Abstract
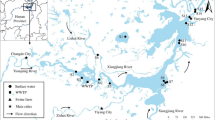
The aims of this study are to investigate the fate of tetracycline (TC) and degradation products (DPs) in municipal biological wastewater treatment plant (MBWWTP) located in Elazığ City (Turkey) and to determine the occurrence and transport of TC and DPs in surface water (SW) (Kehli Stream) which the effluents of the plant discharged. The aqueous phase removal of TC, 4-epitetracycline (ETC), 4-epianhydrotetracycline (EATC), and anhydrotetracycline (ATC) in the studied treatment plant was 39.4 ± 1.9, 31.8 ± 1.5, 15.1 ± 0.7, and 16.9 ± 0.8 %, respectively. According to the analyses’ results of SW samples taken from downstream at every 500-m distance, TC and DPs decreased by the increase in the distance. In downstream, at 2000 m, TC, ETC, EATC, and ATC were 4.12 ± 0.20, 6.70 ± 0.33, 8.31 ± 0.41, and 3.57 ± 0.17 μg/L, respectively. As a result, antibiotic pollution in the SW that takes the effluent of MBWWTP exists.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Aukidy, M., Verlicchi, P., Jelic, A., Petrovic, M., & Barcelò, D. (2012). Monitoring release of pharmaceutical compounds: occurrence and environmental risk assessment of two WWTP effluents and their receiving bodies in the Po Valley, Italy. Science of the Total Environment, 438, 15–25.
Auerbach, E. A., Seyfried, E. E., & McMahon, K. D. (2007). Tetracycline resistance genes in activated sludge wastewater treatment plants. Water Research, 41, 1143–1151.
Brain, R. A., Wilson, C. J., Johnson, D. J., Sanderson, H., Bestari, K., Hanson, M. L., Sibley, P. K., & Solomon, K. R. (2005). Effects of a mixture of tetracyclines to Lemna gibba and Myriophyllum sibiricum evaluated in aquatic microcosms. Environmental Pollution, 138(3), 425–442.
Chen, Y., Yu, G., Cao, Q., Zhang, H., Lin, Q., & Hong, Y. (2013). Occurrence and environmental implications of pharmaceuticals in Chinese municipal sewage sludge. Chemosphere, 93(9), 1765–1772.
Gao, P., Munir, M., & Xagoraraki, I. (2012). Correlation of tetracycline and sulfonamide antibiotics with corresponding resistance genes and resistant bacteria in a conventional municipal wastewater treatment plant. Science of the Total Environment, 421–422, 173–183.
Halling Sørensen, B., Sengelov, G., & Tjornelund, J. (2002). Toxicity of tetracyclines and tetracycline degradation products to environmentally relevant bacteria, including selected tetracycline-resistant bacteria. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 42(3), 263–271.
He, Y., Chen, W., Zheng, X., Wang, X., & Huang, X. (2013). Fate and removal of typical pharmaceuticals and personal care products by three different treatment processes. The Science of the Total Environment, 447, 248–254.
Hopkins, Z. R., & Blaney, L. (2014). A novel approach to modeling the reaction kinetics of tetracycline antibiotics with aqueous ozone. Science of the Total Environment, 468–469, 337–344.
Jeong, J., Song, W., Cooper, W. J., Jung, J., & Greaves, J. (2010). Degradation of tetracycline antibiotics: mechanisms and kinetic studies for advanced oxidation/reduction processes. Chemosphere, 78(5), 533–40.
Jia, A., Xiao, Y., Hu, J., Asami, M., & Kunikane, S. (2009). Simultaneous determination of tetracyclines and their degradation products in environmental waters by liquid chromatography–electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A, 1216(22), 4655–4662.
Karthikeyan, K. G., & Meyer, M. T. (2006). Occurrence of antibiotics in wastewater treatment facilities in Wisconsin, USA. Science of the Total Environment, 361(1–3), 196–207.
Kim, S. C., & Carlson, K. (2007). Temporal and spatial trends in the occurrence of human and veterinary antibiotics in aqueous and river sediment matrices. Environmental Science and Technology, 41, 50–57.
Köck-Schulmeyer, M., Villagrasa, M., López de Alda, M., Céspedes-Sánchez, R., Ventura, F., & Barceló, D. (2013). Occurrence and behavior of pesticides in wastewater treatment plants and their environmental impact. The Science of the Total Environment, 458, 466–76.
Kolpin, D. W., Furlong, E. T., Meyer, M. T., Thurman, E. M., Zaugg, S. D., Barber, L. B., & Buxton, H. T. (2002). Pharmaceuticals, hormones, and other organic wastewater contaminants in U.S. streams, 1999–2000: a national reconnaissance. Environmental Science and Technology, 36(6), 1202–1211.
Kummerer, K. (2003). Significance of antibiotics in the environment. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 52(1), 5–7.
Kummerer, K. (2010). Pharmaceuticals in the environment. Annual Review of Environment and Resources, 35, 57–75.
Le-Minh, N., Khan, S. J., Drewes, J. E., & Stuetz, R. M. (2010). Fate of antibiotics during municipal water recycling treatment processes. Water Research, 44(15), 4295–4323.
Leung, H. W., Minh, T. B., Murphy, M. B., Lam, J. C. W., So, M. K., Martin, M., Lam, P. K. S., & Richardson, B. J. (2012). Distribution, fate and risk assessment of antibiotics in sewage treatment plants in Hong Kong, South China. Environment International, 42, 1–9.
Lian, F., Song, Z., Liu, Z., Zhu, L., & Xing, B. (2013). Mechanistic understanding of tetracycline sorption on waste tire powder and its chars as affected by Cu2+ and pH. Environmental Pollution, 178, 264–270.
Lillenberg, M., Herodes, K., Kipper, K., Nei, L., (2010). Plant uptake of some pharmaceuticals from fertilized soils, proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology, 161–165.
Luo, Y., Xu, L., Rysz, M., Wang, Y., Zhang, H., & Alvarez, P. J. J. (2011). Occurrence and transport of tetracycline, sulfonamide, quinolone, and macrolide antibiotics in the Haihe River Basin, China. Environmental Science & Technology, 45, 1827–1833.
Luo, Y., Guo, W., Ngo, H. H., Nghiem, L. D., Hai, F. I., Zhang, J., Liang, S., & Wang, X. C. (2014). A review on the occurrence of micropollutants in the aquatic environment and their fate and removal during wastewater treatment. Science of the Total Environment, 473–474, 619–641.
Mispagel, H., & Gray, J. T. (2005). Antibiotic resistance from wastewater oxidation ponds. Water Environment Research, 77, 2996–3002.
Pamreddy, A., Hidalgo, M., Havel, J., & Salvadó, V. (2013). Determination of antibiotics (tetracyclines and sulfonamides) in biosolids by pressurized liquid extraction and liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography, A, 1298, 68–75.
Saitoh, T., Shibata, K., & Hiraide, M. (2014). Rapid removal and photodegradation of tetracycline in water by surfactant-assisted coagulation–sedimentation method. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2(I3), 1852–1858.
Škrášková, K., Santos, L. H. M. L. M., Šatínský, D., Pena, A., Montenegro, M. C. B. S. M., Solich, P., & Nováková, L. (2013). Fast and sensitive UHPLC methods with fluorescence and tandem mass spectrometry detection for the determination of tetracycline antibiotics in surface waters. Journal of Chromatography B, 927, 201–208.
Szczepanowski, R., Linke, B., Krahn, I., Gartemann, K. H., Gotzkow, T., Eichler, W., et al. (2009). Detection of 140 clinically relevant antibiotic resistance genes in the plasmid metagenome of wastewater treatment plant bacteria showing reduced susceptibility to selected antibiotics. Microbiology, 155, 2306–2319.
Topal, M., & Arslan Topal, E. I. (2011). Evaluation of the Elazig municipal wastewater treatment plant with some parameters in 2010–2011 winter season. Cumhuriyet Science Journal, 32(2), 1–12.
Topal, M., & Arslan Topal, E. I. (2014). Determination of the effect of municipal wastewater treatment plant effluents on the water quality of Kehli Stream. BEU Journal of Science, 3(1), 53–64.
Topal, M., Uslu, G., Şahin, M., Arslan Topal, E.I., (2012). Investigation of the presence of antibiotic residues in influent of Elazig municipal wastewater treatment plant, consumer society and environment symposium. Karabük, 33–47.
Topal, M., Uslu Şenel, G., Öbek, E., Arslan Topal, E.I., (2015). Bioaccumulation of tetracycline and degradation products in Lemna gibba L. exposed to secondary effluents. Desalination and Water Treatment, 1–8. doi:10.1080/19443994.2015.1018332
Urtiaga, A. M., Pérez, G., Ibáñez, R., & Ortiz, I. (2013). Removal of pharmaceuticals from a WWTP secondary effluent by ultrafiltration/reverse osmosis followed by electrochemical oxidation of the RO concentrate. Desalination, 331, 26–34.
Watkinson, A. J., Murby, E. J., & Costanzo, S. D. (2007). Removal of antibiotics in conventional and advanced wastewater treatment: implications for environmental discharge and wastewater recycling. Water Research, 41(18), 4164–4176.
Watkinson, A. J., Murby, E. J., Kolpin, D. W., & Costanzo, S. D. (2009). The occurrence of antibiotics in an urban watershed: from wastewater to drinking water. The Science of the Total Environment, 407(8), 2711–2723.
Zhou, L. J., Ying, G. G., Liu, S., Zhao, J. L., Yang, B., Chen, Z. F., & Lai, H. J. (2013a). Occurrence and fate of eleven classes of antibiotics in two typical wastewater treatment plants in South China. Science of the Total Environment, 452–453, 365–376.
Zhou, L. J., Ying, G. G., Liu, S., Zhang, R. Q., Lai, H. J., Chen, Z. F., & Pan, C. G. (2013b). EXcretion masses and environmental occurrence of antibiotics in typical swine and dairy cattle farms in China. Science of the Total Environment, 444, 183–195.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Topal, M., Arslan Topal, E.I. Occurrence and fate of tetracycline and degradation products in municipal biological wastewater treatment plant and transport of them in surface water. Environ Monit Assess 187, 750 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4978-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4978-4