Abstract
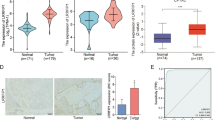
APE1 is a multifunctional protein that plays important roles in cancer development. However, the association between APE1 expression and the clinicopathological parameters of HCC patients has not been fully characterized. In this study, bioinformatics analysis of APE1 was performed in several databases, including the TCGA, GeneCard, Human Protein Atlas and Ualcan databases. The relationship between APE1 mRNA expression and several attributes of liver cancer patients in TCGA was investigated. Then, the protein expression of APE1 was detected by IHC analysis in 95 HCC samples and the association between APE1 expression and the clinicopathological parameters of HCC patients was explored. GSEA-KEGG analysis was performed to predict the potential signaling pathways that associated with APE1 expression. Then the siRNA-mediated knockdown model of APE1 was constructed in HCC cell line to further detect the detailed function of APE1 in HCC development in vitro and in vivo. The results of the bioinformatics analysis showed that APE1 expression was primarily located in the cell nucleus. APE1 mRNA expression was substantially correlated with pathological grade and T status in TCGA database. Elevated APE1 expression was observed in HCC samples and was associated with unfavorable survival time in liver cancer patients. IHC data demonstrated that the nuclear expression of APE1 in HCC tissues was significantly higher than that in noncancerous tissues. The expression level of the APE1 protein in HCC was strongly associated with tumor diameter and overall survival. Survival analysis indicated that APE1 nuclear expression is an independent prognostic marker for the overall survival of HCC patients. GSEA-KEGG results confirmed that APE1 associated with the base excision repair signaling pathway. The data of phenotypic experiments indicated that APE1 remarkably promoted tumor growth both in HCC cells and xenografts. The findings firstly imply that nuclear expression of APE1 is a valuable prognostic marker for HCC. APE1 significantly facilitate HCC development and targeting APE1 may be a promising strategy for HCC treatment.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allemani C et al (2018) Global surveillance of trends in cancer survival 2000–2014 (CONCORD-3): analysis of individual records for 37 513 025 patients diagnosed with one of 18 cancers from 322 population-based registries in 71 countries. Lancet 391:1023–1075. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(17)33326-3
Bhat AA, Lu H, Soutto M, Capobianco A, Rai P, Zaika A, El-Rifai W (2018) Exposure of Barrett’s and esophageal adenocarcinoma cells to bile acids activates EGFR-STAT3 signaling axis via induction of APE1. Oncogene 37:6011–6024. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0388-8
Biswas A, Khanna S, Roy S, Pan X, Sen CK, Gordillo GM (2015) Endothelial cell tumor growth is Ape/ref-1 dependent. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 309:C296-307. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00022.2015
Chen S et al (2017) SESN2 correlates with advantageous prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Diagn Pathol 12:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13000-016-0591-2
Choi S, Joo HK, Jeon BH (2016a) Dynamic regulation of APE1/Ref-1 as a therapeutic target protein. Chonnam Med J 52:75–80. https://doi.org/10.4068/cmj.2016.52.2.75
Choi S et al (2016b) Urinary APE1/Ref-1: a potential bladder cancer biomarker. Dis Mark 2016:7276502. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/7276502
Cun Y et al (2013) Silencing of APE1 enhances sensitivity of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells to radiotherapy in vitro and in a xenograft model. PLoS ONE 8:e55313. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0055313
Di Maso V et al (2007) Subcellular localization of APE1/Ref-1 in human hepatocellular carcinoma: possible prognostic significance. Mol Med 13:89–96. https://doi.org/10.2119/2006-00084.DiMaso
Hsia KT et al (2016) Impact of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1/redox factor-1 on treatment response and survival in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 38:550–559. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.23927
Hua F, Liu S, Zhu L, Ma N, Jiang S, Yang J (2017) Highly expressed long non-coding RNA NNT-AS1 promotes cell proliferation and invasion through Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in cervical cancer. Biomed Pharmacother 92:1128–1134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.03.057
Jia L et al (2019) Translation elongation factor eEF1Balpha is identified as a novel prognostic marker of gastric cancer. Int J Biol Macromol 126:345–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.12.126
Jiang S et al (2015a) Ape1 regulates WNT/beta-catenin signaling through its redox functional domain in pancreatic cancer cells. Int J Oncol 47:610–620. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2015.3048
Jiang X et al (2015b) Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 regulates angiogenesis in a transforming growth factor beta-dependent manner in human osteosarcoma. Cancer Sci 106:1394–1401. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.12763
Jin J et al (2017) Application of AFP whole blood one-step rapid detection kit in screening for HCC in Qidong. Am J Cancer Res 7:1384–1388
Kan G, Dong W (2015) The expression of PD-L1 APE1 and P53 in hepatocellular carcinoma and its relationship to clinical pathology. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 19:3063–3071
Kim HB, Cho WJ, Choi NG, Kim SS, Park JH, Lee HJ, Park SG (2017) Clinical implications of APEX1 and Jagged1 as chemoresistance factors in biliary tract cancer. Ann Surg Treat Res 92:15–22. https://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2017.92.1.15
Kulik L, El-Serag HB (2019) Epidemiology and management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 156(477–491):e471. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2018.08.065
Kumar KJS, Wang SH, Tseng YH, Tsao NW, Kuo YH, Wang SY (2018) Trans-3-Methoxy-5-hydroxystilbene (MHS) from the rhizome of Alpinia nantonensis inhibits metastasis in human lung cancer cells. Phytomedicine 50:223–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2018.04.010
Lei Y et al (2020) Inhibition of MGMT-mediated autophagy suppression decreases cisplatin chemosensitivity in gastric cancer. Biomed Pharmacother 125:109896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.109896
Li D, Sedano S, Allen R, Gong J, Cho M, Sharma S (2019) Current treatment landscape for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: patient outcomes and the impact on quality of life. Cancers. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11060841
Lin F et al (2017) Thioredoxin-1 promotes colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis through crosstalk with S100P. Cancer Lett 401:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2017.04.036
Mol CD, Izumi T, Mitra S, Tainer JA (2000) DNA-bound structures and mutants reveal abasic DNA binding by APE1 and DNA repair coordination [corrected]. Nature 403:451–456. https://doi.org/10.1038/35000249
Qing Y et al (2015) Upregulation of PD-L1 and APE1 is associated with tumorigenesis and poor prognosis of gastric cancer. Drug Des Dev Ther 9:901–909. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S75152
Santana T, Sa MC, de Moura SE, Galvao HC, Coletta RD, Freitas RA (2017) DNA base excision repair proteins APE-1 and XRCC-1 are overexpressed in oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med 46:496–503. https://doi.org/10.1111/jop.12529
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2019) Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin 69:7–34. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21551
Sun Z, Zhu Y, Aminbuhe FQ, Peng J, Zhang N (2018) Differential expression of APE1 in hepatocellular carcinoma and the effects on proliferation and apoptosis of cancer cells. Biosci Trends 12:456–462. https://doi.org/10.5582/bst.2018.01239
Tell G, Damante G, Caldwell D, Kelley MR (2005) The intracellular localization of APE1/Ref-1: more than a passive phenomenon? Antioxid Redox Signal 7:367–384. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2005.7.367
Tell G, Quadrifoglio F, Tiribelli C, Kelley MR (2009) The many functions of APE1/Ref-1: not only a DNA repair enzyme. Antioxid Redox Signal 11:601–620. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2008.2194
Wen X et al (2016) APE1 overexpression promotes the progression of ovarian cancer and serves as a potential therapeutic target. Cancer Biomark 17:313–322. https://doi.org/10.3233/CBM-160643
Woo J, Park H, Sung SH, Moon BI, Suh H, Lim W (2014) Prognostic value of human apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 (APE1) expression in breast cancer. PLoS ONE 9:e99528. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0099528
Zheng ZH, Du W, Li YJ, Gao MQ, Huang AM, Liu JF (2015) Lentiviral-mediated short hairpin RNA silencing of APE1 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and migration: a potential therapeutic target for hepatoma treatment. Oncol Rep 34:95–102. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2015.3976
Acknowledgement
This study is supported by the grant from the Nantong Basic Science Research Project (No. JC2018138).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10735_2020_9939_MOESM1_ESM.png
Supplementary Figure S1. Protein interaction network construction. The predicted protein interactome of APE1 was extracted and analyzed in the STRING 10.5 database. This protein interaction network was constructed by Cytoscape 3.61. The protein encoded by APE1 is colored by red square, and the other neighboring proteins are shown by other colorful ellipses. Pearson's correlation analysis was performed in matched samples (linear regression analysis), and Pearson's correlation coefficients (R) are demonstrated in each plot. APE1 expression was positively correlated with the expression of PRMT5 (r = 0.72), TIMM9 (r = 0.72), DHX9 (r = 0.72), CHD8 (r = 0.73), SUPT16H (r = 0.82) and HNRNPC (r = 0.74). (PNG 181 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, X., Zhao, H., Yuan, H. et al. High nuclear expression of APE1 correlates with unfavorable prognosis and promotes tumor growth in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Mol Histol 52, 219–231 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-020-09939-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-020-09939-9