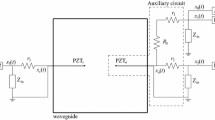
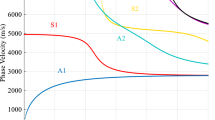
Abstract
The detection of cracks in mechanical engineering is mainly based on ultrasonic testing and Foucault currents. But even if they are efficient tools, this technology requires an important handling and is limited to the detection of cracks which are close to the source. Recently, several searchers have discussed the possibility of using waves as Lamb waves, for thin plates and shells, but also Love waves for bimaterials. In both cases the structure works as a wave guide and enables a long range propagation which is a promising possibility for detecting a crack quite far from the source. In this paper, we discuss the observability property of a small crack inside an open set using Love waves (the goal is to detect the beginning of the growth). It is proved that an adapted selection of these waves is necessary in order to avoid a black out which can occur for particular frequencies. This phenomenon is due to the fact that the crack has two extremities which can cancel their influence in a detection criterion. The main contribution of this paper is to discuss this point from a mathematical point of view, using an energy criterion requiring measurements quite far from the defect which should be detected.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avila-Pozos, O., Mishuris, G., Movchan, A.: Bloch-Floquet waves and localisation within a heterogeneous waveguides with long cracks. Contin. Mech. Thermodyn. 22, 545–553 (2010)
Blum, H., Dobrowolski, M.: On finite element methods for elliptic equations on domains with corners. Computing 28, 53–63 (1982)
Destuynder, Ph., Djaoua, M.: Sur une interpretation mathématique de l’intégrale de Rice en mécanique de la rupture fragile. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 3, 70–87 (1981)
Destuynder, Ph., Fabre, C.: Singularities occurring in multimaterials with transparent boundary conditions. Q. Appl. Math. 3, 443–463 (2016)
Destuynder, Ph., Fabre, C.: Few remarks on the use of Love waves in non destructive testing. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst., Ser. S 9, 427–444 (2016)
Dobrowolski, M.: Numerical Approximation of Elliptic Interface and Corner Problems. Habilitationsschrift, Bonn (1981)
Dumont-Fillon, J-C.: Contrôle non destructif par les ondes de Love et Lamb. Editions Techniques de l’ingénieur (2012)
Dunford, N., Schwartz, J.T.: Linear Operators, Part 1: General Theory. Wiley Classic Library. Wiley New York (1988)
Friedman, A., Vogelius, M.: Determining cracks by boundary measurements. Indiana Univ. Math. J. 38, 527–556 (1989)
Galvagni, A., Cawley, P.: The reflection of guided waves from simple supports in pipes. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 129, 1869–1880 (2011)
Grisvard, P.: Singularity in Domains with Corner. Pitman, London (1988)
Holmgrem, E.: Über Systeme von linearen partiellen Differentialgleichungen. Öfvers. K. Vetensk.-Akad. Förh., vol. 58, pp. 91–103 (1901)
Hutchinson, J.W., Mear, M.E., Rice, J.R.: Cracks paralleling an interface between dissimilar materials. J. Appl. Mech. 109, 828–832 (1987)
Kato, I.: Spectral Theory of Linear Operators. Springer, Berlin (1966)
Lions, J.L., Magenès, E.: Problèmes aux limites non homogènes, T.1. Dunod, Paris (1968)
Lowe, M.J.S.: In: Thompson, D.O., Chimenti, D.E. (eds.) Characteristics of the Reflection of Lamb Waves from Defects in Plates and Pipes. Review of Progress in Quantitative NDE, vol. 17, pp. 113–120. Plenum, New York (2002)
Marty, P.M.: Modelling of ultrasonic guided wave field generated by piezoelectric transducers. Thesis at Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine, University of London (2002). http://www3.imperial.ac.uk/pls/portallive/docs/1/50545711.PDF
Necas, J.: Les méthodes directes en théorie des équations elliptiques. Masson, Paris (1965)
Raviart, P.A., Thomas, J.M.: Approximation des équations aux dérivées partielles. Masson, Paris (1986)
Ribichini, R., Cegla, F., Nagy, P., Cawley, P.: Study and comparison of different EMAT configurations for SH wave inspection. IEEE Trans. UFFC 58, 2571–2581 (2011)
Rice, J.R.: A path-independent integral and the approximate analysis of strain concentration by notches and cracks. J. Appl. Mech. 35, 379–386 (1968)
Rice, J.R.: Two general integrals of singular crack tip deformation fields. J. Elast. 20(2), 131–142 (1988)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Destuynder, P., Fabre, C. Can We Hear the Echos of Cracks?. J Elast 130, 25–58 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10659-017-9632-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10659-017-9632-7