Abstract
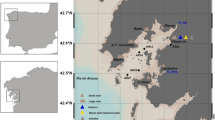
Rapid increase in industrialization and urbanization in the west coast of Peninsular Malaysia has led to the intense release of petroleum and products of petroleum into the environment. Surface sediment samples were collected from the Selangor River in the west coast of Peninsular Malaysia during four climatic seasons and analyzed for PAHs and biomarkers (hopanes). Sediments were soxhlet extracted and further purified and fractionated through first and second step column chromatography. A gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) was used for analysis of PAHs and hopanes fractions. The average concentrations of total PAHs ranged from 219.7 to 672.3 ng g−1 dw. The highest concentrations of PAHs were detected at 964.7 ng g−1 dw in station S5 in the mouth of the Selangor River during the wet inter-monsoonal season. Both pyrogenic and petrogenic PAHs were detected in the sediments with a predominance of the former. The composition of hopanes was homogeneous showing that petroleum hydrocarbons share an identical source in the study area. Diagnostic ratios of hopanes indicated that some of the sediment samples carry the crankcase oil signature.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abas, M., Rahman, N. A., Omar, N. Y. M., Maah, M. J., Abu Samah, A., Oros, D. R., et al. (2004). Organic composition of aerosol particulate matter during a haze episode in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Atmospheric Environment, 38, 4223–4241.
Abas, M. R. B., Simoneit, B. R. T., Elias, V., Cabral, J. A., & Cardoso, J. N. (1995). Composition of higher molecular weight organic matter in smoke aerosol from biomass combustion in Amazonia. Chemosphere, 30, 995–1015.
Bahry, P. S., Zakaria, M. P., Bin Abdullah, A. M., Abdullah, D. K., Sakari, M., Chandru, K., et al. (2009). Forensic Characterization of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Hopanes in Aerosols from Peninsular Malaysia. Environmental Forensics, 10, 240–252.
Bakhtiari, A. R., Zakaria, M. P., Yaziz, M. I., Lajis, M. N. H., & Bi, X. (2009). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and n-alkanes in suspended particulate matter and sediments from the Langat River, Peninsular Malaysia. Environment Asia, 2, 1–10.
Bakhtiari, A. R., Zakaria, M. P., Yaziz, M. I., Lajis, H., Nordin, M., Bi, X., et al. (2010). Distribution of PAHs and n-alkancs in Klang River surface Sediments, Malaysia. Pertanika Journal of Science & Technology, 18, 167–179.
Barrick, R. C., & Prahl, F. G. (1987). Hydrocarbon geochemistry of the Puget Sound region—III. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 25, 175–191.
Baumard, P., Budzinski, H., & Garrigues, P. (1998). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments and mussels of the western Mediterranean sea. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 17, 765–776.
Boonyatumanond, R., Wattayakorn, G., Togo, A., & Takada, H. (2006). Distribution and origins of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in riverine, estuarine, and marine sediments in Thailand. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 52, 942–956.
Bouloubassi, I., Roussiez, V., Azzoug, M., & Lorre, A. (2012). Sources, dispersal pathways and mass budget of sedimentary polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) in the NW Mediterranean margin, Gulf of Lions. Marine Chemistry, 142, 18–28.
Budzinski, H., Jones, I., Bellocq, J., Pierard, C., & Garriques, P. (1997). Evaluation of sediment contaminant by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Gironde estuary. Marine Chemistry, 58, 85–97.
Burton, G. A., Jr. (2002). Sediment quality criteria in use around the world. Limnology, 3, 65–76.
Cailleaud, K., Forget-Leray, J., Peluhet, L., LeMenach, K., Souissi, S., & Budzinski, H. (2009). Tidal influence on the distribution of hydrophobic organic contaminants in the Seine Estuary and biomarker responses on the copepod Eurytemora affinis. Environmental Pollution, 157, 64–71.
Cao, B., Nagarajan, K., & Loh, K. C. (2009). Biodegradation of aromatic compounds: Current status and opportunities for biomolecular approaches. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 85, 207–228.
Chalov, S. R., Jarsjö, J., Kasimov, N. S., Romanchenko, A. O., Pietroń, J., Thorslund, J., et al. (2015). Spatio-temporal variation of sediment transport in the Selenga River Basin, Mongolia and Russia. Environmental Earth Sciences, 73, 663–680.
Chandru, K., Zakaria, M. P., Anita, S., Shahbazi, A., Sakari, M., Bahry, P. S., et al. (2008). Characterization of alkanes, hopanes, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in tar-balls collected from the East Coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 56, 950–962.
Chen, C. W., & Chen, C. F. (2011). Distribution, origin, and potential toxicological significance of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in sediments of Kaohsiung Harbor, Taiwan. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 63, 417–423.
Commendatore, M. G., Esteves, J. L., & Colombo, J. C. (2000). Hydrocarbons in coastal sediments of Patagonia, Argentina: Levels and probable sources. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 40, 989–998.
Daka, E. R., & Ugbomeh, A. P. (2013). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediment and tissues of the Crab Callinectes pallidus from the Azuabie Creek of the Upper Bonny Estuary in the Niger Delta. Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology, 6, 2594–2600.
Dobbins, R. A., Fletcher, R. A., Benner, B. A., & Hoeft, S. (2006). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in flames, in diesel fuels, and in diesel emissions. Combustion and Flame, 144, 773–781.
El Nemr, A., El-Sadaawy, M. M., Khaled, A., & El-Sikaily, A. (2013). Distribution patterns and risks posed of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons contaminated in the surface sediment of the Red Sea coast (Egypt). Desalination and Water Treatment, 52, 7964–7982.
Fang, M., Zheng, M., Wang, F., To, K. L., Jaafar, A. B., & Tong, S. L. (1999). The solventextractable organic compounds in the Indonesia biomass burning aerosols–characterization studies. Atmospheric Environment, 33, 783–795.
Feng, C., Xia, X., Shen, Z., & Zhou, Z. (2007). Distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Wuhan section of the Yangtze River, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 133, 447–458.
Gallon, C., Tessier, A., Gobeil, C., & Beaudin, L. (2005). Sources and chronology of atmospheric lead deposition to a Canadian Shield lake: Inferences from Pb isotopes and PAH profiles. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 69, 3199–3210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2005.02.028.
Garrigues, P., Budzinski, H., Manitz, M., & Wise, S. (1995). Pyrolytic and petrogenic inputs in recent sediments: A definitive signature through phenanthrene and chrysene compound distribution. Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds, 7, 275–284.
González, J., Viñas, L., Franco, M., Fumega, J., Soriano, J., Grueiro, G., et al. (2006). Spatial and temporal distribution of dissolved/dispersed aromatic hydrocarbons in seawater in the area affected by the Prestige oil spill. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 53, 250–259.
Guo, Z., Lin, T., Zhang, G., Yang, Z., & Fang, M. (2006). High-resolution depositional records of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the central continental shelf mud of the East China Sea. Environmental Science and Technology, 40, 5304–5311.
Harji, R. R., Yvenat, A., & Bhosle, N. B. (2008). Sources of hydrocarbons in sediments of the Mandovi estuary and the Marmugoa harbour, west coast of India. Environment International, 34, 959–965.
Hartmann, P. C., Quinn, J., King, J. W., Tsutsumi, S., & Takada, H. (2000). Intercalibration of LABs in marine sediment SRM1941a and their application as a molecular marker in Narragansett Bay sediments. Environmental Science and Technology, 34, 900–906.
He, J., Zielinska, B., & Balasubramanian, R. (2010). Composition of semi-volatile organic compounds in the urban atmosphere of Singapore: influence of biomass burning. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 10, 11401–11413.
Hu, L., Guo, Z., Feng, J., Yang, Z., & Fang, M. (2009). Distributions and sources of bulk OM and aliphatic hydrocarbons in the surface sediments of the Bohai Sea, China. Marine Chemistry, 113, 197–211.
Iqbal, J., Overton, E. B., & Gisclair, D. (2008). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Louisiana Rivers and coastal environments: source fingerprinting and forensic analysis. Environmental Forensics, 9, 63–74.
Irwin, R. (1997). National Park Service. Environmental Contaminants Encyclopedia, PAHs Entry. Colorado: National Park Service.
Jiang, J. J., Lee, C. L., Fang, M. D., & Liu, J. T. (2009). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in coastal sediments of Southwest Taiwan: An appraisal of diagnostic ratios in source recognition. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 58, 752–760.
Karacik, B., Okay, O., Henkelmann, B., Bernhöft, S., & Schramm, K. W. (2009). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and effects on marine organisms in the Istanbul Strait. Environment International, 35, 599–606.
Karami, A., Christianus, A., Ishak, Z., Shamsuddin, Z. H., Masoumian, M., & Courtenay, S. C. (2012). Use of intestinal Pseudomonas aeruginosa in fish to detect the environmental pollutant benzo [a] pyrene. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 215–216, 108–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.02.038.
Karyab, H., Nasseri, S., Ahmadkhaniha, R., Rastkari, N., Mahvi, A. H., Nabizadeh, R., et al. (2014). Determination and source identification of polycyclic aromatics hydrocarbons in Karaj River, Iran. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 92, 50–56.
Katsoyiannis, A., Terzi, E., & Cai, Q. Y. (2007). On the use of PAH molecular diagnostic ratios in sewage sludge for the understanding of the PAH sources. Chemosphere, 69, 1337–1339.
Keshavarzifard, M., Zakaria, M. P., & Hwai, T. S. (2017). Bioavailability of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) to short-neck clam (Paphia undulata) from sediment matrices in mudflat areas of West coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Environmental Geochemistry and Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-016-9835-z.
Keshavarzifard, M., Zakaria, M. P., Hwai, T. S., Mustafa, S., Vaezzadeh, V., Magam, S. M., et al. (2014). Baseline distributions and sources of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the surface sediments from the Prai and Malacca Rivers, Peninsular Malaysia. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 88, 366–372.
Keshavarzifard, M., Zakaria, M. P., Hwai, T. S., Yusuff, F. M., & Mustafa, S. (2015). Distributions and source apportionment of sediment-associated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and hopanes in rivers and estuaries of Peninsular Malaysia. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4093-7.
Keshavarzifard, M., Zakaria, M. P., & Keshavarzifard, S. (2016). Evaluation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons contamination in the sediments of the Johor Strait, Peninsular Malaysia. Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds. https://doi.org/10.1080/10406638.2016.1257997.
Khalili, N. R., Scheff, P. A., & Holsen, T. M. (1995). PAH source fingerprints for coke ovens, diesel and gasoline engines, highway tunnels, and wood combustion emissions. Atmospheric Environment, 29, 533–542.
Larsen, R. K., III, & Baker, J. E. (2003). Source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the urban atmosphere: A comparison of three methods. Environmental Science and Technology, 37, 1873–1881.
Liang, Y., Tse, M., Young, L., & Wong, M. (2007). Distribution patterns of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the sediments and fish at Mai Po Marshes Nature Reserve, Hong Kong. Water Research, 41, 1303–1311.
Liu, Y., Chen, L., Jianfu, Z., Qinghui, H., Zhiliang, Z., & Hongwen, G. (2008). Distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments of rivers and an estuary in Shanghai, China. Environmental Pollution, 154, 298–305.
Liu, A., Egodawatta, P., Guan, Y., & Goonetilleke, A. (2013). Influence of rainfall and catchment characteristics on urban stormwater quality. Science of the Total Environment, 444, 255–262.
Long, E., Macdonald, D., Smith, S., & Calder, F. (1995). Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environmental Management, 19, 81–97.
Luellen, D. R., & Shea, D. (2003). Semipermeable membrane devices accumulate conserved ratios of sterane and hopane petroleum biomarkers. Chemosphere, 53, 705–713.
Luo, X. J., Chen, S. J., Ni, H. G., Yu, M., & Mai, B. X. (2008). Tracing sewage pollution in the Pearl River Delta and its adjacent coastal area of South China Sea using linear alkylbenzenes (LABs). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 56, 158–162.
Ma, X., Ran, Y., Gong, J., & Zou, M. (2007). Concentrations and inventories of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and organochlorine pesticides in watershed soil in the Pearl River Delta, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 145, 453–464.
Macdonald, D. D., Carr, R. S., Calder, F. D., Long, E. R., & Ingersoll, C. G. (1996). Development and evaluation of Sediment quality guidelines for Florida coastal waters. Ecotoxicology, 5, 253–278.
Magi, E., Bianco, R., Ianni, C., & Di Carro, M. (2002). Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the sediments of the Adriatic Sea. Environmental Pollution, 119, 91–98.
Mai, B. X., Fu, J. M., Sheng, G. Y., Kang, Y. H., Lin, Z., Zhang, G., et al. (2002). Chlorinated and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in riverine and esturine sediments from Pearl River Delta China. Environmental Pollution, 117, 457–474.
Maioli, O. L. G., Rodrigues, K. C., Knoppers, B. A., & Azevedo, D. A. (2010). Polycyclic aromatic and aliphatic hydrocarbons in Mytella charruana, a bivalve mollusk from Mundaú Lagoon, Brazil. Microchemical Journal, 96, 172–179.
Mandalakis, M., Gustafsson, O., Reddy, C. M., & Xu, L. (2004). Radiocarbon apportionment of fossil versus biofuel combustion sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Stockholm metropolitan area. Environmental Science and Technology, 38, 5344–5349.
Masiol, M., Hofer, A., Squizzato, S., Piazza, R., Rampazzo, G., & Pavoni, B. (2012). Carcinogenic and mutagenic risk associated to airborne particle-phase polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: A source apportionment. Atmospheric Environment, 60, 375–382.
Masood, N., Zakaria, M. P., Ali, M. M., Magam, S. M., Alkhadher, S. A., Keshavarzifard, M., et al. (2014). Distribution of petroleum hydrocarbons in surface sediments from selected locations in Kuala Selangor River, Malaysia. In A. Z. Aris, et al. (Eds.), From sources to solution (pp. 351–356). Singapore: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-4560-70-2_64.
Masood, N., Zakaria, M. P., Halimoon, N., Aris, A. Z., Magam, S. M., Kannan, N., et al. (2016). Anthropogenic waste indicators (AWI) particularly PAHs and LABs in Malaysian sediments: Application of aquatic environment for identifying anthropogenic pollution. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 102, 160–175.
Mirsadeghi, S. A., Zakaria, M. P., Yap, C. K., & Gobas, F. (2013). Evaluation of the potential bioaccumulation ability of the blood cockle (Anadara granosa) for assessment of environmental matrices of mudflats. Science of the Total Environment, 454, 584–597.
Mirsadeghi, S. A., Zakaria, M. P., Yap, C. K., & Shahbazi, A. (2011). Risk assessment for the daily intake of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from the ingestion of cockle (Anadara granosa) and exposure to contaminated water and sediments along the west coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 23, 336–345.
Mitchell, P. K. K., Mills, G., Fisher-Niwa, G., Eason-Landcare, C., (1998). Technical paper No. 37 Toxic.
Nozar, S. L. M., Ismail, W. R., & Zakaria, M. P. (2014). Distribution, sources identification, and ecological risk of PAHs and PCBs in coastal surface sediments from the Northern Persian Gulf. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal, 20, 1507–1520.
Okuda, T., Kumata, H., Zakaria, M. P., Naraoka, H., Ishiwatari, R., & Takada, H. (2002). Source identification of Malaysian atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons nearby forest fires using molecular and isotopic compositions. Atmospheric Environment, 36, 611–618.
Omar, N.-Y.-M.-J., Abas, M.-R.-B., Ketuly, K.-A., & Tahir, N-Md. (2002). Concentrations of PAHs in atmospheric particles (PM-10) and road side soil particles collected in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Atmospheric Environment, 36, 247–254.
Omar, N.-Y.-M.-J., Mon, T.-C., Rahman, N.-A., & Abas, M.-R.-B. (2006). Distributions and health risks of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in atmospheric aerosols of Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Science of the Total Environment, 369, 76–81.
Ouyang, Y., Zhang, J. E., & Ou, L. T. (2006). Temporal and spatial distributions of sediment total organic carbon in an estuary river. Journal of Environmental Quality, 35, 93–100.
Pereira, W. E., Hostettler, F. D., Luoma, S. N., Van Geen, A., Fuller, C. C., & Anima, R. J. (1999). Sedimentary record of anthropogenic and biogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in San Francisco Bay, California. Marine Chemistry, 64, 99–113.
Peters, K. E., & Moldowan, J. M. (1993). The Biomarker Guide: Interpreting molecular fossils in petroleum and ancient sediments. Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
Phelps, H. L. (2000). DC AES contaminated Anacostia Estuary sediments: A biomonitoring approach. Report, DC Water Resources Research Center, Washington, DC.
Prahl, F. G., Crecelius, E., & Carpenter, R. (1984). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Washington coastal sediments: An evaluation of atmospheric and riverine routes of introduction. Environmental Science and Technology, 18, 687–693.
Prince, R. C., Elmendorf, D. L., Lute, J. R., Hsu, C. S., Halth, C. E., Senlus, J. D., et al. (1994). 17a(H),21a(H)-Hopane as a conservative internal marker for estimating the biodegradation of crude oil. Environmental Science and Technology, 28, 142–145.
Qiao, M., Wang, C., Huang, S., Wang, D., & Wang, Z. (2006). Composition, sources, and potential toxicological significance of PAHs in the surface sediments of the Meiliang Bay, Taihu Lake, China. Environment International, 32, 28–33.
Ramdahl, T. (1983). Retene—A molecular marker of wood combustion in ambient air. Nature, 306, 580–582.
Raza, M., Zakaria, M. P., Hashim, N. R., Yim, U. H., Kannan, N., & Ha, S. Y. (2013). Composition and source identification of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in mangrove sediments of Peninsular Malaysia: Indication of anthropogenic input. Environmental Earth Sciences, 70, 2425–2436.
Retnam, A., Zakaria, M. P., Juahir, H., Aris, A. Z., Zali, M. A., & Kasim, M. F. (2013). Chemometric techniques in distribution, characterisation and source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHS) in aquaculture sediments in Malaysia. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 69, 55–66.
Saha, M., Togo, A., Mizukawa, K., Murakami, M., Takada, H., Zakaria, M. P., et al. (2009). Sources of sedimentary PAHs in tropical Asian waters: Differentiation between pyrogenic and petrogenic sources by alkyl homolog abundance. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 58, 189–200.
Sakari, M., & Zakaria, M. P. (2013). Distribution, characterization and origins of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in surficial sediment of Penang, Malaysia: The presence of fresh and toxic substances. World Applied Sciences Journal, 23, 1481–1488.
Sakari, M., Zakaria, M. P., Junos, M. B. M., Annuar, N. A., Yun, H. Y., Heng, Y. S., et al. (2008a). Spatial distribution of petroleum hydrocarbon in sediments of major rivers from east coast of peninsular Malaysia. Estuarine and Coastal Marine Science, 31, 9–18.
Sakari, M., Zakaria, M. P., Lajis, N. H., Mohamed, C. A. R., Bahry, P. S., & Anita, S. (2008b). Characterization, distribution, sources and origins of aliphatic hydrocarbons from surface sediment of Prai Strait, Penang, Malaysia: A widespread anthropogenic input. Environment Asia, 2, 1–14.
Sakari, M., Zakaria, M. P., Mohamed, C. A. R., Lajis, N. H., Chandru, K., Bahry, P. S., et al. (2010). Urban vs. Marine based oil pollution in the strait of Johor, Malaysia: A century record. Soil and Sediment Contamination, 19, 644–666.
Sanger, D. M., Holland, A. F., & Scott, G. I. (1999). Tidal creek and salt marsh sediments in South Carolina coastal estuaries: II. Distribution of organic contaminants. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 37, 458–471.
Schumacher, B. A. (2002). Methods for the determination of total organic carbon (TOC). Soils and Sediments. Washington DC: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
Sicre, M., Marty, J., Saliot, A., Aparicio, X., Grimalt, J., & Albaiges, J. (1987). Aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons in different sized aerosols over the Mediterranean Sea: Occurrence and origin. Atmospheric Environment, 21, 2247–2259.
Simoneit, B. R. T. (2002). Biomass burning—A review of organic tracers for smoke from incomplete combustion. Applied Geochemistry, 17, 129–162.
Soclo, H. H., Garrigues, P., & Ewald, M. (2000). Origin of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in coastal marine sediments: Case Studies in Cotonou (Benin) and Aquitaine (France) areas. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 40, 387–396.
Stout, S. A., Uhler, A. D., & Emsbo-Mattingly, S. D. (2004). Comparative evaluation of background anthropogenic hydrocarbons in surficial sediments from nine urban waterway. Environmental Science and Technology, 38, 2987–2994.
Suneel, V., Vethamony, P., Naik, B. G., Vinod Kumar, K., Sreenu, L., Samiksha, S. V., et al. (2014). Source investigation of the Tar Balls deposited along the Gujarat Coast, India, using chemical fingerprinting and transport modeling techniques. Environmental Science and Technology, 48, 11343–11351.
Tahir, N. M., Fadzil, M. F., Ariffin, J., Maarop, H., & Wood, A. K. H. J. (2011). Sources of polycylic aromatic hydrocarbons in mangrove sediments of pulau cik wan dagang, kemaman. Journal of Sustainability and Science Management, 6, 98–106.
Takada, H., Onda, T., Harada, M., & Ogura, N. (1991). Distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in street dust from the Tokyo Metropolitan area. Science of the Total Environment, 107, 45–69.
Tee, L. T., & Mohamed, C. A. R. (2005). Activities of 210Po and 210Pb in the water column at Kuala Selangor, Malaysia. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 80, 273–286.
Tsymbalyuk, K. K., Den’ga, Y. M., Berlinsky, N. A., & Antonovich, V. P. (2011). Determination of 16 priority polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in bottom sediments of the Danube estuarine coast by GC/MS. Geo-Eco-Marina, 17, 67–72.
Vaezzadeh, V., Zakaria, M. P., & Bong, C. W. (2017a). Aliphatic hydrocarbons and triterpane biomarkers in mangrove oyster (Crassostrea belcheri) from the west coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Marine Pollution Bulletin. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.07.008.
Vaezzadeh, V., Zakaria, M. P., Bong, C. W., Masood, N., Mohsen Magam, S., & Alkhadher, S. (2017b). Mangrove oyster (Crassostrea belcheri) as a biomonitor species for bioavailability of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from sediment of the West Coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds. https://doi.org/10.1080/10406638.2017.1348366.
Vaezzadeh, V., Zakaria, M. P., Mustafa, S., Ibrahim, Z. Z., Shau-Hwai, A. T., Keshavarzifard, M., et al. (2015a). Source type evaluation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in surface sediments from the Muar River and Pulau Merambong, Peninsular Malaysia. Environmental Forensic, 16, 135–142.
Vaezzadeh, V., Zakaria, M. P., Mustafa, S., Ibrahim, Z. Z., Shau-Hwai, A. T., Keshavarzifard, M., et al. (2014). Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in sediment from Muar River and Pulau Merambong, Peninsular Malaysia. In A. Z. Aris, et al. (Eds.), From sources to solution (pp. 451–455). Singapore: Springer.
Vaezzadeh, V., Zakaria, M. P., Shau-Hwai, A. T., Ibrahim, Z. Z., Mustafa, S., Jahromi, F. A., et al. (2015b). Forensic investigation of aliphatic hydrocarbons in the sediments from selected mangrove ecosystems in the west coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 100, 311–320.
Volkman, J. K. (1986). A review of sterol markers for marine and terrigenous OM. Organic Geochemistry, 9, 83–99.
Volkman, J. K., Revill, A. T., & Murray, A. P. (1997). Applications of biomarkers for identifying sources of natural and pollutant hydrocarbons in aquatic environments. ACS Symposium Series (pp. 110–132). Washington DC: American Chemical Society.
Wang, Z., Fingas, M., & Sergy, G. (1994). Study of 22-year-old Arrow oil samples using biomarker compounds by GC/MS. Environmental Science and Technology, 28, 1733–1746.
Wang, H. S., Liang, P., Kang, Y., Shao, D. D., Zheng, G. J., Wu, S. C., et al. (2010). Enrichment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in mariculture sediments of Hong Kong. Environmental Pollution, 158, 3298–3308.
Wang, Z., Stout, S. A., & Fingas, M. (2006). Forensic fingerprinting of biomarkers for oil spill characterization and source identification. Environmental Forensics, 7, 105–146.
Wang, Z., Yang, C., Fingas, M., Hollebone, B., Yim, U. H., & Oh, J. R. (2007). Petroleum biomarker fingerprinting for oil spill characterization and source identification. In Z. Wang & S. A. Stout (Eds.), Oil spill environmental forensics: Fingerprinting and source identification (p. 73). London: Academic Press.
Witt, G., & Trost, E. (1999). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in sediments of the Baltic Sea and of the German coastal waters. Chemosphere, 38, 1603–1614.
Yang, H.-H., & Chen, C. M. (2004). Emission inventory and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the atmosphere at a suburban area in Taiwan. Chemosphere, 56, 879–887.
Yang, H. H., Chien, S. M., Lo, M. Y., Lan, J. C. W., Lu, W. C., & Ku, Y. Y. (2007). Effects of biodiesel on emissions of regulated air pollutants and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons under engine durability testing. Atmospheric Environment, 41, 7232–7240.
Yang, Y., & Hofmann, T. (2009). Aqueous accelerated solvent extraction of native polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from carbonaceous river floodplain soils. Environmental Pollution, 157, 2604–2609.
Yang, H.-H., Jung, R.-C., Wang, Y.-F., & Hsieh, L.-T. (2005). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons emission from joss paper furnaces. Atmospheric Environment, 39, 3305–3312.
Ye, B., Zhang, Z., & Mao, T. (2006). Pollution sources identification of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons of soils in Tianjin area, China. Chemosphere, 64, 525–534.
Youngblood, W. W., & Blumer, M. (1975). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the environment: Homologous series in soils and recent marine sediments. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 39, 1303–1314.
Yunker, M. B., Macdonald, R. W., Vingarzan, R., Mitchell, R. H., Goyette, D., & Sylvestre, S. (2002). PAHs in the Fraser River basin: A critical appraisal of PAH ratios as indicators of PAH source and composition. Organic Geochemistry, 33, 489–515.
Zaghden, H., Kallel, M., Louati, A., Elleuch, B., Oudot, J., & Saliot, A. (2005). Hydrocarbons in surface sediments from the Sfax coastal zone (Tunisia), Mediterranean Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 50, 1287–1294.
Zakaria, M. P., Horinouchi, A. I., Tsutsumi, S., Takada, H., Tanabe, S., & Ismail, A. (2000). Oil pollution in the Straits of Malacca, Malaysia: Application of molecular markers for source identification. Environmental Science and Technology, 34, 1189–1196.
Zakaria, M. P., & Mahat, A. A. (2006). Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAHs) in sediments in the Langat Estuary. Coastal Marine Science, 30, 387–395.
Zakaria, M. P., Okuda, T., & Takada, H. (2001). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAHs) and hopanes in stranded tar-balls on the coasts of Peninsular Malaysia: Applications of biomarkers for identifying sources of oil pollution. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 42, 1357–1366.
Zakaria, M. P., Takada, H., Tsutsumi, S., Ohno, K., Yamada, J., Kouno, E., et al. (2002). Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in rivers and estuaries in Malaysia: A widespread input of petrogenic PAHs. Environmental Science and Technology, 36, 1907–1918.
Zemo, D. A. (2009). Use of parent polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) proportions to attribute PAH sources in sediments: A case study from the Pacific Northwest. Environment Forensics, 10, 229–239.
Zhao, X., Ding, J., & You, H. (2014). Spatial distribution and temporal trends of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in water and sediment from Songhua River, China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 36, 131–143.
Acknowledgements
This study was a part of Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) Asian Core Project on Straits of Malacca funded by the Ministry of Higher Education of Malaysia, through Universiti Putra Malaysia (Project No. 6379005) and HICoE-MOHE Grant IOES-2014. We would like to thank them for supporting this research financially.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Masood, N., Halimoon, N., Aris, A.Z. et al. Seasonal variability of anthropogenic indices of PAHs in sediment from the Kuala Selangor River, west coast Peninsular Malaysia. Environ Geochem Health 40, 2551–2572 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0122-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0122-z