Abstract
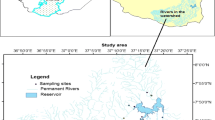
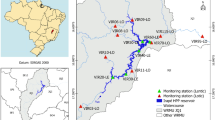
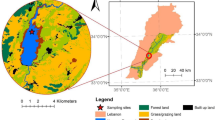
This research investigated the spatiotemporal variation of water quality in the Gilgel Gibe reservoir, Ethiopia, using physicochemical water quality parameters. Nonparametric tests and multivariate statistical techniques were used to evaluate data sets measured during dry and rainy seasons. Electrical conductivity (EC), pH, biochemical oxygen demand (BOD5), total phosphorus (TP), total nitrogen (TN), nitrate (NO3−), total dissolved solids (TDSs), and total suspended solids (TSSs) were all significantly different among seasons (Mann-Whitney U test, p < 0.01). In addition, principal component analysis distinguished dry season samples from wet season samples. The dry season was positively associated with EC, pH, TP, TN, NO3−, TDS, and TSS and negatively associated with BOD5. The wet season was in contrast associated with high values of turbidity, soluble reactive phosphorus (SRP), water temperature, and dissolved oxygen (DO). Within the reservoir, spatial variation was observed for some of the water quality parameters, with significant difference at p = < 0.05. Overall, high nutrient concentrations suggest eutrophic conditions, likely due to high nutrient loading from the watershed. Levels of TSS, attributed to inputs from tributaries, have been excessive enough to inhibit light penetration and thus have a considerable impact on the aquatic food web. Our findings indicate that the reservoir is at high risk of eutrophication and siltation, and hence, urgent action should target the planning and implementation of integrated watershed management for this and similar reservoirs in the region.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aladesanmi, O. T., KayodeAgboola, F., & Adeniyi, I. F. (2014). Seasonal limnological variation of selected streams and their associated fish ponds in Osun State, Nigeria. Environmental Energy and. Biotechnology, 76(9), 42–46.
Alam, A., Badruzzaman, A. B. M., & Ali, M. A. (2012). Spatio-temporal assessment of water quality of the Sitalakhya River , Bangladesh. Internatinal Journal of. Engineering and Technology, 2(6), 953–962.
Ambelu, A., Koen, L., Peter, L. M., & Goethals. (2013). Hydrological and anthropogenic influence in the Gilgel Gibe I reservoir (Ethiopia) on marcroinvertebrate assemblages. Lake Reservoir Management, 29(3), 143–150.
American Public Health Association (APHA). (1999). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (20th ed.). Washington, DC: American Public Health Association.
Araoye, P. A. (2009). The seasonal variation of pH and dissolved oxygen (DO2) concentration in Asa lake Ilorin, Nigeria. International Journal of Physical Sciences, 4(5), 271–274.
Atobatele, O. E., & Ugwumba, O. A. (2008). Seasonal variation in the physicochemistry of a small tropical reservoir (Aiba Reservoir, Iwo, Osun, Nigeria). African Journal of Biotechnology, 7(12), 1962–1971.
Awulachew, S. B., Yilma, A. D., Loulseged, M., Loiskandl, W., Ayana, M. and Alamirew, T. (2007). Water resource and irrigation in Ethiopia. Working paper.
Berhanu, B., Seleshi, Y., & Melesse, A. M. (2014). Surface water and groundwater resources of Ethiopia: potentials and challenges of water resources development. In A. M. Melesse, W. Abtew, & S. G. Setegn (Eds.), Nile River basin ecohydrological challenges, climate change and hydropolitics (pp. 97–117). Springer International Publishing.
Broothaerts, N., Kissi, E., Poesen, J., Van Rompaey, A., Getahun, K., Van Ranst, E., & Diels, J. (2012). Spatial patterns, causes and consequences of landslides in the Gilgel Gibe catchment, SW Ethiopia. Catena, 97(2012), 127–136.
Carpenter, S. R., Caraco, N. F., Correll, D. L., Howarth, R. W., Sharpley, A. N., & Smith, V. H. (1998). Nonpoint pollution of surface waters with phosphorus and nitrogen. Ecological Applications, 8(3), 559–568.
Chapman, D. V. (1996). Water quality assessments: a guide to the use of biota, sediments and water in environmental monitoring. 2nded. New York: UNESCO/ WHO/ UNEP.
Demissie, T., Saathoff, F., Seleshi, Y., Gebissa, A. (2013). Evaluating the effectiveness of best management practices in Gilgel Gibe basin watershed—Ethiopia. Journal of Civil Engineering and Architecture, 7(10), 1240–1252.
Department of Water Affairs and Forestry (DWAF). (1996). South African water quality guidelines, volume 7: Aquatic ecosystems (1st ed.). Pretoria: South Africa.
Devi, R., Tesfahune, E., Legesse, W., Deboch, B., & Beyene, A. (2008). Assessment of siltation and nutrient enrichment of Gilgel Gibe dam, Southwest Ethiopia. BiosourceTechnology, 99(2008), 975–979.
Dou, M., Zhang, Y., & Li, G. (2016). Temporal and spatial characteristics of the water pollutant concentration in Huaihe River Basin from 2003 to 2012, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188(9), 1–18.
Ebisa, N. (2010). Water quality and phytoplankton dynamics in Geffersa reservoir/Ethiopia. MSc thesis: Addis Ababa University.
Environmental Protection Authority and The United Nations Industrial Development Organization (EPA and UNIDO) (2003). Guideline ambient environment standards for Ethiopia. Addis Ababa.
Ethiopian Electric Power Corporation (EEPC) (2011). Gilgel Gibe Hydroelectric Project – Environmental Management Plan. Hydropower for Sustainable Development. www.h4sd.info/Contact-Us/H4SD_PRESS_Case-Study_GG-I_31-03-2011_Final.aspx. Accessed 2nd May 2015.
FAO (2003). Fishery country profile. ftp://ftp.fao.org/fi/DOCUMENT/fcp/en/FI_CP_ET.pd. Accessed 21January 2015.
FAO (2008). Water profile of Ethiopia, Encyclopedia of Earth. http://www.eoearth.org/article. Accessed 10th March 2015.
Garg, R. K., Rao, R. J., Uchchariya, D., Shukla, G., & Saksena, D. N. (2010). Seasonal variations in water quality and major threats to Ramsagar reservoir, India. African Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 4(2), 061–076.
Goshu, G. (2007). The physico-chemical characteristics of a highland crater lake and two reservoirs in north-west Amhara region ( Ethiopia ). Ethiopian Journal of Scince and Technolology, 5(1), 17–41.
Gu, Q., Zhang, Y., Ma, L., Li, J., Wang, K., Zheng, K., Zhang, X., & Li, S. (2016). Assessment of reservoir water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of Qiandao Lake, China. Journal of Sustainability, 8(243), 1–17.
Ibrahim, B., Auta, J., & Balogun, J. (2009). An assessment of the physico-chemical parameters of Kontagora reservoir, Niger state, Nigeria. Bayero. Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences, 2(1), 64–69.
Irenosen, O. G., Festus, A. A., & Coolborn, A. F. (2012). Water quality assessment of the Owena Multi-Purpose Dam, Ondo State, southwestern Nigeria. Journal of Environmental Protection, 3, 14–25.
Jorgensen, S.E., Loffler, H., Rast, W., and Straskraba, M. (2005). Lake and reservoir management.UK : Oxford, Elsevier.
Khan, M. A. G. M. I., & Parveen, M. (2012). Seasonal variations in physico-chemical characteristics of Pahuj reservoir, district Jhansi, Bundelkhand region, central India. Available at http://www.journalcra.com. Accessed 10 September 2015.
Makhlough, A. (2008). Water quality characteristics of Mengkuang reservoir based on phytoplankton community structure and physico-chemical analysis. MSc thesis: University of Sains Malaysia.
Meme, F. K., Arimoro, F. O., & Nwadukwe, F. O. (2014). Analyses of physical and chemical parameters in surface waters nearby a cement factory in north central, Nigeria. Journal of Environmental Protection, 5(10), 826–834.
Menetrey, N., Sager, L., Oertli, B., & Lachavanne, J. B. (2005). Looking for metrics to assess the trophic state of ponds. Macroinvertebrates and amphibians. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems, 15(6), 653–664.
Mustapha, M. K. (2009). Influence of watershed activities on the water quality and fish assemblages of a tropical African reservoir. International journal of Tropical. Biology, 57(3), 707–719.
Ndebele-Murisa, M. R., Musil, C. F., & Raitt, L. (2010). A review of phytoplankton dynamics in tropical African lakes. South African Journal of Science, 106(1–2), 13–18.
Carr, G. M., & Neary, J. P. (2008). Water quality for ecosystem and human health (2nd ed.). Canada: UNEP/Earth print.
Palma, P., Ledo, L., Soares, S., Barbosa, I. R., & Alvarenga, P. (2014). Spatial and temporal variability of the water and sediments quality in the Alqueva reservoir (Guadiana Basin; southern Portugal). Science of the Total Environment, 470(2014), 780–790.
Parashar, C., Dixit, S., & Shrivastava, R. (2006). Seasonal variations in physico-chemical characteristics in Upper Lake of Bhopal introduction. Asian Journal of Experimental. Science, 20(2), 297–302.
Quinn, G. P., & Keough, M. J. (2002). Experimental design and data analysis for biologists. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Saxena, M., & Saksena, D. (2012). Water quality and trophic status of Raipur reservoir in Gwalior , Madhya Pradesh. Journal of Natural Sciences Research, 2(8), 82–96.
Shen, D. (2002). Study on limiting factors of water eutrophication of the network of rivers in plain. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agriculture and Life Sciences), 28(1), 94–97.
Tessema, A., Mohammed, A., Birhanu, T., & Negu, T. (2014). Assessment of physico-chemical water quality of Bira Dam, Bati Wereda. Journal of Aquaculture Research. Development, 5(6), 1–4.
Umerfaruq, M. Q., & Solanki, H. A. (2015). Physico-chemical parameters of water in Bibi Lake, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India. Journal of Pollution Effects and Control, 3(2), 1–5.
UNESCO (2004). National water development report for Ethiopia. Water resources (vol. 2006/7).
Venkatesharaju, K., Ravikumar, P., Somashekar, R., & Prakash, K. (2010). Physico-chemical and bacteriological investigation on the river Cauvery of Kollegal stretch in Karnataka. Journal of Science, Engineering and Technology, 6(1), 50–59.
Wakjira, T., Tamene, A., & Dawud, T. (2016). Land use land cover change analysis using multi temporal Landsat data in Gilgel Gibe, Omo Gibe Basin, Ethiopia. International Journal of Science and Technology, 5(7), 309–323.
Wetzel, R. G. (2001). Limnology: Lake and river ecosystems. Gulf Professional Publishing.
Williams, P. (2003). Comparative biodiversity of rivers, streams, ditches and ponds in an agricultural landscape in southern England. Biological Conservation, 115(2), 329–341.
Wolancho, K. W. (2012). Watershed management: an option to sustain dam and reservoir function in Ethiopia. Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 5(5), 262–273.
Yewhalaw, D., Legesse, W., Van Bortel, W., Gebre-Selassie, S., Kloos, H., Duchateau, L., & Speybroeck, N. (2009). Malaria and water resource development: The case of Gilgel-Gibe hydroelectric dam in Ethiopia. Malaria Journal, 8(1), 1–10.
Zinabu, G. M. (2002). The effects of wet and dry seasons on concentrations of solutes and phytoplankton biomass in seven Ethiopian rift-valley lakes. Limnologica-Ecology and Management of Inland Waters, 32(2), 169–179.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Jimma University and Mada Walabu University of Ethiopia for financing this study and VLIR-UOS for the logistic support. The authors also wish to thank Mr. Yihun Abdie, Zewdu Efrem, Seyoum Derb, and the local community, who helped us during field work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Woldeab, B., Beyene, A., Ambelu, A. et al. Seasonal and spatial variation of reservoir water quality in the southwest of Ethiopia. Environ Monit Assess 190, 163 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6527-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6527-4