Abstract
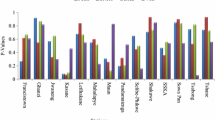
Monitoring and detecting trends of climatic variables like rainfall and temperature are essential for agricultural developments in the context of climate change. The present study has detected trends in annual and cropping seasonal rainfall and temperature data for the period of 1961–2011 using Mann–Kendall (MK) test, Spearman’s rho (SR) test and modified Mann–Kendall test that has been applied to the significant lag-1 serial correlated time series data, and slope has been estimated using Sen’s Slope estimator for twelve meteorological stations located in the western part of Bangladesh covering about 41 % of the country. Almost 71 % trends explored by MK test in annual rainfall are statistically insignificant, and SR test also complies it. The spatial distribution of rainfall trend shows insignificant positive trends in major part of the area. Significant positive trends both by MK test and by SR test at 95 % confidence levels are observed at rates of 8.56, 11.15 and 13.66 mm/year at Dinajpur, Rangpur and Khepupara stations, respectively, and the Kharif season rainfall of these stations also shows significant increasing trends except Dinajpur. On the other hand, significant decreasing trends in annual rainfall are found at Bhola (−11.67 mm/year) and Rajshahi (−5.951 mm/year) stations and decreasing trends in rainfall dominated the Pre-Kharif season over the area. But, 83.33 % of the stations show rising trends in annual mean temperature with significant positive trends (as observed by both MK test and SR test) at Rangpur, Bogra, Faridpur, Jessore and Bhola stations where the rate of changes vary from 0.013 °C/year at Faridpur to 0.08 °C/year at Bhola. Most of the trends in Rabi and Pre-Kharif seasons of mean temperatures are not statistically significant. However, all stations except Barisal show significant rising trends in temperature in Kharif season. To cope with this changing pattern of rainfall and temperature, effective adaptation strategies should be taken to keep up the agricultural production that is related to livelihood of the most people and to ensure the country’s food security.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahasan, M. N., Chowdhary, M. A. M., & Quadir, D. A. (2010). Variability and trends of summer monsoon rainfall over Bangladesh. Journal of Hydrology and Meteorology, 7, 1–7.
Ahmed, A. U. (2004). Adaptation to climate change in Bangladesh: learning by doing. Germany: UNFCCC Workshop on Adaptation, Bonn.
Allen, R. J., & DeGaetano, A. T. (2001). Estimating missing daily temperature extremes using an optimized regression approach. International Journal of Climatology, 21, 1305–1319. doi:10.1002/joc.679.
Azad, A. S., Hasan, M. K., Rahman, M. A. I., Rahman, M. M., & Shahriar, N. (2012). Changing trends of climate in Bangladesh and a noble procedure of distribution of rainfall by clustering. In International conference proceeding: Statistical data mining for bioinformatics, health, agriculture and environment (pp. 405–411), ISBN: 978-984-33-5876-9.
Banglapedia. (2003). Banglapedia: National encyclopedia of Bangladesh. In S. Islam (Ed.), Dhaka: Asiatic Society of Bangladesh.
BARC. (1991). Agro-ecological database. Dhaka, Bangladesh: BARC Computer Center, Bangladesh Agricultural Research Council.
BBS (Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics). (2012). Population Census 2011: National Report (Provisional). Dhaka, Bangladesh: Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics.
Croitoru, A. E., Holobaca, I. H., Lazar, C., Moldovan, F., & Imbroane, A. (2012). Air temperature trend and the impact on winter wheat phenology in Romania. Climate Change, 111(2), 393–410. doi:10.1007/s10584-011-0133-6.
Del, R. S., Herrero, L., Pinto-Gomes, C., & Penas, A. (2011). Spatial analysis of mean temperature trends in Spain over the period 1961–2006. Global and Planetary Change, 78, 65–75.
Eischeid, J. K., Baker, C. B., Karl, T. R., & Diaz, H. F. (1995). The quality control of long-term climatological data using objective data analysis. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 34, 2787–2795.
El Kenawy, A., Lopez-Moreno, J. I., & Vicente-Serrano, S. M. (2011). Recent trends in daily temperature extremes over northeastern Spain. Natural Hazards Earth System Science, 11, 2583–2603.
Enders, C. K. (2010). Applied missing data analysis. New York: The Guilford Press. Retrieved from July 30, 2011 from http://books.google.co.ke/. ISBN: 978-1 60623-639-0.
Gajbhiya, S., Meshram, C., Singh, S. K., Srivastava, P. K., & Islam, T. (2016). Precipitation trend analysis of Sindh River basin, India, from 102-year record (1901–2002). Atmospheric Science Letters, 17(1), 71–77.
Gyau-Boakye, P., & Tumbulto, J. W. (2000). The Volta Lake and declining rainfall and stream flows in the Volta River Basin. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 2(1), 1–11.
Hamed, K. H., & Rao, A. R. (1998). A modified Mann–Kendall trend test for autocorrelated data. Journal of Hydrology, 204(1–4), 182–196.
Hasan, A. B. M. S. U., & Rahman, M. Z. (2013). Change in temperature over Bangladesh associated with degrees of global warming. Asian Journal of Applied Science and Engineering, 2(2), 62–75.
Ingsrisawang, L., & Potawee, D. (2012). Multiple imputations for missing data in repeated measurements using MCMC and copulas. In Proceedings of the international multi conference of engineers and computer scientist 2012. Retrieved from July 20, 2013 http://www.iaeng.org/publication/IMECS2012/.
IPCC. (2007). In M. L. Parry, O. F. Canziani, J. P. Palutikof, P. J. van der Linden, & C.E. Hanson (Eds.), Climate change 2007: Impacts, adaptation and vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
IPCC. (2014). In Core Writing Team, R. K. Pachauri, & L.A. Meyer (Eds.), Climate change 2014: Synthesis report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Geneva, Switzerland: IPCC.
Jahan, C. S., Rahman, A. T. M. S., Mazumder, Q. H., & Kamruzzaman, M. (2015). Adaptation for Climate Change Effect on Groundwater Resource through MAR Technique in Drought Prone Barind Area, Rural Bangladesh. In S. M. Ali (Ed.), Bangladesh: Combating Land Degradation and Drought (pp. 61–83). Dhaka: Series-II, Department of Environment (DoE), Ministry of Environment (MoEF), Government of Bangladesh. ISBN 978-984-33-9991-5.
Jones, P. D., & Moberg, A. (2003). Hemispheric and large-scale surface air temperature variations: An extensive revision and an update to 2001. Journal of Climate, 16, 206–223.
Kampata, J. M., Parida, B. P., & Moalafhi, D. B. (2008). Trend analysis of rainfall in the headstreams of the Zambezi River Basin in Zambia. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 33, 621–625.
Kamruzzaman, M., Rahman, A. T. M. S., & Jahan, C. S. (2015). Adapting cropping systems under changing climate in NW Bangladesh. Germany: Lambert Academic Publishing. ISBN 978-3-659-69174-4.
Kendall, M. G. (1975). Rank correlation methods (4th ed.). London: Charles Griffin.
Kerr, R. A. (2009). What happened to global warming? Scientists say just wait a bit. Science, 326, 28–29.
Lorentzen, T. (2014). A statistical analysis of sea temperature data. Theoretical and Applied Climatology,. doi:10.1007/s00704-014-1119-x.
Mann, H. B. (1945). Non-parametric tests against trend. Econometrica, 13, 245–259.
Oliver, J. E. (1973). Climate and Man’s Environment. Chichester: Wiley.
Rahman, M. A., & Begum, M. (2013). Application of non-parametric test for trend detection of rainfall in the largest island of Bangladesh. ARPN Journal of Earth Sciences, 2(2), 40–44.
Rahman, A. T. M. S., Jahan, C. S., Mazumder, Q. H., Kamruzzaman, M., & Hossain, A. (2016a). Evaluation of spatio-temporal dynamics of water table in NW Bangladesh—An integrated approach of GIS and statistics. Sustainable Water Resource Management,. doi:10.1007/s40899-016-0057-4.
Rahman, A., Jiban, M. J. H., & Munna, S. A. (2015). Regional variation of temperature and rainfall in Bangladesh: Estimation of trend. Published Online December 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojs, http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojs.2015.57066.
Rahman, A. T. M. S., Kamruzzaman, M., Jahan, C. S., & Mazumder, Q. H. (2016b). Long-term trend analysis of water table using ‘MAKESENS’ model and sustainability of groundwater resources in drought prone Barind Area, NW Bangladesh. Journal of Geological Society of India, 87, 179–193.
Rahman, M. R., & Lateh, H. (2015). Spatio-temporal analysis of warming in Bangladesh using recent observed temperature data and GIS. Climate Dynamics,. doi:10.1007/s00382-015-2742-7.
Recha, C. W., Makokha, G. L., Traore, P. S., Shisanya, C., Lodoun, T., & Sako, A. (2012). Determination of seasonal rainfall variability, onset and cessation in semi-arid Tharaka district, Kenya. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 108, 479–494. doi:10.1007/s00704-011-0544-3.
Salmi, T., Maatta, A., Anttila, P., Airola, T. R., & Amnell, T. (2002). Detecting trends of annual values of atmospheric pollutants by the Mann-Kendal test and Sen’s Slope estimates—The Excel template application MAKESENS (p. 35). Finish Meteorological Institute: User manual, Publication on air quality.
Sen, P. K. (1968). Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. Journal of American Statistical Association, 63, 1379–1389.
Shadmani, M., Marofi, S., & Roknian, M. (2012). Trend analysis in reference evapotranspiration using Mann–Kendall and Spearman’s Rho tests in arid regions of Iran. Water Resource Management, 26, 211–224. doi:10.1007/s11269-011-9913-z.
Shahid, S., & Khairulmaini, O. S. (2009). Spatial and temporal variability of rainfall in Bangladesh. Asia-pacific Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 45(3), 375–389.
Shifteh Some’e, B., Ezani, A., & Tabari, H. (2012). Spatio-temporal trends of aridity index in arid and semi-arid regions of Iran. Theoretical Applied Climatology, 111, 149–160. doi:10.1007/s00704-012-0650-x.
Siddik, M. A. Z., & Rahman, M. (2014). Trend analysis of maximum, minimum, and average temperatures in Bangladesh: 1961–2008. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 116, 721–730. doi:10.1007/s00704-014-1135-x.
Solomon, S., Qin, D., Manning, M., Chen, Z., Marquis, M., Averyt, K. B., Tignor, M., & Miller, H. L. (Eds.). (2007a). Climate change 2007: The physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA: Cambridge University Press.
Solomon, S., Qin, D., Manning, M., Chen, Z., Marquis, M., Averyt, K. B., Tignor, M., & Miller, H. L. (Eds.) (2007b). Climate change 2007: The synthesis report. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York: Cambridge University Press.
Tabari, H., Abghani, H., & Hosseinzadeh, T. P. (2012). Temporal trends and spatial characteristics of drought and rainfall in arid and semiarid regions of Iran. Hydrological Processes,. doi:10.1002/hyp.8460.
Tonkaz, T., Çetin, M., & Kâzım, T. (2007). The impact of water resources development projects on water vapor pressure trends in a semi-arid region, Turkey. Climatic Change, 82, 195–209.
Touch, V., Matrin, R. J., Scott, F., Cowie, A., & Li Liu, D. (2016). Climate change impacts on rainfed cropping production systems in the tropics and the case of smallholder farms in North-West Cambodia. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 1–17. doi:10.1007/s10668-016-9818-3.
Yue, S., Pilon, P., Phinney, B., & Cavadias, G. (2002). The influence of autocorrelation on the ability to detect trend in hydrological series. Hydrological Processes, 16, 1807–1829.
Zhang, Q., Xu, C. Y., Zhang, Z., Chen, Y. D., & Liu, C. L. (2008). Spatial and temporal variability of precipitation over China, 1951–2005. Theoretical and Applied Climatology,. doi:10.1007/s00704-007-0375-4.
Acknowledgments
Funding was provided by Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (Grant No. 03G0806C).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamruzzaman, M., Rahman, A.T.M.S., Ahmed, M.S. et al. Spatio-temporal analysis of climatic variables in the western part of Bangladesh. Environ Dev Sustain 20, 89–108 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-016-9872-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-016-9872-x