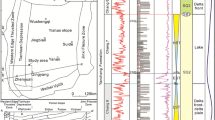
In order to clarify the diagenesis of the conglomerate reservoir in the Lower Wuerhe Formation in Mahu 1 well area, Junggar Basin, the reservoir in the study area was studied in detail on the basis of core observation, thin section identification and analysis data. The results show that the Lower Wuerhe Formation is a reservoir with low porosity and low permeability. The pore types are mainly residual intergranular pores, followed by dissolution pores, and occasionally structural fractures and microfractures. The reservoir physical property is closely related to the rock facies type, among which the fine conglomerate is the best, the small conglomerate is the second, and the middle conglomerate is the worst. The Lower Wuerhe Formation in the study area mainly experienced diagenesis such as compaction, cementation and dissolution. In the later stage of diagenesis, zeolite minerals were transformed and dissolved, and a large number of dissolution pores were formed, which had a positive effect on reservoir physical property and oil content. Through three solution pore porosity intersection method to establish evaluation model, and solution pore zeolites in the studied area development situation to carry on the quantitative evaluation, fine recognition, effectively guide the advantage dessert for reservoir evaluation and subsequent development provides new ideas and methods, as well as neighbors area and the development of other clastic rock area reservoir development for reference.












Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Xiangchao M., Yang X., Shouhua H. Distribution rule of laumontite and favorable reservoir forecast of P3w in Zhongguairegion [J]. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 2013, 37(1): 16.
Shan X., Guo H., Zou Z. Diagenesis in alkaline environment and its influences on reservoir quality: A case study of Middle-Lower Permian Clastic Reservoirs in northwestern margin of Junggar Basin [J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2018, 39(1): 55-62.
Ma Y., Zhang X., Huang L. et al. Characteristics and controlling factors of glutenite reservoir rock quality of retrogradational fan Delta: A case study of the Upper Wuerhe Formation of the Mahu Sag, the Junggar Basin [J]. Energy Exploration & Exploitation, 2021, 39(6): 2006-2026.
Zhu N., Cao Y., Xi K. et al. Multisourced CO2 Injection in Fan Delta Conglomerates and Its Influence on Reservoir Quality: Evidence from Carbonate Cements of the Baikouquan Formation of Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin, Northwestern China [J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2021, 32(4): 901-918.
Tang W., Zhang Y., Pe-Piper G. et al. Permian to early Triassic tectono-sedimentary evolution of the Mahu sag, Junggar Basin, western China: sedimentological implications of the transition from rifting to tectonic inversion [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2021, 123: 104730.
Feng C., Lei D., Qu J. et al. Controls of paleo-overpressure, faults and sedimentary facies on the distribution of the high pressure and high production oil pools in the lower Triassic Baikouquan Formation of the Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin, China [J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2019, 176: 232-248.
Jia H., Ji H., Wang L. et al. Reservoir quality variations within a conglomeratic fan-delta system in the Mahu sag, northwestern Junggar Basin: characteristics and controlling factors [J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2017, 152: 165-181.
Pittman E. D. Porosity diagenesis and productive capability of sandstone reservoirs [J]. 1979.
Pittman E D, Larese R E. Compaction of lithic sands: experimental results and applications [J]. AAPG bulletin, 1991, 75(8): 1279-1299.
Beard D. C., Weyl P. K. Influence of texture on porosity and permeability of unconsolidated sand [J]. AAPG bulletin, 1973, 57(2): 349-369.
Aoyagi K., Kazama T. Transformational changes of clay minerals, zeolites and silica minerals during diagenesis [J]. Sedimentology, 1980, 27(2): 179-188.
Wang J., Zhou L., Liu J. et al. Genesis of diagenetic zeolites and their impact on reservoir formation in the Middle Permian Lower-Wuerhe Formation of the Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin, Northwest China[J]. Energy Exploration & Exploitation, 2020, 38(6): 2541-2557.
Sun Y., Liu X., Zhang Y. et al. Analcite cementation facies and forming mechanism of high-quality secondary clastic rock reservoirs in western China [J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2014, 16(4): 517-526.
Broxton D. E., Bish D. L., Warren R. G. Distribution and chemistry of diagenetic minerals at Yucca Mountain, Nye County, Nevada[J]. Clays and Clay Minerals, 1987, 35(2): 89-110.
Hay R. L., Sheppard R. A. Occurrence of zeolites in sedimentary rocks: An overview [J]. Reviews in mineralogy and geochemistry, 2001, 45(1): 217-234.
Machel H. G., Lonnee J. Hydrothermal dolomite—A product of poor definition and imagination [J]. Sedimentary geology, 2002, 152(3-4): 163-171.
Davies G. R., Smith Jr L. B. Structurally controlled hydrothermal dolomite reservoir facies: An overview [J]. AAPG bulletin, 2006, 90(11): 1641-1690.
Yang L., Wang S., Jiang Q. et al. Effects of microstructure and rock mineralogy on movable fluid saturation in tight reservoirs [J]. Energy & Fuels, 2020, 34(11): 14515-14526.
Gu J. Y., He B. Study on Triassic fan delta sedimentation and reservoir in Lunnan area, Tarim Basin [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1994, 12(2): 54-62.
Ahammod S., Hai M. A., Islam M. R. et al. Petro-Physical Analysis Of Reservoir Rock Of Fenchuganj Gas Field (Well# 03) Using Wireline Log[J]. American Journal of Engineering Research, 2014, 3(8): 37-48.
Ge H., Yang L., Shen Y.et al. Experimental investigation of shale imbibition capacity and the factors influencing loss of hydraulic fracturing fluids. Petroleum Science [J], 2015, 12(4):636-650.
Yang L., Ge H., Shi X. et al. The effect of microstructure and rock mineralogy on water imbibition characteristics in tight reservoirs. Journal of Natural Gas and Science and Engineering [J], 2016, 34: 1461-1471.
Acknowledgments
This study was strongly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC), “Development Characteristics of conglomerate in large fan-delta facies of continental Lacustrine Basin and its influence from Paleoclimate: A Case study of Triassic Baikouquan Formation in Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin” (No. 41872118).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Khimiya i Tekhnologiya Topliv i Masel, No. 6, pp. 97–102 November – December, 2022.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Li, S., Zhang, J. et al. Quantitative Study of Diagenesis and Dissolution Porosity in Conglomerate Reservoirs. Chem Technol Fuels Oils 58, 1035–1045 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-023-01486-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-023-01486-9