Abstract
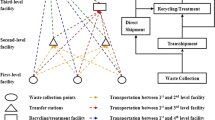
With the rapid development of population and urbanization, municipal solid waste (MSW) management has become an urgent problem in city sustainable management. Since the MSW transportation cost is the largest part in the MSW management in China, the optimization location study of MSW transfer station is necessary for the MSW management. Considering the dynamic characteristics of MSW generation, a MSW transfer station location model with dynamic capacity constraints is established to obtain the integrated strategic and tactical decisions for MSW transfer station location problem. Since it is a NP-Hard problem, the genetic algorithm is applied to solve the model. Taking 76 MSW collection points in the Huangshi as a case study, integrated dynamic MSW transfer station location decisions in three periods are studied. The integrated strategic and tactical decisions of 18 MSW transfer station are obtained. The feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed model are verified. In addition, the model not only expands the research field for the MSW transfer station location problem, but also provides reference for the government to design an economical and optimal MSW transportation system.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ardjmand, E., Young, W. A., II., Weckman, G. R., et al. (2016). Applying genetic algorithm to a new bi-objective stochastic model for transportation, location, and allocation of hazardous materials. Expert Systems with Applications, 51, 49–58.
Asefi, H., & Lim, S. (2017). A novel multi-dimensional modeling approach to integrated municipal solid waste management. Journal of Cleaner Production, 166, 1131–1143.
Badran, M. F., & El-Haggar, S. M. (2006). Optimization of municipal solid waste management in Port Said–Egypt. Waste Management, 26(5), 534–545.
Bovea, M. D., Powell, J. C., Gallardo, A., et al. (2007). The role played by environmental factors in the integration of a transfer station in a municipal solid waste management system. Waste Management, 27(4), 545–553.
Carter, C., & Rogers, D. (2008). A framework of sustainable operations management: Moving toward new theory. International Journal of Physical Distribution and Logistics Management, 38(5), 360–387.
Chatzouridis, C., & Komilis, D. (2012). A methodology to optimally site and design municipal solid waste transfer stations using binary programming. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 60, 89–98.
Chen, H. W., & Chang, N. B. (2000). Prediction analysis of solid waste generation based on grey fuzzy dynamic modeling. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 29, 1–18.
Eiselt, H. A., & Marianov, V. (2014). A bi-objective model for the location of landfills for municipal solid waste. European Journal of Operational Research, 235(1), 187–194.
Feng, D., Guihua, N., & Yi, C. (2020). The municipal solid waste generation distribution prediction system based on FIG–GA-SVR model. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management, 22(5), 1352–1369.
Gold, S., Seuring, S., & Beske, P. (2010). Sustainable supply chain management and inter-organizational resources: A literature review. Corporate Social Responsibility & Environmental Management, 17(4), 230–245.
Habibi, F., Asadi, E., Sadjadi, S. J., et al. (2017). A multi-objective robust optimization model for site-selection and capacity allocation of municipal solid waste facilities: A case study in Tehran. Journal of Cleaner Production, 166, 816–834.
Hemmelmayr, V. C., Doerner, K. F., Hartl, R. F., et al. (2013). Models and algorithms for the integrated planning of bin allocation and vehicle routing in solid waste management. Transportation Science, 48(1), 103–120.
Hemmelmayr, V. C., Doerner, K. F., Hartl, R. F., et al. (2014). Models and algorithms for the integrated planning of bin allocation and vehicle routing in solid waste management. Transportation Science, 48(1), 103–120.
Khan, M. M. U. H., Vaezi, M., & Kumar, A. (2018). Optimal siting of solid waste-to-value-added facilities through a GIS-based assessment. Science of the Total Environment, 610, 1065–1075.
Komilis, D. P. (2008). Conceptual modeling to optimize the haul and transfer of municipal solid waste. Waste Management, 28(11), 2355–2365.
Krarup, J., & Pruzan, P. M. (1983). The simple plant location problem: Survey and synthesis. European Journal of Operational Research, 12, 36–81.
Luken, R., & Rompaey, F. V. (2008). Drivers for and barriers to environmentally sound technology adoption by manufacturing plants in nine developing countries. Journal of Cleaner Production, 16, S67–S77.
Lyeme, H. (2012). Optimization of municipal solid waste management system. Lap Lambert Academic Publ.
Nayak, P., Sudheer, K., Rangan, D., & Ramasastri, K. (2004). A neuro-fuzzy computing technique for modeling hydrological time series. Journal of Hydrology, 291(1–2), 52–66.
Or, I., & Curi, K. (1993). Improving the efficiency of the solid waste collection system in Izmir, Turkey, through mathematical programming. Waste Management & Research, 11(4), 297–311.
Rada, E. C., Ragazzi, M., & Fedrizzi, P. (2013). Web-GIS oriented systems viability for municipal solid waste selective collection optimization in developed and transient economies. Waste Management, 33(4), 785–792.
Rong, L., Zhang, C., Jin, D., et al. (2017). Assessment of the potential utilization of municipal solid waste from a closed irregular landfill. Journal of Cleaner Production, 142, 413–419.
Samadder, S. R., Prabhakar, R., Khan, D., et al. (2017). Analysis of the contaminants released from municipal solid waste landfill site: A case study. Science of the Total Environment, 580, 593–601.
Tajbakhsh, A., & Hassini, E. (2015). A data envelopment analysis approach to evaluate sustainability in supply chain networks. Journal of Cleaner Production, 105, 74–85.
Tavares, G., Zsigraiova, Z., Semiao, V., et al. (2009). Optimisation of MSW collection routes for minimum fuel consumption using 3D GIS modelling. Waste Management, 29(3), 1176–1185.
Wang, K., Zhao, X., Peng, B., & Zeng, Y. (2020). Spatio-temporal pattern and driving factors of municipal solid waste generation in China: New evidence from exploratory spatial data analysis and dynamic spatial models. Journal of Cleaner Production, 270, 121794. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121794
Yadav, P., & Samadder, S. R. (2018). Environmental impact assessment of municipal solid waste management options using life cycle assessment: A case study. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(1), 838–854.
Yadav, V., Karmakar, S., Dikshit, A. K., et al. (2016). A feasibility study for the locations of waste transfer stations in urban centers: A case study on the city of Nashik, India. Journal of Cleaner Production, 126, 191–205.
Yadav, V., Karmakar, S., Dikshit, A. K., et al. (2018). Interval-valued facility location model: An appraisal of municipal solid waste management system. Journal of Cleaner Production, 171, 250–263.
Zurbrugg, C. (2002). Urban solid waste management in low-income countries of Asia how to cope with the garbage crisis. Presented for: Scientific committee on problems of the environment (SCOPE) urban solid waste management review session, Durban, South Africa, 1–13.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Social Science Fund of China (Grant No. 21BGL085).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, F., Chen, Y. Integrated dynamic municipal solid waste transfer station location decision study based on the dynamic MSW generation. Environ Dev Sustain 25, 6033–6047 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-022-02292-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-022-02292-9