Abstract
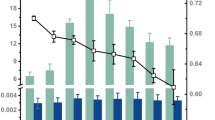
Microbial-driven biogeochemical cycles in wetlands impacted by global warming pose a potential downstream eutrophication risk. However, the consequences of ongoing warming on the functional and metabolic potential of sediment microbial communities are largely unknown. We incubated sediment samples under both ambient temperature conditions (control) and simulated warming conditions of 5°C above ambient temperature (warmed) using a novel field microcosm system. In warmed samples, we observed in situ a decreased thickness of the oxidized sediment layer and associated lower sediment redox potential. GeoChip 4.0, a comprehensive functional gene microarray, demonstrated that many functional genes that are involved in oxidation–reduction reactions and in phosphorus (P) degradation were preferentially enriched under warming conditions. The enriched genes included those genes encoding carbon monoxide dehydrogenase, acetyl-CoA carboxylase biotin carboxylase (ppc), and ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase (Rubisco) for carbon fixation; nitrate reductases (narG) and nitrous oxide reductases (nosZ) for denitrification; cytochrome c for metal reduction; and exopolyphosphatase (ppx) for polyphosphate degradation. The redox potential was one of the most significant parameters linked to microbial functional gene structure. These results demonstrate that the enhanced hypoxia and anaerobic metabolic pathways accelerated sediment P mobilization in freshwater wetland subject to warming, raising the potential of water eutrophication.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achtnich, C., F. Bak & R. Conrad, 1995. Competition for electron-donors among nitrate reducers, ferric iron reducers, sulfate reducers, and methanogens in anoxic paddy soil. Biology and Fertility of Soils 19(1): 65–72.
Allison, S. D. & K. K. Treseder, 2008. Warming and drying suppress microbial activity and carbon cycling in boreal forest soils. Global Change Biology 14(12): 2898–2909.
Angel, R., P. Claus & R. Conrad, 2012. Methanogenic archaea are globally ubiquitous in aerated soils and become active under wet anoxic conditions. ISME Journal 6(4): 847–862.
Bond-Lamberty, B. & A. Thomson, 2010. Temperature-associated increases in the global soil respiration record. Nature 464(7288): U132–U579.
Borcard, D., P. Legendre & P. Drapeau, 1992. Partialling out the spatial component of ecological variation. Ecology 73(3): 1045–1055.
Bradford, M. A., C. A. Davies, S. D. Frey, T. R. Maddox, J. M. Melillo, J. E. Mohan, J. F. Reynolds, K. K. Treseder & M. D. Wallenstein, 2008. Thermal adaptation of soil microbial respiration to elevated temperature. Ecology Letters 11(12): 1316–1327.
Brown, J. H., J. F. Gillooly, A. P. Allen, V. M. Savage & G. B. West, 2004. Toward a metabolic theory of ecology. Ecology 85(7): 1771–1789.
Brune, A., P. Frenzel & H. Cypionka, 2000. Life at the oxic-anoxic interface: microbial activities and adaptations. FEMS Microbiology Reviews 24(5): 691–710.
Cheng, W. G., H. Sakai, M. Matsushima, K. Yagi & T. Hasegawa, 2010. Response of the floating aquatic fern Azolla filiculoides to elevated CO2, temperature, and phosphorus levels. Hydrobiologia 656(1): 5–14.
Conley, D. J., S. Bjorck, E. Bonsdorff, J. Carstensen, G. Destouni, B. G. Gustafsson, S. Hietanen, M. Kortekaas, H. Kuosa, H. E. M. Meier, B. Muller-Karulis, K. Nordberg, A. Norkko, G. Nurnberg, H. Pitkanen, N. N. Rabalais, R. Rosenberg, O. P. Savchuk, C. P. Slomp, M. Voss, F. Wulff & L. Zillen, 2009. Hypoxia-related processes in the Baltic Sea. Environmental Science and Technology 43(10): 3412–3420.
Cypionka, H., 1994. Novel metabolic capacities of sulfate-reducing bacteria, and their activities in microbial mats. In Stal, L. J. & P. Caumette (eds), Microbial Mats. Springer Verlag, Berlin: 367–376.
Diaz, R. J. & R. Rosenberg, 2008. Spreading dead zones and consequences for marine ecosystems. Science 321(5891): 926–929.
Feuchtmayr, H., R. Moran, K. Hatton, L. Connor, T. Heyes, B. Moss, I. Harvey & D. Atkinson, 2009. Global warming and eutrophication: effects on water chemistry and autotrophic communities in experimental hypertrophic shallow lake mesocosms. Journal of Applied Ecology 46(3): 713–723.
Fierer, N., J. W. Leff, B. J. Adams, U. N. Nielsen, S. T. Bates, C. L. Lauber, S. Owens, J. A. Gilbert, D. H. Wall & J. G. Caporaso, 2012. Cross-biome metagenomic analyses of soil microbial communities and their functional attributes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 109(52): 21390–21395.
Fierer, N., J. Ladau, J. C. Clemente, J. W. Leff, S. M. Owens, K. S. Pollard, R. Knight, J. A. Gilbert & R. L. McCulley, 2013. Reconstructing the microbial diversity and function of pre-agricultural tallgrass prairie soils in the United States. Science 342(6158): 621–624.
Frostegard, A., A. Tunlid & E. Baath, 2011. Use and misuse of PLFA measurements in soils. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 43(8): 1621–1625.
Gilbert, J. A., D. Field, Y. Huang, R. Edwards, W. Z. Li, P. Gilna & I. Joint, 2008. Detection of large numbers of novel sequences in the metatranscriptomes of complex marine microbial communities. PLoS One 3(8). Doi:10.1371/Journal.Pone.0003042.
Goericke, R., 2002. Bacteriochlorophyll a in the ocean: is anoxygenic bacterial photosynthesis important? Limnology and Oceanography 47(1): 290–295.
Gudasz, C., D. Bastviken, K. Steger, K. Premke, S. Sobek & L. J. Tranvik, 2010. Temperature-controlled organic carbon mineralization in lake sediments. Nature 466(7305): U3–U478.
Hazen, T. C., E. A. Dubinsky, T. Z. DeSantis, G. L. Andersen, Y. M. Piceno, N. Singh, J. K. Jansson, A. Probst, S. E. Borglin, J. L. Fortney, W. T. Stringfellow, M. Bill, M. E. Conrad, L. M. Tom, K. L. Chavarria, T. R. Alusi, R. Lamendella, D. C. Joyner, C. Spier, J. Baelum, M. Auer, M. L. Zemla, R. Chakraborty, E. L. Sonnenthal, P. D’haeseleer, H. Y. N. Holman, S. Osman, Z. M. Lu, J. D. Van Nostrand, Y. Deng, J. Z. Zhou & O. U. Mason, 2010. Deep-sea oil plume enriches indigenous oil-degrading bacteria. Science 330(6001): 204–208.
He, Z. L., Y. Deng, J. D. Van Nostrand, Q. C. Tu, M. Y. Xu, C. L. Hemme, X. Y. Li, L. Y. Wu, T. J. Gentry, Y. F. Yin, J. Liebich, T. C. Hazen & J. Z. Zhou, 2010. GeoChip 3.0 as a high-throughput tool for analyzing microbial community composition, structure and functional activity. ISME Journal 4(9): 1167–1179.
Henderson, R., N. Kabengi, N. Mantripragada, M. Cabrera, S. Hassan & A. Thompson, 2012. Anoxia-induced release of colloid- and nanoparticle-bound phosphorus in grassland soils. Environmental Science and Technology 46(21): 11727–11734.
Himmelheber, D. W., S. H. Thomas, F. E. Loffler, M. Taillefert & J. B. Hughes, 2009. Microbial colonization of an in situ sediment cap and correlation to stratified redox zones. Environmental Science and Technology 43(1): 66–74.
Hui, D. F., M. A. Mayes & G. S. Wang, 2013. Kinetic parameters of phosphatase: a quantitative synthesis. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 65: 105–113.
Hupfer, M. & J. Lewandowski, 2008. Oxygen controls the phosphorus release from lake sediments: a long-lasting paradigm in limnology. International Review of Hydrobiology 93(4–5): 415–432.
Hupfer, M., S. Gloess & H. P. Grossart, 2007. Polyphosphate-accumulating microorganisms in aquatic sediments. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 47(3): 299–311.
Jensen, H. S. & F. O. Andersen, 1992. Importance of temperature, nitrate, and pH for phosphate release from aerobic sediments of four shallow, eutrophic lakes. Limnology and Oceanography 37(3): 577–589.
Jerman, V., M. Metje, I. Mandic-Mulec & P. Frenzel, 2009. Wetland restoration and methanogenesis: the activity of microbial populations and competition for substrates at different temperatures. Biogeosciences 6(6): 1127–1138.
Kleeberg, A., C. Herzog & M. Hupfer, 2013. Redox sensitivity of iron in phosphorus binding does not impede lake restoration. Water Research 47(3): 1491–1502.
Korosi, J. B., B. K. Ginn, B. F. Cumming & J. P. Smol, 2013. Establishing past environmental conditions and tracking long-term environmental change in the Canadian Maritime provinces using lake sediments. Environmental Reviews 21(1): 15–27.
Lepš, J. & P. Šmilauer, 2003. Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data Using CANOCO. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Liang, Y. T., J. D. Van Nostrand, L. A. N’Guessan, A. D. Peacock, Y. Deng, P. E. Long, C. T. Resch, L. Y. Wu, Z. L. He, G. H. Li, T. C. Hazen, D. R. Lovley & J. Z. Zhou, 2012. Microbial functional gene diversity with a shift of subsurface redox conditions during in situ uranium reduction. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 78(8): 2966–2972.
Liu, M., Z. J. Zhang, Q. He, H. Wang, X. Li & J. Schoer, 2014. Exogenous phosphorus inputs alter complexity of soil-dissolved organic carbon in agricultural riparian wetlands. Chemosphere 95: 572–580.
Lovley, D. R., S. J. Giovannoni, D. C. White, J. E. Champine, E. J. P. Phillips, Y. A. Gorby & S. Goodwin, 1993. Geobacter-metallireducens gen-nov sp-nov, a microorganism capable of coupling the complete oxidation of organic-compounds to the reduction of iron and other metals. Archives of Microbiology 159(4): 336–344.
Lu, Z. M., Y. Deng, J. D. Van Nostrand, Z. L. He, J. Voordeckers, A. F. Zhou, Y. J. Lee, O. U. Mason, E. A. Dubinsky, K. L. Chavarria, L. M. Tom, J. L. Fortney, R. Lamendella, J. K. Jansson, P. D’haeseleer, T. C. Hazen & J. Z. Zhou, 2012. Microbial gene functions enriched in the deepwater horizon deep-sea oil plume. ISME Journal 6(2): 451–460.
Martins, G., A. Terada, D. C. Ribeiro, A. M. Corral, A. G. Brito, B. F. Smets & R. Nogueira, 2011. Structure and activity of lacustrine sediment bacteria involved in nutrient and iron cycles. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 77(3): 666–679.
Murphy, J. & J. P. Riley, 1962. A modified single solution method for determination of phosphate in natural waters. Analytica Chimica Acta 26(1): 31–36.
Nurnberg, G. K., L. A. Molot, E. O’Connor, H. Jarjanazi, J. Winter & J. Young, 2013. Evidence for internal phosphorus loading, hypoxia and effects on phytoplankton in partially polymictic Lake Simcoe, Ontario. Journal of Great Lakes Research 39(2): 259–270.
Penn, M. R., M. T. Auer, S. M. Doerr, C. T. Driscoll, C. M. Brooks & S. W. Effler, 2000. Seasonality in phosphorus release rates from the sediments of a hypereutrophic lake under a matrix of pH and redox conditions. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 57(5): 1033–1041.
Rabenhorst, M. C. & K. L. Castenson, 2005. Temperature effects on iron reduction in a hydric soil. Soil Science 170(9): 734–742.
Reddy, K. R., E. M. D’angelo & W. G. Harris, 1998. Biogeochemistry of wetlands. In Summer, M. E. (ed.), Handbook of Soil Science. CRC Press, Boca Raton: 89–119.
Reeve, J. R., C. W. Schadt, L. Carpenter-Boggs, S. Kang, J. Z. Zhou & J. P. Reganold, 2010. Effects of soil type and farm management on soil ecological functional genes and microbial activities. ISME Journal 4(9): 1099–1107.
Reitzel, K., J. Ahlgren, H. DeBrabandere, M. Waldeback, A. Gogoll, L. Tranvik & E. Rydin, 2007. Degradation rates of organic phosphorus in lake sediment. Biogeochemistry 82(1): 15–28.
Sanz-Lazaro, C., T. Valdemarsen, A. Marin & M. Holmer, 2011. Effect of temperature on biogeochemistry of marine organic-enriched systems: implications in a global warming scenario. Ecological Applications 21(7): 2664–2677.
Smayda, T. J., 2005. Benthic phosphorus release from sediment to water. In Wassmann, P. & K. Olli (eds), Drainage Basin Nutrient Inputs and Eutrophication: An Integrated Approach. Univ Tromsoe, Norway, http://www.ut.ee/~olli/eutr/.
Solomon, S., D. Qin, M. Manning, Z. Chen, M. Marquis, K. B. Averyt, M. Tignor, & H. L. Miller, 2007. Climate change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the IPCC. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Sondergaard, M., J. P. Jensen & E. Jeppesen, 2003. Role of sediment and internal loading of phosphorus in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 506(1–3): 135–145.
Vaughan, K. L., M. C. Rabenhorst & B. A. Needelman, 2009. Saturation and temperature effects on the development of reducing conditions in soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal 73(2): 663–667.
Verhoeven, J. T. A., B. Arheimer, C. Q. Yin & M. M. Hefting, 2006. Regional and global concerns over wetlands and water quality. Trends in Ecology and Evolution 21(2): 96–103.
Vuillemin, A., D. Ariztegui & P. S. Team, 2013. Geomicrobiological investigations in subsaline maar lake sediments over the last 1500 years. Quaternary Science Reviews 71: 119–130.
Wang, H., Z. L. He, Z. M. Lu, J. Z. Zhou, J. D. Van Nostrand, X. H. Xu & Z. J. Zhang, 2012. Genetic linkage of soil carbon pools and microbial functions in subtropical freshwater wetlands in response to experimental warming. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 78(21): 7652–7661.
Wang, H., J. Holden, K. Spera, X. H. Xu, Z. D. Wang, J. H. Luan, X. Xu & Z. J. Zhang, 2013. Phosphorus fluxes at the sediment-water interface in subtropical wetlands subjected to experimental warming: a microcosm study. Chemosphere 90(6): 1794–1804.
Wang, Z. D., J. X. Yao, S. A. Li, J. Y. Zhang, J. J. Li, X. Y. Lin & Z. J. Zhang, 2010. Spatial status and retention potential of phosphorus in riparian wetlands of the Southern Taihu Basin, China. Wetlands 30(1): 149–157.
Weedon, J. T., R. Aerts, G. A. Kowalchuk, R. van Logtestijn, D. Andringa & P. M. van Bodegom, 2013. Temperature sensitivity of peatland C and N cycling: does substrate supply play a role? Soil Biology and Biochemistry 61: 109–120.
Wei, F., 2002. Water and Wastewater Monitoring and Analysis. Environmental Science Press, Beijing.
Yergeau, E., S. Bokhorst, S. Kang, J. Z. Zhou, C. W. Greer, R. Aerts & G. A. Kowalchuk, 2012. Shifts in soil microorganisms in response to warming are consistent across a range of Antarctic environments. ISME Journal 6(3): 692–702.
Zhang, Z. J., Z. D. Wang, J. Holden, X. H. Xu, H. Wang, J. H. Ruan & X. Xu, 2012. The release of phosphorus from sediment into water in subtropical wetlands: a warming microcosm experiment. Hydrological Processes 26(1): 15–26.
Zhou, J. Z., K. Xue, J. P. Xie, Y. Deng, L. Y. Wu, X. H. Cheng, S. F. Fei, S. P. Deng, Z. L. He, J. D. Van Nostrand & Y. Q. Luo, 2012. Microbial mediation of carbon-cycle feedbacks to climate warming. Nature Climate Change 2(2): 106–110.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41373074), National Ministry of Science and Technology (2013GB23600658), and National Ministry of Water Resources (201301092). This work was also partially supported by the United States Department of Energy, Biological Systems Research on the Role of Microbial Communities in Carbon Cycling Program (DE-SC0004601), and the Oklahoma Bioenergy Center (OBC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Handling editor: Stefano Amalfitano
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Wang, H., Zhou, J. et al. Redox potential and microbial functional gene diversity in wetland sediments under simulated warming conditions: implications for phosphorus mobilization. Hydrobiologia 743, 221–235 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-014-2039-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-014-2039-6