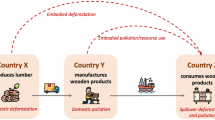
Abstract
In the preceding years, the rapid industrial growth in the BRICS nations has widened the scope for imported technology and other factor inputs. The literature suggests that these kinds of economic developments often exert negative pressure on the established ecosystem. In order to confirm this notion, therefore, in the present study, we examined the impact of import product diversification and import concentration on ecological footprint in the BRICS nations using the annual data ranging from 1995 to 2018. By addressing the possibility of cross-country convergence, the elasticity coefficients are calculated using the cross-sectional augmented autoregressive distributed lag procedure. Industrial value-added, technological innovations and renewable energy solutions are considered as the controlled variables. The empirical results revealed that diversified imports led to an increase in ecological footprints, whereas concentrated imports helped in controlling ecological footprints. As expected, the increased industrial production elevated ecological footprints, whereas the association between renewable energy solutions and ecological footprints is found negative and significant. Based on the association between ecological footprint and its drivers, we endorsed an SDG-based policy framework where interdependency among various SDGs is being considered.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on the request.
Code availability
Data will be made available on the request.
Notes
Using the World Bank’s (2021) database, the above-mentioned figures are calculated by authors’.
References
Afridi, M., Kehelwalatenna, S., Naseem, I., & Tahir, M. (2019). Per capita income, trade openness, urbanization, energy consumption, and CO2 emissions: An empirical study on the SAARC Region. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(29), 29978–29990.
Agence-France-Presse. (2019). Faisalabad, Lahore in top 10 of world's most polluted cities list dominated by India. Dawn, p. https://www.dawn.com/news/1467997.
Agnolucci, P., & Arvanitopoulos, T. (2019). Industrial characteristics and air emissions: Long-term determinants in the UK manufacturing sector. Energy Economics, 78, 546–566.
Ahmad, R., Etudaiye-Muhtar, O., Matemilola, B., & Bany-Ariffin, A. (2016). Financial market development, global financial crisis and economic growth: Evidence from developing nations. Portuguese Economic Journal, 15(3), 199–214.
Ahmed, K., Rehman, M., & Ozturk, I. (2017). What drives carbon dioxide emissions in the long-run? Evidence from selected South Asian Countries. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Review, 70, 1142–1153.
Ali, G., Ashraf, A., Bashir, M., & Cui, S. (2017). Exploring environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) in relation to green revolution: A case study of Pakistan. Environmental Science and Policy, 77, 166–171.
Allard, A., Takman, J., Uddin, G., & Ahmed, A. (2018). The N-shaped environmental Kuznets curve: An empirical evaluation using a panel quantile regression approach. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25, 5848–5861.
Alola, A., Bekun, F., & Sarkodie, S. (2019). Dynamic impact of trade policy, economic growth, fertility rate, renewable and non-renewable energy consumption on ecological footprint in Europe. Science of the Total Environment, 685, 702–709.
Altinoz, B., & Dogan, E. (2021). How renewable energy consumption and natural resource abundance impact environmental degradation? New findings and policy implications from quantile approach. Energy Sources, Part B: Economics, doi:https://doi.org/10.1080/15567249.2021.1885527.
Altıntaş, H., & Kassouri, Y. (2020). Is the environmental Kuznets Curve in Europe related to the per-capita ecological footprint or CO2 emissions? Ecological Indicators. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106187
Amin, A., Dogan, E., & Khan, Z. (2020). The impacts of different proxies for financialization on carbon emissions in top-ten emitter countries. Science of the Total Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140127
Aoyagi, C., & Ganelli, G. (2015). Asia’s quest for inclusive growth revisited. Journal of Asian Economics, 40, 29–46.
Aslan, A., Apergis, N., & Topcu, M. (2014). Banking development and energy consumption: Evidence from a panel of Middle Eastern countries. Energy, 72, 427–433.
Asongu, S., Agboola, M., Alola, A., & Bekun, F. (2020). The criticality of growth, urbanization, electricity and fossil fuel consumption to environment sustainability in Africa. Science of the Total Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136376
Balsalobre-Lorente, D., Shahbaz, M., Roubaud, D., & Farhani, S. (2018). How economic growth, renewable electricity and natural resources contribute to CO2 emissions? Energy Policy, 113, 356–367.
Balsalobre-Lorente, D., Sinha, A., Driha, O., & Mubarik, M. (2021). Assessing the impacts of ageing and natural resource extraction on carbon emissions: A proposed policy framework for European economies. Journal of Cleaner Production. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126470
Bekun, F., Alola, A., & Sarkodie, S. (2019). Toward a sustainable environment: Nexus between CO2 emissions, resources rent, renewable and nonrenewable energy in 16-EU countries. Science of the Total Environment, 657(2019), 1023–1029.
Bekun, F., Emir, F., & Sarkodie, S. (2019). Another look at the relationship between energy consumption, carbon dioxide emissions, and economic growth in South Africa. Science of the Total Environment, 655, 759–765.
Bougherira, N., Hani, A., Djabri, L., Toumi, F., Chaffai, H., Haied, N., et al. (2014). Impact of the urban and industrial waste water on surface and groundwater, in the region of Annaba, (Algeria). Energy Procedia, 50, 692–701.
Breusch, T., & Pagan, A. (1980). The lagrange multiplier test and its applications to model specification in econometrics. The Review of Economic Studies, 47(1), 239–253.
BRICS-Energy-Research-Cooperation-Platform. (2020). BRICS Energy Report 2020. Russia.
Brini, R. (2021). Renewable and non-renewable electricity consumption, economic growth and climate change: Evidence from a panel of selected African countries. Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.120064
Caglar, A., Balsalobre-Lorente, D., & Akin, C. (2021). Analysing the ecological footprint in EU-5 countries under a scenario of carbon neutrality: Evidence from newly developed sharp and smooth structural breaks in unit root testing. Journal of Environmental Management. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113155
Campiglio, E. (2016). Beyond carbon pricing: The role of banking and monetary policy in financing the transition to a low-carbon economy. Ecological Economics, 121, 220–230.
Can, M., & Gozgor, G. (2017). The impact of economic complexity on carbon emissions: Evidence from France. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24, 16364–16370.
Chakraborty, D., & Roy, J. (2015). Ecological footprint of paperboard and paper production unit in India. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 17, 909–921.
Chaturvedi, S., Saha, S., & Shaw, P. (2016). Trade in high technology products: trends and policy imperatives for BRICS. Discussion Paper No. 207, Research and Information System for Developing Countries, New Delhi.
Cherniwchan, J. (2012). Economic growth, industrialization, and the environment. Resource and Energy Economics, 34(4), 442–467.
Chien, F., Anwar, A., Hsu, C.-C., Sharif, A., Razzaq, A., & Sinha, A. (2021). The role of information and communication technology in encountering environmental degradation: Proposing an SDG framework for the BRICS countries. Technology in Society. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2021.101587
Chudik, A., Mohaddes, K., Pesaran, M., & Raissi, M. (2013a). Debt, inflation and growth robust estimation of long-run effects in dynamic panel data models. Working Paper No. 162, Globalization and Monetary Policy Institute, Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas.
Chudik, A., Mohaddes, K., Pesaran, M., Hashem, & Raissi, M. (2013b). Debt, inflation and growth: robust estimation of long-run effects in dynamic panel data models. Globalization Institute Working Papers 162, Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas.
Çoban, S., & Topcu, M. (2013). The nexus between financial development and energy consumption in the EU: A dynamic panel data analysis. Energy Economics, 39, 81–88.
Danish, U. R., & Khan, S. (2020). Determinants of the ecological footprint: role of renewable energy, natural resources, and urbanization. Sustainable Cities and Society. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2019.101996
Destek, M., & Aslan, A. (2020). Disaggregated renewable energy consumption and environmental pollution nexus in G-7 countries. Renewable Energy, 151, 1298–1306.
Destek, M., & Sinha, A. (2020). Renewable, non-renewable energy consumption, economic growth, trade openness and ecological footprint: Evidence from organisation for economic Co-operation and development countries. Journal of Cleaner Production. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118537
Dinda, S. (2018). Production technology and carbon emission: Long-run relation with short-run dynamics. Journal of Applied Economics, 21(1), 106–121.
Dogan, E., & Seker, F. (2016). The influence of real output, renewable and non-renewable energy, trade and financial development on carbon emissions in the top renewable energy countries. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 60, 1074–1085.
Dogan, B., Madaleno, M., Tiwari, A., & Hammoudeh, S. (2020). Impacts of export quality on environmental degradation: Does income matter? Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27, 13735–13772.
Dogan, E., Ulucak, R., Kocak, E., & Isik, C. (2020). The use of ecological footprint in estimating the Environmental Kuznets Curve hypothesis for BRICST by considering cross-section dependence and heterogeneity. Science of the Total Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138063
Domar, E. D. (1946). Capital expansion, rate of growth, and employment. Econometrica, 14(2), 137–147.
Downie, C. (2018). After the Paris agreement: What role for the BRICS in Global Climate Governance? Global Policy, 9(3), 398–407.
Dutt, A. (2020). Accelerating renewable energy investments in Sri Lanka: drivers, risks, and opportunities. Cetre for Energy Finance, Council on Energy, Environment and Water (CEEW), New Delhi.
Export-Import-Bank-of-India. (2014). Research & development in BRICS: an insight. Occasional Paper No. 168, Mumbai, https://www.brics-ibcm.org/images/publications/Research_and_Development_in_BRICS-An_Insight.pdf.
EXPORT-IMPORT-BANK-OF-INDIA. (2016). Intra-BRICS trade: an Indian perspective. Working Paper No. 56, EXIM Bank.
Farhani, S., & Ozturk, I. (2015). Causal relationship between CO2 emissions, real GDP, energy consumption, financial development, trade openness, and urbanization in Tunisia. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22(20), 15663–15676.
Fetahi-Vehapi, M., Sadiku, L., & Petkovski, M. (2015). Empirical analysis of the effects of trade openness on economic growth: An evidence for South East European countries. Procedia Economics and Finance, 19, 17–26.
Finger, J., & Kreinin, M. (1979). A measure of export similarity and its possible uses. Economic Journal, 89, 905–912.
Fisher-Vanden, K., Jefferson, G., Jingkui, M., & Jianyi, X. (2006). Technology development and energy productivity in China. Energy Economics, 28(5–6), 690–705.
Godil, D., Sharif, A., Rafique, S., & Jermsittiparsert, K. (2020). The asymmetric effect of tourism, financial development, and globalization on ecological footprint in Turkey. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09937-0
Hakimi, A., & Hamdi, H. (2016). Trade liberalization, FDI inflows, environmental quality and economic growth: A comparative analysis between Tunisia and Morocco. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 58, 1445–1456.
Harrod, R. F. (1939). An essay in dynamic theory. The Economic Journal, 49(193), 14–33.
Hettige, H., Mani, M., & Wheeler, D. (2000). Industrial pollution in economic development: The environmental Kuznets curve revisited. Journal of Development Economics, 62(2), 445–476.
Holma, A., Leskinen, P., Myllyviita, T., Manninen, K., Sokka, L., Sinkko, T., & Pasanen, K. (2018). Environmental impacts and risks of the national renewable energy targets: a review and a qualitative case study from Finland. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 82(1), 1433–1441.
Hu, G., Can, M., Paramati, S., Doğan, B., & Fang, J. (2020). The effect of import product diversification on carbon emissions: New evidence for sustainable economic policies. Economic Analysis and Policy, 65, 198–210.
Huang, Q., Chen, G., Wang, Y., Chen, S., Xu, L., & Wang, R. (2020). Modelling the global impact of China’s ban on plastic waste imports. Resources, Conservation and Recycling,. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.104607
Hussain, M., & Dogan, E. (2021). The role of institutional quality and environment-related technologies in environmental degradation for BRICS. Journal of Cleaner Production. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127059
Ibrahim, M., & Vo, X. (2021). Exploring the relationships among innovation, financial sector development and environmental pollution in selected industrialized countries. Journal of Environmental Management. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112057
Ibrahim, R., & Ajide, K. (2021). Nonrenewable and renewable energy consumption, trade openness, and environmental quality in G-7 countries: The conditional role of technological progress. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13926-2
Indian-Steel-Association. (2019). The Indian steel industry: growth, challenges and digital disruption. Price Waterhouse, India. https://www.pwc.in/assets/pdfs/consulting/technology/the-indian-steel-industry-growth-challenges-and-digital-disruption.pdf.
International-Financel-Corporation. (2020). IFC investment in Sri Lankan wind power preserves environment, supports tourism. Retrieved October 10, 2020, from International Financel Corporation: World Bank Group. https://www.ifc.org/wps/wcm/connect/news_ext_content/ifc_external_corporate_site/news+and+events/news/sl_windpower
Kamat, T. (2020). Renewable energy: why BRICS needs to take charge. The Geopolitics. https://thegeopolitics.com/renewable-energy-why-brics-needs-to-take-charge/.
Kassouri, Y., & Altıntaş, H. (2020). Human well-being versus ecological footprint in MENA countries: A trade-off? Journal of Environmental Management. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110405
Khan, Z., Malik, M., Latif, K., & Jiao, Z. (2020). Heterogeneous effect of eco-innovation and human capital on renewable and non-renewable energy consumption: Disaggregate analysis for G-7 countries. Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.118405
Khan, Z., Shahbaz, M., Ahmad, M., Rabbi, F., & Siqun, Y. (2019). Total retail goods consumption, industry structure, urban population growth and pollution intensity: An application of panel data analysis for China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26, 32224–32242.
Kiani, K. (2020). Pakistan offers $100bn investment opportunities in energy sector: Ayub. Dawn. https://www.dawn.com/news/1536503.
Kongkuah, M., Yao, H., & Yilanci, V. (2021). The relationship between energy consumption, economic growth, and CO2 emissions in China: The role of urbanisation and international trade. Environment, Development and Sustainability,. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01628-1
Kumar, J., & Majid, M. (2020). Renewable energy for sustainable development in India: Current status, future prospects, challenges, employment, and investment opportunities. Energy, Sustainability and Society, 10(2), 1–36. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13705-019-0232-1
Kumar, S. (2016). Assessment of renewables for energy security and carbon mitigation in Southeast Asia: The case of Indonesia and Thailand. Applied Energy, 163, 63–70.
Li, B., & Piachaud, D. (2019). Technological innovations and social development in Asia. Journal of Asian Public Policy, 12, 1–14.
Liddle, B. (2018). Consumption-based accounting and the trade-carbon emissions nexus. Energy Economics, 69, 71–81.
Lin, B., & Wang, M. (2021). The role of socio-economic factors in China’s CO2 emissions from production activities. Sustainable Production and Consumption, 27, 217–227.
Liu, Y. (2013). Energy production and regional economic growth in China: a more comprehensive analysis using a panel model. 6, 1409-1420.
Lopez-Menendez, A., Perez, R., & Moreno, B. (2014). Environmental costs and renewable energy: Re-visiting the environmental Kuznets curve. Journal of Environmental Management, 145, 368–373.
Machado, G., Schaeffer, R., & Worrell, E. (2001). Energy and carbon embodied in the international trade of Brazil: An input–output approach. Ecological Economics, 39(3), 409–424.
Majeed, S. (2019). role and responsibility of BRICS countries in air pollution control: An evaluation of scholarly communication. Journal of Scientometric Research, 8(2), 94–101.
Mendonça, A., Barni, G., Moro, M., Bornia, A., Kupek, E., & Fernandes, L. (2020). Hierarchical modeling of the 50 largest economies to verify the impact of GDP, population and renewable energy generation in CO2 emissions. Sustainable Production and Consumption, 22, 58–67.
Mirza, F., & Kanwal, A. (2017). Energy consumption, carbon emissions and economic growth in Pakistan: Dynamic causality analysis. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 72, 1233–1240.
Nasreen, S., & Anwar, S. (2014). Causal relationship between trade openness, economic growth and energy consumption: A panel data analysis of Asian countries. Energy Policy, 69, 82–91.
Opoku, E., & Yan, I. (2019). Industrialization as driver of sustainable economic growth in Africa. The Journal of International Trade and Economic Development, 28(1), 30–56.
Özokcu, S., & Özdemir, Ö. (2017). Economic growth, energy, and environmental Kuznets curve. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 72, 639–647.
Padilla, E., & Serrano, A. (2006). Inequality in CO2 emissions across countries and its relationship with income inequality: A distributive approach. Energy Policy, 34(14), 1762–1772.
Pandey, S., Dogan, E., & Taskin, D. (2020). Production-based and consumption-based approaches for the energy-growth-environment nexus: Evidence from Asian countries. Sustainable Production and Consumption, 23, 274–281.
Paramati, S., Mo, D., & Gupta, R. (2017). The effects of stock market growth and renewable energy use on CO2 emissions: Evidence from G20 countries. Energy Economics, 66, 360–371.
Park, S., & Labys, W. (1998). Industrial Development and Environmental Degradation. Edward Elgar Publishing.
Parteka, A., & Tamberi, M. (2013). Product diversification, relative specialisation and economic development: Import-export analysis. Journal of Macroeconomics, 38, 121–135.
Pathak, L., & Shah, K. (2019). Renewable energy resources, policies and gaps in BRICS countries and the global impact. Frontiers in Energy, 13, 506–521.
Pesaran, M. (2004). General diagnostic tests for cross section dependence in panels. Cambridge Working Papers in Economics 0435, Faculty of Economics, University of Cambridge.
Pesaran, M. (2007). A simple panel unit root test in the presence of cross-section dependence. Journal of Applied Economics, 22(2), 265–312.
Ponomarenko, A. (2019). Do sterilized foreign exchange interventions create money? Journal of Asian Economics, 62, 1–16.
Rahman, M., Saidi, K., & Mbarek, M. (2020). Economic growth in South Asia: the role of CO2 emissions, population density and trade openness. Heliyon, 6(5), e03903.
Rodrik, D. (2018). Will new technology in developing countries be a help or a hindrance? Retrieved from World Economic Forum. https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2018/10/will-new-technologies-help-or-harm-developing-countries/
Sadorsky, P. (2010). The impact of financial development on energy consumption in emerging economies. Energy Policy, 38, 2528–2535.
Sadorsky, P. (2012). Energy consumption, output and trade in South America. Energy Economics, 34(2), 476–488.
Salahuddin, M., Alam, K., Ozturk, I., & Sohag, K. (2018). The effects of electricity consumption, economic growth, financial development and foreign direct investment on CO2 emissions in Kuwait. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 81(P2), 2002–2010.
Salman, M., Long, X., Dauda, L., Mensah, C., & Muhammad, S. (2019). Different impacts of export and import on carbon emissions across 7 ASEAN countries: A panel quantile regression approach. Science of the Total Environment, 686, 1019–1029.
Samarakoon, L. (2016). Sri Lanka capital market assessment. Project Number: 49273 , Asian Development Bank, Colombo, Sri Lanka .
Santiago, F. (2020). The role of industrial policies in the BRICS economic integration process. Working Paper 1/2020, United Nations Industrial Development Organization, Department of Policy, Research and Statistics, Vienna.
Shahbaz, M., Sharma, R., Sinha, A., & Jiao, Z. (2021a). Analyzing nonlinear impact of economic growth drivers on CO2 emissions: designing an SDG framework for India. Energy Policy, 148(Part B). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0301421520306765.
Shahbaz, M., Sharma, R., Sinha, A., & Jiao, Z. (2021b). Analyzing nonlinear impact of economic growth drivers on CO2 emissions: designing and SDG framework for India. Energy Policy, 148, 111965.
Shahbaz, M., Balsalobre-Lorente, D., & Sinha, A. (2019). Foreign direct investment-CO2 emissions nexus in Middle East and North African countries: Importance of biomass energy consumption. Journal of Cleaner Production, 217, 603–614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.01.282
Shahbaz, M., Gozgor, G., & Hammoudeh, S. (2019). Human capital and export diversification as new determinants of energy demand in the United States. Energy Economics, 78, 335–349.
Shahbaz, M. M., Mahalik, M., & Loganathan, N. (2015). Does globalization impede environmental quality in India? Ecological Indicators, 52, 379–393.
Shahbaz, M., Mallick, H., Mahalik, M., & Loganathan, N. (2015b). Does globalization impede environmental quality in India? Ecological Indicators, 52(2015), 379–393.
Shahbaz, M., Mallick, H., Mahalik, M., & Loganathan, N. (2015c). Does globalization impede environmental quality in India? Ecological Indicators, 52, 379–393.
Shahbaz, M., Nasir, M., & Roubaud, D. (2018). Environmental degradation in France: The effects of FDI, financial development, and energy innovations. Energy Economics, 74, 843–857.
Shahbaz, M., Uddin, G., Rehman, I., & Imran, K. (2014). Industrialization, electricity consumption and CO2 emissions in Bangladesh. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 31, 575–586.
Shahzad, U., Doğan, B., Sinha, A., & Fareed, Z. (2021). Does Export product diversification help to reduce energy demand: Exploring the contextual evidences from the newly industrialized countries. Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.118881
Sharif, A., Baris-Tuzemen, O., Uzuner, Z., & Sinha, A. (2020). Revisiting the role of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption on Turkey’s ecological footprint: Evidence from Quantile ARDL approach. Sustainable Cities and Society, 57, 102138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2020.102138
Sharma, R., & Kautish, P. (2020a). Examining the nonlinear impact of coal and oil-based electricity production on CO2 emissions in India. The Electricity Journal. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tej.2020.106775
Sharma, R., & Kautish, P. (2020b). Linkages between financial development and economic growth in the middle-income countries of South Asia: a panel data investigation. Vision: The Journal of Business Perspective, 24(2), 140–150.
Sharma, G., & Bodla, B. (2011). Growing competitiveness of South Asian Stock exchanges on the global scenario. Research Journal of Business Management, 5, 130–145.
Sharma, R., Kautish, P., & Uddin, M. (2020). Do the international economic endeavors affect CO2 emissions in open economies of South Asia? An empirical examination under nonlinearity. Management of Environmental Quality, 31(1), 89–110.
Sharma, R., Sinha, A., & Kautish, P. (2021a). Do economic endeavors complement sustainability goals in the emerging economies of South and Southeast Asia? Management of Environmental Quality. https://doi.org/10.1108/MEQ-10-2020-0218
Sharma, R., Sinha, A., & Kautish, P. (2021b). Does renewable energy consumption reduce ecological footprint? Evidence from eight developing countries of Asia. Journal of Cleaner Production, 285, 124867.
Sharma, R., Sinha, A., & Kautish, P. (2021c). Does financial development reinforce environmental footprints? Evidence from emerging Asian countries. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28, 9067–9083.
Sharvini, S., Noor, Z., Chong, C., Stringer, L., & Yusuf, R. (2018). Energy consumption trends and their linkages with renewable energy policies in East and Southeast Asian countries: Challenges and opportunities. Sustainable Environment Research, 28, 257–266.
Shukla, A., Sudhakar, K., & Baredar, K. (2017a). Renewable energy resources in South Asian countries: Challenges, policy and recommendations. Resource-Efficient Technologies, 3(3), 342–346.
Sinha, A., Gupta, M., Shahbaz, M., & Sengupta, T. (2019). Impact of corruption in public sector on environmental quality: Implications for sustainability in BRICS and next 11 countries. Journal of Cleaner Production, 232, 1379–1393.
Sinha, A., Sengupta, T., & Saha, T. (2020). Technology policy and environmental quality at crossroads: Designing SDG policies for select Asia Pacific countries. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 161, 1–13.
Sinha, A., Shah, M., Sengupta, T., & Jiao, Z. (2020). Analyzing technology-emissions association in Top-10 polluted MENA countries: How to ascertain sustainable development by quantile modeling approach. Journal of Environmental Management. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110602
Sinha, A., & Shahbaz, M. (2018). Estimation of Environmental Kuznets Curve for CO2 emission: Role of renewable energy generation in India. Renewable Energy, 119, 703–711.
Sinha, A., Shahbaz, M., & Balsalobre, D. (2017). Exploring the relationship between energy usage segregation and environmental degradation in N-11 countries. Journal of Cleaner Production, 168, 1217–1229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.09.07
Steffen, B. (2020). Estimating the cost of capital for renewable energy projects. Energy Economics. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2020.104783
Sun, J., Mooney, C., Wu, W., Tang, H., Tong, Y., Xu, Z., et al. (2018). Importing food damages domestic environment: Evidence from global soybean trade. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 115(21), 5415–5419.
Tamazian, A., Chousa, J., & Vadlamannati, K. (2009). Does higher economic and financial development lead to environmental degradation: Evidence from BRIC countries. Energy Policy, 37(1), 246–253.
Terrell, T. (2020). Carbon flux and N- and M-shaped environmental Kuznets curves: Evidence from international land use change. Journal of Environmental Economics and Policy. https://doi.org/10.1080/21606544.2020.1809527
The-Economics-Times. (2020). Opinion: is India's renewable energy investment on track? ETEnergy World-The Economics Times. https://energy.economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/renewable/opinion-is-indias-renewable-energy-investment-on-track/76229607.
The-Economic-Times. (2019). Out of top 10 most polluted cities in the world, 7 cities are from India alone. The Economic Times. https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/politics-and-nation/out-of-top-10-most-polluted-cities-in-the-world-7-cities-are-from-india-alone/south-asias-battle/slideshow/68266564.cms.
The-fifth-BRICS-Ministers-of-Environment-Meeting. (2019). Joint Statement for Fifth BRICS Ministers of Environment Meeting. São Paulo, Brazil. https://sdg.iisd.org/news/brics-ministers-commit-to-urban-environmental-management-global-climate-and-biodiversity-issues/.
The-Living-Planet-Report. (2014). The Living Planet Report 2014: Species and spaces, people and places. WWF International, Gland, Switzerland. https://www.footprintnetwork.org/content/images/article_uploads/Living_Planet_Report_2014.pdf.
Todaro, M., & Smith, S. (2017). Economic Development (12th ed.). Pearson Education.
Topcu, M., Tugcu, C. (2020). How does environmental degradation react to stock market development in developing countries? In: M. Shahbaz, & D. Balsalobre-Lorente, Econometrics of Green Energy Handbook. Springer, Cham.
UNCTAD. (2017). The role of stock exchanges in fostering economic growth and sustainable development. United Nations, World Federation of Exchanges. https://unctad.org/en/PublicationsLibrary/WFE_UNCTAD_2017_en.pdf.
UNCTAD. (2019). The impact of rapid technological change on sustainable development. UNCTAD/DTL/STICT/2019/10, United Nations , New York.
UNCTAD. (2021). UNCTAD: Stat. https://unctadstat.unctad.org/wds/ReportFolders/reportFolders.aspx
UNEP. (2015). Sustainable consumption and production: a handbook for policymakers. Global edition, United Nations Environment Programme, Nairobi, Kenya.
UNEP. (2020). used vehicles and the environment. United Nations Environment Programme, Kenya. https://www.unep.org/resources/report/global-trade-used-vehicles-report.
United-Nations. (2019). World economic situation and prospects 2019. United Nations, New York. https://www.un.org/development/desa/dpad/wp-content/uploads/sites/45/WESP2019_BOOK-CH3-5-south-asia-en.pdf.
Wang, H., Huang, J., Zhou, H., Deng, C., & Fang, C. (2020). Analysis of sustainable utilization of water resources based on the improved water resources ecological footprint model: a case study of Hubei Province, China. Journal of Environmental Management. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110331.
Wang, Q., Hang, Y., Su, B., & Zhou, P. (2018). Contributions to sector-level carbon intensity change: An integrated decomposition analysis. Energy Economics, 70, 12–25.
Westerlund, J. (2007). Testing for error correction in panel data. Oxford Bulletin of Economics and Statistics, 69(6), 709–748.
World-Bank. (2019). World Development Indicators. The World Banks. https://data.worldbank.org/indicator
World-Bank. (2020). World development report 2020: trading for development in the age of global value chains. World Bank, Washington, DC. doi:https://doi.org/10.1596/978-1-4648-1457-0.
World-Bank. (2021). World Development Indicators. The World Banks. https://data.worldbank.org/indicator
Xu, B., & Lin, B. (2015). How industrialization and urbanization process impacts on CO2 emissions in China: Evidence from nonparametric additive regression models. Energy Economics, 48, 188–202.
Xu, Y., Dietzenbacher, E., & Los, B. (2020). International trade and air pollution damages in the United States. Ecological Economics. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2020.106599
Yasmeen, H., Tan, Q., Zameer, H., Tan, J., & Nawaz, K. (2020). Exploring the impact of technological innovation, environmental regulations and urbanization on ecological efficiency of China in the context of COP21. Journal of Environmental Management. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111210
Yu, W., Nataliia, D., Yoo, S.-J., & Hwang, Y.-S. (2019). Does trade openness convey a positive impact for the environmental quality? Evidence from a panel of CIS countries. Eurasian Geography and Economics, 60(3), 333–356.
Zafar, A., Majeed, M., Nosheen, M., & Iqbal, J. (2021). Globalization, financial development, and environmental sustainability: Evidence from heterogenous income groups of Asia. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14152-6
Zafar, A., Ullah, S., Majeed, T., & Yashmeen, R. (2020). Environmental pollution in Asian economies: Does the industrialisation matter? OPEC Energy Review, 44(3), 227–248.
Zafar, M., Mirza, F., Zaidi, S., & Hou, F. (2019). The nexus of renewable and nonrenewable energy consumption, trade openness, and CO2 emissions in the framework of EKC: Evidence from emerging economies. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(15), 15162–15173.
Zafar, M., Zaidi, S., Sinha, A., Gedikl, A., & Hou, F. (2019). The role of stock market and banking sector development, and renewable energy consumption in carbon emissions: Insights from G-7 and N-11 countries. Resources Policy, 62, 427–436.
Zahonogo, P. (2016). Trade and economic growth in developing countries: Evidence from sub-Saharan Africa. Journal of African Trade, 3(1–2), 41–56.
Zeqiraj, V., Sohag, K., & Soytas, U. (2020). Stock market development and low-carbon economy: The role of innovation and renewable energy. Energy Economics. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2020.104908
Zhongping, W., Changliang, S., Qiang, L., & Gang, W. (2011). Impact of Heavy Industrialization on the Carbon Emissions: An Empirical Study of China. Energy Procedia, 5, 2610–2616.
Acknowledgements
The authors of the manuscript would like to express their heartfelt condolences for Dr. Rajesh Sharma, who happened to be an excellent teacher, and scholar par excellence. In a very short span of time, he achieved the position of notable researcher in the field of energy economics, sustainability, and environment-related research domains. We acknowledge the void his untimely and sudden demise has created in our personal and professional lives and we pray to God for his noble soul to rest in peace.
Funding
This study is not supported by any funding agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
There is no conflict of interest among authors or any other third party.
Ethics approval
We followed the desired ethical procedure while writing this manuscript.
Consent to participate
We have required consent from the authors and their respective Institutes.
Consent for publication
We provide consent to publish it online and offline.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, R., Shahbaz, M., Kautish, P. et al. Diversified imports as catalysts for ecological footprint: examining the BRICS experience. Environ Dev Sustain 25, 3153–3181 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-022-02177-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-022-02177-x