Abstract
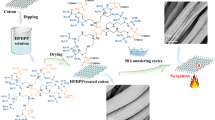
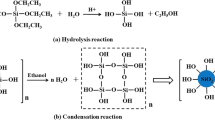
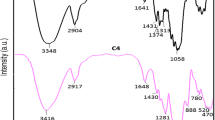
Textiles with superior anti-flammability properties combined with minimal environmental impact are extremely necessary to reduce fire-related issues. In this regard, diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings on cotton fabrics may represent promising candidates as potential flame-retardant (FR) materials. Herein, superhydrophobic and fire-resistant cotton fabrics were fabricated through a two-step plasma strategy by alternately exposing substrates to H2 and O2 plasma pre-treatments and subsequent DLC deposition. Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopy analysis has revealed that different plasma pre-treatments can impose surface modifications on the chemical structure of cotton, especially in carboxylic and hydroxyl groups, leading to a radical alteration of surface roughness and of the crystalline cellulosic external structure. These changes deeply influenced the growth of DLC thin films and the surface properties of cotton fabric because of the combination of a hierarchical structure and surface chemistry as verified using field emission gun-scanning electron microscopy and water contact angle measurements. The effects of both specific gases used in the pre-treatment step and duration of pre-treatment were analysed and compared using thermogravimetric analyses. The H2-pre-treated DLC cottons exhibited good potential as an FR material, showing improved thermal stability in respect to untreated cotton, as evidenced by increased ignition times. Moreover, vertical burning tests have demonstrated that DLC-cotton systems exhibit enhanced flammability resistance.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balu B, Breedveld V, Hess DW (2008) Fabrication of "roll-off" and "sticky" superhydrophobic cellulose surfaces via plasma processing. Langmuir 24(9):4785–4790
Caschera D, Cossari P, Federici F, Kaciulis S, Mezzi A, Padeletti G, Trucchi D (2011) Influence of PE-CVD parameters on the properties of diamond-like carbon films. Thin Solid Films 519:4087–4091
Caschera D, Cortese B, Mezzi A, Brucale M, Ingo GM, Gigli G, Padeletti G (2013) Ultra hydrophobic/superhydrophilic modified cotton textiles through functionalized diamond-like carbon coatings for self-cleaning applications. Langmuir 29:2775–2783
Caschera D, Mezzi A, Cerri L, de Caro T, Riccucci C, Biasiucci M, Ingo GM, Padeletti G, Gigli G, Cortese B (2014) Effects of plasma treatments for improving extreme wettability of cotton fabrics. Cellulose 21:741–756
Chan CM (1994) Polymer surface modification and characterization. Hanser/Gardner Publications, Munich, pp 265–279
Chen DQ, Wang YZ, Hu XP, Wang DY, Qu MH, Yang B (2005) Flame-retardant and anti-dripping effects of a novel char-forming flame retardant for the treatment of poly(ethylene terephthalate) fabrics. Polym Degrad Stabil 88(2):349–356
Ciolacu D, Ciolacu F, Popa VI (2011) Amorphous cellulose-structure and characterization. Cellul Chem Technol 45(1):213–221
Cortese B, Caschera D, Padeletti G, Ingo GM, Gigli G (2013) A brief review of surface functionalized cotton fabrics. Surf Innov 1(3):140–156
Cortese B, Caschera D, Federici F, Ingo GM, Gigli G (2014) Superhydrophobic fabrics for oil/water separation through a diamond like carbon (DLC) coating. J Mater Chem A 2:6781–6789
Eichhorn SJ (2011) Cellulose nanowhiskers: promising materials for advanced applications. Soft Matter 7:303–315
Gaan S, Sun G (2007) Effect of phosphorus flame retardants on thermo-oxidative decomposition of cotton. Polym Degrad Stabil 92(6):968–974
Hobart SR, Rowland SP (1978) Burning rate of layered combinations of flame-retardant and untreated cotton. Text Res J 48(8):437–442
Horrocks AR (2011) Flame retardant challenges for textiles and fibres: new chemistry versus innovatory solutions. Polym Degrad Stabil 96:377–392
Karahan HA, Özdogan E (2008) Improvements of surface functionality of cotton fibers by atmospheric plasma treatment. Fibers Polym 9:21–26
Kim YS, Li YC, Pitts WM, Werrell M, Davis RD (2014) Rapid growing clay coatings to reduce the fire threat of furniture. ACS Appl Mater Inter 6(3):2146–2152
Kitahara N, Sato T, Isogawa H, Ohgoe Y, Masuko S, Shizuku F, Hirakuri KK (2010) Antibacterial property of DLC film coated on textile material. Diam Rel Mater 19:690–694
Lam YL, Kan CW, Yuen CWM (2011) Physical and chemical analysis of plasma-treated cotton fabric subjected to wrinkle-resistant finishing. Cellulose 18(2):493–503
Laufer G, Carosio F, Martinez R, Camino G, Grunlan JC (2011) Growth and fire resistance of colloidal silica–polyelectrolyte thin film assemblies. J Colloid Interface Sci 356:69–77
Lavoine N, Desloges I, Dufresne A, Bras J (2012) Microfibrillated cellulose: its barrier properties and applications in cellulosic materials—a review. Carbohyd Polym 90(2):735–764
Li Y-C, Mannen S, Morgan AB, Chang S, Yang Y-H, Condon B, Grunlan JC (2011a) Intumescent all-polymer multilayer nanocoating capable of extinguishing flame on fabric. Adv Mater 23:3926–3931
Li Y-C, Mannen S, Schulz J, Grunlan JC (2011b) Growth and fire protection behavior of POSS-based multilayer thin films. J Mater Chem 21:3060–3069
Malek RMA, Holme I (2003) The effect of plasma treatment on some properties of cotton. Iran Polym J 12(4):271–280
Matsumoto R, Sato K, Ozeki K, Hirakuri K, Fukui Y (2008) Cytotoxicity and tribological property of DLC films deposited on polymeric materials. Diam Rel Mater 17:1680–1684
Moon RJ, Martini A, Nairn J, Simonsen J, Youngblood J (2011) Cellulose nanomaterials review: structure, properties and nanocomposites. Chem Soc Rev 40:3941–3994
Peng BL, Dhar N, Liu HL, Tam KC (2011) Chemistry and applications of nanocrystalline cellulose and its derivatives: a nanotechnology perspective. Can J Chem Eng 89(5):1191–1206
Proniewicz M, Pulaszkiewicz C, Weselucha-Birczynska A, Majcherczyk H, Baranski A, Konieczna A (2001) FT-IR and FT-Raman study on hydrothermally degradated cellulose. J Mol Struct 596:163–169
Samanta KK, Jassal M, Agrawa AK (2009) Improvement in water and oil absorbency of textile substrate by atmospheric pressure cold plasma treatment. Surf Coat Technol 203:1336–1342
Shin B, Lee KR, Moon MW, Kim HY (2012) Extreme water repellency of nanostructured low-surface-energy non-woven fabrics. Soft Matter 8:1817–1823
Tipson RS (1968) Infrared spectroscopy of carbohydrates. National Bureau of Standards Monograph 110, U.S. Department of Commerce, DC
Tu AT, Lee J, Milanovich FP (1979) Laser-Raman spectroscopic study of cyclohexaamylose and related compounds; Spectral analysis and structural implications. Carbohyd Res 76:239–244
Wang X, Quintero MR, Zhang XQ, Wang R, Wang DY (2015) Intumescent multilayer hybrid coating for flame retardant cotton fabrics based on layer-by-layer assembly and sol–gel process. RSC Adv 5:10647–10655
Wu W, Yang CHQ (2006) Comparison of different reactive organophosphorus flame retardant agents for cotton: part I. The bonding of the flame retardant agents to cotton. Polym Degrad Stabil 91:2541–2548
Yang Z, Wang X, Lei D, Fei B, John H, Xin A (2012) Durable flame retardant for cellulosic fabrics. Polym Degrad Stabil 97:2467–2472
Zhang M, Wang C (2013) Fabrication of cotton fabric with superhydrophobicity and flame retardancy. Carbohydr Polym 96(2):396–402
Zhang CD, Price LM, Daly WH (2006) Synthesis and characterization of a trifunctional aminoamide cellulose derivative. Biomacromolecules 7(1):139–145
Zhou Z, Zhou W (1987) The flame-retardant standards of textile overseas. Institute of Textile Standard at Textile Ministry, Beijing
Zhou H, Lei X, Ogino A, Nagatsu M (2008) Investigation into the antibacterial property of carbon films. Diam Rel Mater 17:1416–1419
Zhu P, Sui S, Wang B, Sun K, Sun G (2004) A study of pyrolysis and pyrolysis products of flame retardant cotton fabrics by DSC, TGA and PY-GC-MS. J Anal Appl Pyrol 71:645–655
Acknowledgments
The authors want to thank Dr. S. Nunziante Cesaro for her assistance and technical support for FT-IR analysis. This work was financially supported by PON-PANREX (Project no. PON01_01322), PON-MAAT (Project no. PON02_00563_3316357) and EFOR-CNR and funded by the Regione Puglia (APQ-Reti di Laboratorio, Project PHOEBUS, cod. 31).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caschera, D., Toro, R.G., Federici, F. et al. Flame retardant properties of plasma pre-treated/diamond-like carbon (DLC) coated cotton fabrics. Cellulose 22, 2797–2809 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0661-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0661-8