusion
These actions can be related to the differential selectivity of the drugs for inhibition of COX isoforms and also to the several additional antinociception mechanisms and pathways initiated by the analgesic drugs on pain transmission. Since the efficacy of the combination of metamizol with paracetamol has been demonstrated in the present study, this association could have a potential beneficial effect on the pharmacological treatment of clinical pain.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbadie C, Besson JM (1994) Chronic treatments with aspirin or acetaminophen reduce both the development of polyarthritis and Fos-like immunoreactivity in rat lumbar spinal cord. Pain 57:45–54
Ayoub SS, Colville-Nash PR, Willoughby DA, Botting RM (2006) The involvement of a cyclooxygenase 1 gene-derived protein in the antinociceptive action of paracetamol in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 538:57–65
Barrera NP, Morales B, Torres S, Villalón M (2005) Principles: mechanisms and modeling of synergism in cellular responses. Trends Pharmacol Sci 26:526–532
Beirith A, Santos AR, Rodrígues AL et al (1998) Spinal and supraspinal antinociceptive action of metamizol in formalin, capsaicin and glutamate tests. Study of mechanism of action. Eur J Pharmacol 345:233–245
Bertolini A, Ferrari A, Ottani A et al (2006) Paracetamol: new vistas of an old drug. CNS Drug Rev 12:250–275
Botting R (2003) COX-1 and COX-3 inhibitors. Thrombosis Res 110:269–272
Boutaud O, Aronoff DM, Richardson JH, Marnett LJ, Oates JA (2002) Determinants of the cellular specificity of acetaminophen as an inhibitor of prostaglandin H2 synthases. PNAS 99:7130–7135
Chandrasekharan NV, Dai H, Roos LT et al (2002) COX-3, a cyclooxygenase-1 variant inhibited by acetaminophen and other analgesic/antipyretic drugs: cloning, structure and expression. Proc Nat Acad Sci 99:13926–13931
Chou TC (2006) Theoretical basis, experimental design, and computerized simulation of synergism and antagonism in drug combination studies. Pharmacol Rev 58:621–681
Gelgor L, Cartmell S, Mitchell D (1992) Intracerebroventricular micro-injections of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs abolish reperfusion hyperalgesia in the rat’s tail. Pain 50:323–329
Godfrey L, Bailey I, Toms NJ et al (2007) Paracetamol inhibits nitric oxide synthesis in murine spinal cord slices. Eur J Pharmacol 562:68–71
Hernández N, Vanegas H (2001) Antinociception induced by PAG-microinjected metamizol (metamizol) in rats: involvement of spinal endogenous opioids. Brain Res 896:175–178
Hinz B, Cheremina O, Bachmakov J et al (2007a) Metamizol elicits substantial inhibition of peripheral cyclooxygenases in humans: new insights into the pharmacology of an old analgesic. FASEB J 21:2343–2351
Hinz B, Cheremina O, Bachmakov J et al (2007b) Acetaminophen (paracetamol) is a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor in man. FASEB J 22:383–390
Kolesnikov YA, Wilson RS, Pasternak GW (2003) Synergistic analgesic interactions between hydrocodone and ibuprofen. Anesth Analg 97:1721–1723
Lokken P, Skjelbred P (1980) Analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of paracetamol evaluated by bilateral oral surgery. Br J Clin Pharmacol 10(Suppl 2):253–260
Lorenzetti BB, Ferreira SH (1985) Mode of analgesic action of metamizol: direct antagonism of inflammatory hyperalgesia. Eur J Pharmacol 114:375–381
Luccarini P, Childeric A, Gayder AM et al (2006) The orofacial formalin test in the mouse: a behavioral model for studying physiology and modulation of trigeminal nociception. Pain 7:908–914
Miranda HF, Puig MM, Prieto JC, Pinardi G (2006) Synergism between paracetamol and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in experimental acute pain. Pain 121:22–28
Miranda HF, Puig MM, Dursteler C, Prieto JC, Pinardi G (2007) Dexketoprofen-induced antinociception in animal models of acute pain: synergy with morphine and paracetamol. Neuropharmacology 52:291–296
Ortiz MI, Castañeda-Hernández G, Granados-Soto V (2003) Possible involvement of potassium channels in peripheral antinociception induced by metamizol: lack of participation of ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 74:465–470
Pierre SC, Schmidt R, Brenneis C, Michaelis M, Geisslinger G, Scholich K (2007) Inhibition of cyclooxygenases dy dipirone. Br J Pharmacol 151:494–503
Pini LA, Vitale G, Ottani A, Sandrini M (1997) Naloxone-reversible antinociception by paracetamol in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 280:934–940
Qiu HX, Liu J, Kong H et al (2007) Isobolographic analysis of the antinociceptive interactions between ketoprofen and paracetamol. Eur J Pharmacol 557:141–146
Raboisson P, Dallel R (2004) The orofacial formalin test. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 28:219–226
Schug SA (2006) Combination analgesia in 2005—a rational approach: focus on paracetamol-tramadol. Clin Rheumatol 25(Suppl 1):S16–S21
Schug SA, Manopas A (2007) Update on the role of non-opioids for postoperative pain treatment. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol 21:15–30
Seideman P (1993) Additive effect of combined naproxen and paracetamol in rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol 32:1077–1082
Shimada SG, Otterness IG, Stitt JT (1994) A study of the mechanism of action of the mild analgesic metamizol. Agents Actions 41:188–192
Tallarida RJ (2000) Drug synergism and dose-effect data analysis. Chapman & Hall, Boca Raton, pp 59–63
Vinegar R, Truax JF, Selph JL (1976) Quantitative comparison of the analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities of aspirin, phenacetin and acetaminophen in rodents. Eur J Pharmacol 37:23–30
Warner TD, Mitchell JA (2004) Cyclooxygenases: new forms, new inhibitors, and lessons from the clinic. FASEB J 18:790–804
Zelcer S, Kolesnikov Y, Kovalyshyn I et al (2005) Selective potentiation of opioid analgesia by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Brain Res 1040:151–156
Acknowledgments
The expert technical assistance of José López and Alejandro Correa is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muñoz, J., Navarro, C., Noriega, V. et al. Synergism between COX-3 inhibitors in two animal models of pain. Inflammopharmacol 18, 65–71 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-009-0019-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-009-0019-7