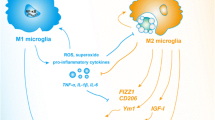
Abstract
Microglia has been reported to be able to regulate the proliferation, differentiation and survival of adult neural stem/progenitor cells (NSPCs) by modulating the microenvironment, which results in different consequences of adult neurogenesis. However, whether the microglial activation is beneficial or harmful to NSPCs is still controversial because of the complexity and variability of microglial activation phenotypes. In this study, we systematically explored the activation phenotypes of IFN-γ- or IL-4-induced microglia at different time after stimulation, and investigated the effects of the secretome of different phenotype of microglia on the process of proliferation, differentiation and survival of NSPCs. Moreover, the possible molecular pathways of secretory influence on NSPCS were further explored using western blotting. The result showed that IFN-γ and IL-4 differently regulate microglial phenotypes, IL-4 induced a M2-like phenotype, while IFN-γ induced a M1-like phenotype. These phenotypes of microglia can only be maintained for 24 h after removal of IFN-γ or IL-4 intervention. The secretome from IFN-γ- or IL-4-induced microglia also had opposite effects on NSPCs proliferation, differentiation and survival. The secretome from the IL-4-treated microglia promoted NSPCs proliferation, survival and differentiation into neurons and oligodendrocytes, while factors secreted by the INF-γ-treated microglia stimulated the NSPCs differentiation into astrocyte, inhibited the neurogenesis and oligodendrogliogenesis, and induced NSPCs apoptosis. Furthermore, the PI3K-Akt pathway mediates the effects of the secretome from IFN-γ- or IL-4-induced microglia on NSPC proliferation, differentiation, and survival. In conclusion, our results suggested that the secretome of microglia induced by IL-4 of IFN-γ differently regulate proliferation, differentiation and survival of adult neural stem/progenitor cell by targeting the PI3K-Akt pathway. These findings will help further study the biological mechanism of microglia regulating neurogenesis, and provide a therapeutic strategy for neurological diseases by regulating microglial phenotypes to affect neurogenesis.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Berger T, Lee H, Young AH, Aarsland D, Thuret S (2020) Adult hippocampal neurogenesis in major depressive disorder and Alzheimer’s Disease. Trends Mol Med 26:803–818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2020.03.010
Cacci E, Ajmone-Cat MA, Anelli T, Biagioni S, Minghetti L (2008) In vitro neuronal and glial differentiation from embryonic or adult neural precursor cells are differently affected by chronic or acute activation of microglia. Glia 56:412–425. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.20616
Chu W, Yuan J, Huang L, Xiang X, Zhu H, Chen F, Feng H (2015) Valproic acid arrests proliferation but promotes neuronal differentiation of adult spinal NSPCs from SCI rats. Neurochem Res 40:1472–1486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1618-x
Hu X, Li P, Guo Y, Wang H, Leak RK, Chen S, Chen J (2012) Microglia/macrophage polarization dynamics reveal novel mechanism of injury expansion after focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 43:3063–3070. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.112.659656
Jiang X, He H, Mo L, Liu Q, Yang F, Zhou Y, Zhang J (2021) Mapping the plasticity of morphology, molecular properties and function in mouse primary microglia. Front Cell Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2021.811061
Kawabori M, Yenari MA (2015) The role of the microglia in acute CNS injury. Metab Brain Dis 30(2):381–392. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-014-9531-6
Li Q, Barres BA (2018) Microglia and macrophages in brain homeostasis and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 18:225–242. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri.2017.125
Mastrangelo MA, Sudol KL, Narrow WC, Bowers WJ (2009) Interferon-{gamma} differentially affects Alzheimer’s disease pathologies and induces neurogenesis in triple transgenic-AD mice. Am J Pathol 175:2076–2088. https://doi.org/10.2353/ajpath.2009.090059
Matsui TK, Mori E (2018) Microglia support neural stem cell maintenance and growth. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 503:1880–1884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.07.130
Nakanishi M, Niidome T, Matsuda S, Akaike A, Kihara T, Sugimoto H (2007) Microglia-derived interleukin-6 and leukaemia inhibitory factor promote astrocytic differentiation of neural stem/progenitor cells. Eur J Neurosci 25:649–658. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05309.x
Nikolakopoulou AM, Dutta R, Chen Z, Miller RH, Trapp BD (2013) Activated microglia enhance neurogenesis via trypsinogen secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:8714–8719. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1218856110
Osman AM, Rodhe J, Shen X, Dominguez CA, Joseph B, Blomgren K (2019) The secretome of microglia regulate neural stem cell function. Neuroscience 405:92–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.10.034
Panagiotakopoulou V, Ivanyuk D, De Cicco S, Haq W, Arsić A, Yu C, Deleidi M (2020) Interferon-γ signaling synergizes with LRRK2 in neurons and microglia derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Nat Commun 11:5163. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-18755-4
Paolicelli RC, Bolasco G, Pagani F, Maggi L, Scianni M, Panzanelli P, Gross CT (2011) Synaptic pruning by microglia is necessary for normal brain development. Science 333:1456–1458. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1202529
Taylor SE, Morganti-Kossmann C, Lifshitz J, Ziebell JM (2014) Rod microglia: a morphological definition. PLoS ONE 9:e97096. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0097096
Toni N, Laplagne DA, Zhao C, Lombardi G, Ribak CE, Gage FH, Schinder AF (2008) Neurons born in the adult dentate gyrus form functional synapses with target cells. Nat Neurosci 11:901–907. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2156
Wang G, Zhang J, Hu X, Zhang L, Mao L, Jiang X, Chen J (2013) Microglia/macrophage polarization dynamics in white matter after traumatic brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 33:1864–1874. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2013.146
Xu C, Loh HH, Law PY (2016) Effects of addictive drugs on adult neural stem/progenitor cells. Cell Mol Life Sci 73:327–348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-015-2067-z
Yuan J, Ge H, Liu W, Zhu H, Chen Y, Zhang X, Lin J (2017) M2 microglia promotes neurogenesis and oligodendrogenesis from neural stem/progenitor cells via the PPARγ signaling pathway. Oncotarget 8:19855–19865. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.15774
Zhang J, He H, Qiao Y, Zhou T, He H, Yi S, You Z (2020) Priming of microglia with IFN-γ impairs adult hippocampal neurogenesis and leads to depression-like behaviors and cognitive defects. Glia 68:2674–2692. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.23878
Zhang Z, Yao L, Yang J, Wang Z, Du G (2018) PI3K/Akt and HIF-1 signaling pathway in hypoxia-ischemia (Review). Mol Med Rep 18:3547–3554. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2018.9375
Zhao W, Beers DR, Appel SH (2013) Immune-mediated mechanisms in the pathoprogression of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 8(4):888–899. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-013-9489-x
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge Professor Tao Zhou at the Resource Center of the Chinese Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Zili You at University of Electronic Science and Technology of China for giving us guidance on the experiment and writing.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81960811, 82060726), the PhD Start-up Fund of the Guizhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine ([2019]31), Guizhou Science and Technology Plan Project ([2019]5611), the Department of Science and Technology of Guizhou High-level Innovative Talents ([2018]5638-2), and the Department of Science and Technology of Guizhou basic research ([2019]1026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JX, and ZJ designed the conceptual idea for this study and wrote the manuscript. YS, LQ and ZJ performed the experiments. ZJ analyzed these data. All the authors participated in the discussion and approved the manuscript as submitted.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict interest
Author declares that there is no conflict of interest in this research.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
The animal study was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China.
Consent for publication
All authors agree to the publication of this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, X., Yi, S., Liu, Q. et al. The secretome of microglia induced by IL-4 of IFN-γ differently regulate proliferation, differentiation and survival of adult neural stem/progenitor cell by targeting the PI3K-Akt pathway. Cytotechnology 74, 407–420 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-022-00534-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-022-00534-2