Abstract
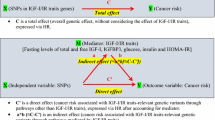
Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and IGF-binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) appear to influence breast cancer risk and are hypothesized to mediate the effects of several cancer risk factors that depend on menopausal status. We investigated associations among cancer risk factors and plasma IGF-I and IGFBP-3 in 882 healthy control women (426 premenopausal, 456 postmenopausal) from two population-based breast cancer case–control studies. Interactions with menopausal status were statistically tested. We observed associations with non-modifiable (age, benign breast disease) and modifiable factors [body mass index (BMI), physical activity, smoking habits, alcohol consumption]. Furthermore, we demonstrated statistical interactions with menopausal status. Premenopausal IGFBP-3 levels increased and postmenopausal levels decreased with age (p-interaction = 0.001). Overweight postmenopausal women had higher IGF-I (p = 0.049) and IGFBP-3 (p = 0.005) levels than women with lower BMI. Postmenopausal IGF-I levels were positively associated with physical activity (p-trend = 0.012, p-interaction = 0.050). Postmenopausal current smokers had lower IGF-I (p = 0.014) and IGFBP-3 levels (p = 0.011). Increasing alcohol consumption was associated with lower premenopausal IGF-I (p-trend = 0.002, p-interaction = 0.004) and higher postmenopausal IGFBP-3 levels (p = 0.019). Benign breast disease was associated with higher premenopausal (p = 0.044) and postmenopausal (p = 0.002) IGF-I levels. IGF-I and/or IGFBP-3 potentially mediate changes in breast cancer risk associated with BMI, benign breast disease, and perhaps alcohol consumption. Other observed associations suggest that neither IGF-I nor IGFBP-3 alone acts as mediator. Consideration of menopausal status may help disentangle carcinogenic pathways involving IGF proteins.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu H, Rohan T (2000) Role of the insulin-like growth factor family in cancer development and progression. J Natl Cancer Inst 92(18):1472–1489
Hartog H, Wesseling J, Boezen HM, van der Graaf WT (2007) The insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in cancer: old focus, new future. Eur J Cancer 43(13):1895–1904
Renehan AG, Zwahlen M, Minder C, O’dwyer ST, Shalet SM, Egger M (2004) Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF binding protein-3, and cancer risk: systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Lancet 363(9418):1346–1353
Shi R, Yu H, McLarty J, Glass J (2004) IGF-I and breast cancer: a meta-analysis. Int J Cancer 111(3):418–423
Baglietto L, English DR, Hopper JL, Morris HA, Tilley WD, Giles GG (2007) Circulating insulin-like growth factor-I and binding protein-3 and the risk of breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 16(4):763–768
Rinaldi S, Peeters PH, Berrino F et al (2006) IGF-I, IGFBP-3 and breast cancer risk in women: the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC). Endocr Relat Cancer 13(2):593–605
Gram IT, Norat T, Rinaldi S et al (2006) Body mass index, waist circumference and waist-hip ratio and serum levels of IGF-I and IGFBP-3 in European women. Int J Obes (Lond) 30(11):1623–1631
Friedenreich CM, Cust AE (2008) Physical activity and breast cancer risk: impact of timing, type and dose of activity and population subgroup effects. Br J Sports Med 42(8):636–647
Monninkhof EM, Elias SG, Vlems FA et al (2007) Physical activity and breast cancer: a systematic review. Epidemiology 18(1):137–157
Rundle A (2005) Molecular epidemiology of physical activity and cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 14(1):227–236
Holmes MD, Pollak MN, Hankinson SE (2002) Lifestyle correlates of plasma insulin-like growth factor I and insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 concentrations. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 11(9):862–867
Yu H, Berkel J (1999) Do insulin-like growth factors mediate the effect of alcohol on breast cancer risk? Med Hypotheses 52(6):491–496
Renehan AG, Tyson M, Egger M, Heller RF, Zwahlen M (2008) Body-mass index and incidence of cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective observational studies. Lancet 371(9612):569–578
World Cancer Research/American Institute for Cancer Research (2007) Food, nutrition, physical activity, and the prevention of cancer: a global perspective.Washington. AICR, DC
Chang-Claude J, Eby N, Kiechle M, Bastert G, Becher H (2000) Breastfeeding and breast cancer risk by age 50 among women in Germany. Cancer Causes Control 11(8):687–695
Steindorf K, Schmidt M, Kropp S, Chang-Claude J (2003) Case–control study of physical activity and breast cancer risk among premenopausal women in Germany. Am J Epidemiol 157(2):121–130
Flesch-Janys D, Slanger T, Mutschelknauss E et al (2008) Risk of different histological types of postmenopausal breast cancer by type and regimen of menopausal hormone therapy. Int J Cancer 123(4):933–941
Bohlscheid-Thomas S, Hoting I, Boeing H, Wahrendorf J (1997) Reproducibility and relative validity of energy and macronutrient intake of a food frequency questionnaire developed for the German part of the EPIC project. European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition. Int J Epidemiol 26(Suppl 1):S71–S81
Ainsworth BE, Haskell WL, Whitt MC et al (2000) Compendium of physical activities: an update of activity codes and MET intensities. Med Sci Sports Exerc 32(9 Suppl):S498–S504
Deal C, Ma J, Wilkin F et al (2001) Novel promoter polymorphism in insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3: correlation with serum levels and interaction with known regulators. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86(3):1274–1280
Rohrbacher M, Risch A, Kropp S, Chang-Claude J (2005) The A(-336C) insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 promoter polymorphism is not a modulator of breast cancer risk in Caucasian women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 14(1):289–290
Becher H (2005) General principles of data analysis: continuous covariables in epidemiological studies. In: Ahrens W, Pigeot I (eds) Handbook of epidemiology. Springer, Berlin, p 595
Lukanova A, Lundin E, Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A et al (2004) Body mass index, circulating levels of sex-steroid hormones, IGF-I and IGF-binding protein-3: a cross-sectional study in healthy women. Eur J Endocrinol 150(2):161–171
Slattery ML, Baumgartner KB, Byers T et al (2005) Genetic, anthropometric, and lifestyle factors associated with IGF-1 and IGFBP-3 levels in Hispanic and non-Hispanic white women. Cancer Causes Control 16(10):1147–1157
dos Santos Silva I, Johnson N, De Stavola B et al (2006) The insulin-like growth factor system and mammographic features in premenopausal and postmenopausal women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 15(3):449–455
Helle SI, Ekse D, Holly JM, Lonning PE (2002) The IGF-system in healthy pre- and postmenopausal women: relations to demographic variables and sex-steroids. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 81(1):95–102
Bezemer ID, Rinaldi S, Dossus L et al (2005) C-peptide, IGF-I, sex-steroid hormones and adiposity: a cross-sectional study in healthy women within the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC). Cancer Causes Control 16(5):561–572
Vrieling A, Voskuil DW, Bueno de Mesquita HB et al (2004) Dietary determinants of circulating insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF binding proteins 1, -2 and -3 in women in The Netherlands. Cancer Causes Control 15(8):787–796
Khosravi J, Diamandi A, Bodani U, Khaja N, Krishna RG (2005) Pitfalls of immunoassay and sample for IGF-I: comparison of different assay methodologies using various fresh and stored serum samples. Clin Biochem 38(7):659–666
Tworoger SS, Missmer SA, Eliassen AH, Barbieri RL, Dowsett M, Hankinson SE (2007) Physical activity and inactivity in relation to sex hormone, prolactin, and insulin-like growth factor concentrations in premenopausal women—exercise and premenopausal hormones. Cancer Causes Control 18(7):743–752
Picardi A, Gentilucci UV, Zardi EM et al (2003) TNF-alpha and growth hormone resistance in patients with chronic liver disease. J Interferon Cytokine Res 23(5):229–235
Meier P, Seitz HK (2008) Age, alcohol metabolism and liver disease. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 11(1):21–26
Angulo P (2002) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N Engl J Med 346(16):1221–1231
Johansson H, Baglietto L, Guerrieri-Gonzaga A et al (2004) Factors associated with circulating levels of insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 in 740 women at risk for breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 88(1):63–73
Jernstrom HC, Olsson H, Borg A (1997) Reduced testosterone, 17 beta-oestradiol and sexual hormone binding globulin, and increased insulin-like growth factor-1 concentrations, in healthy nulligravid women aged 19–25 years who were first and/or second degree relatives to breast cancer patients. Eur J Cancer Prev 6(4):330–340
Lukanova A, Toniolo P, Akhmedkhanov A et al (2001) A cross-sectional study of IGF-I determinants in women. Eur J Cancer Prev 10(5):443–452
Diorio C, Brisson J, Berube S, Pollak M (2008) Intact and total insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) levels in relation to breast cancer risk factors: a cross-sectional study. Breast Cancer Res 10(3):R42
Singer CF, Mogg M, Koestler W et al (2004) Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF-II serum concentrations in patients with benign and malignant breast lesions: free IGF-II is correlated with breast cancer size. Clin Cancer Res 10(12 Pt 1):4003–4009
Dorjgochoo T, Deming SL, Gao YT et al (2008) History of benign breast disease and risk of breast cancer among women in China: a case–control study. Cancer Causes Control 19(8):819–828
Lavigne JA, Baer DJ, Wimbrow HH et al (2005) Effects of alcohol on insulin-like growth factor I and insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 in postmenopausal women. Am J Clin Nutr 81(2):503–507
Lavigne JA, Wimbrow HH, Clevidence BA et al (2004) Effects of alcohol and menstrual cycle on insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 13(12):2264–2267
Garcia-Valdecasas-Campelo E, Gonzalez-Reimers E, Santolaria-Fernandez F et al (2006) Serum osteoprotegerin and RANKL levels in chronic alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol Alcohol 41(3):261–266
Hamajima N, Hirose K, Tajima K et al (2002) Alcohol, tobacco and breast cancer—collaborative reanalysis of individual data from 53 epidemiological studies, including 58,515 women with breast cancer and 95,067 women without the disease. Br J Cancer 87(11):1234–1245
Rinaldi S, Peeters PH, Bezemer ID et al (2006) Relationship of alcohol intake and sex steroid concentrations in blood in pre- and post-menopausal women: the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition. Cancer Causes Control 17(8):1033–1043
Porch JV, Jain K, Reilly A et al (1997) Aging, physical activity, insulin-like growth factor I, and body composition in Guatemalan women. Am J Clin Nutr 66(4):874–879
Chang S, Wu X, Yu H, Spitz MR (2002) Plasma concentrations of insulin-like growth factors among healthy adult men and postmenopausal women: associations with body composition, lifestyle, and reproductive factors. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 11(8):758–766
DeLellis K, Rinaldi S, Kaaks RJ, Kolonel LN, Henderson B, Le ML (2004) Dietary and lifestyle correlates of plasma insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and IGF binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3): the multiethnic cohort. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 13(9):1444–1451
Figueroa A, Going SB, Milliken LA et al (2003) Effects of exercise training and hormone replacement therapy on lean and fat mass in postmenopausal women. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 58(3):266–270
McTiernan A, Sorensen B, Yasui Y et al (2005) No effect of exercise on insulin-like growth factor 1 and insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 in postmenopausal women: a 12-month randomized clinical trial. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 14(4):1020–1021
Haydar ZR, Blackman MR, Tobin JD, Wright JG, Fleg JL (2000) The relationship between aerobic exercise capacity and circulating IGF-1 levels in healthy men and women. J Am Geriatr Soc 48(2):139–145
Morimoto LM, Newcomb PA, White E, Bigler J, Potter JD (2005) Variation in plasma insulin-like growth factor-1 and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3: personal and lifestyle factors (United States). Cancer Causes Control 16(8):917–927
Sandhu MS, Heald AH, Gibson JM, Cruickshank JK, Dunger DB, Wareham NJ (2002) Circulating concentrations of insulin-like growth factor-I and development of glucose intolerance: a prospective observational study. Lancet 359(9319):1740–1745
Xue F, Michels KB (2007) Diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and breast cancer: a review of the current evidence. Am J Clin Nutr 86(3):s823–s835
Sherlock M, Toogood AA (2007) Aging and the growth hormone/insulin like growth factor-I axis. Pituitary 10(2):189–203
Yamaguchi T, Kanatani M, Yamauchi M et al (2006) Serum levels of insulin-like growth factor (IGF); IGF-binding proteins-3, -4, and -5; and their relationships to bone mineral density and the risk of vertebral fractures in postmenopausal women. Calcif Tissue Int 78(1):18–24
Lahmann PH, Hoffmann K, Allen N et al (2004) Body size and breast cancer risk: findings from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer And Nutrition (EPIC). Int J Cancer 111(5):762–771
Schernhammer ES, Tworoger SS, Eliassen AH et al (2007) Body shape throughout life and correlations with IGFs and GH. Endocr Relat Cancer 14(3):721–732
Scacchi M, Pincelli AI, Cavagnini F (1999) Growth hormone in obesity. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 23(3):260–271
Allen NE, Appleby PN, Kaaks R, Rinaldi S, Davey GK, Key TJ (2003) Lifestyle determinants of serum insulin-like growth-factor-I (IGF-I), C-peptide and hormone binding protein levels in British women. Cancer Causes Control 14(1):65–74
Probst-Hensch NM, Wang H, Goh VH, Seow A, Lee HP, Yu MC (2003) Determinants of circulating insulin-like growth factor I and insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 concentrations in a cohort of Singapore men and women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 12(8):739–746
Baibas N, Bamia C, Vassilopoulou E, Sdrolias J, Trichopoulou A, Trichopoulos D (2003) Dietary and lifestyle factors in relation to plasma insulin-like growth factor I in a general population sample. Eur J Cancer Prev 12(3):229–234
Jernstrom H, Deal C, Wilkin F et al (2001) Genetic and nongenetic factors associated with variation of plasma levels of insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 in healthy premenopausal women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 10(4):377–384
Landin-Wilhelmsen K, Wilhelmsen L, Lappas G et al (1994) Serum insulin-like growth factor I in a random population sample of men and women: relation to age, sex, smoking habits, coffee consumption and physical activity, blood pressure and concentrations of plasma lipids, fibrinogen, parathyroid hormone and osteocalcin. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 41(3):351–357
Landin-Wilhelmsen K, Lundberg PA, Lappas G, Wilhelmsen L (2004) Insulin-like growth factor I levels in healthy adults. Horm Res 62(Suppl 1):8–16
Renehan AG, Atkin WS, O’dwyer ST, Shalet SM (2004) The effect of cigarette smoking use and cessation on serum insulin-like growth factors. Br J Cancer 91(8):1525–1531
Ambrosone CB, Kropp S, Yang J, Yao S, Shields PG, Chang-Claude J (2008) Cigarette smoking, N-acetyltransferase 2 genotypes, and breast cancer risk: pooled analysis and meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 17(1):15–26
Acknowledgments
Benjamin Barnes was supported by a German Academic Exchange Service (DAAD) Research Grant (A/05/14276). IGF-I and IGFBP-3 measurement kits were funded through the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) Graduiertenkolleg 793: Epidemiology of communicable and chronic, non-communicable diseases and their interrelationships. The MARIE study was funded by the Deutsche Krebshilfe e. V., grant number 70-2892-BR I, the Hamburg Cancer Society, the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) and the BMBF Germany grant 01KH0402.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barnes, B.B.E., Chang-Claude, J., Flesch-Janys, D. et al. Cancer risk factors associated with insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF-binding protein-3 levels in healthy women: effect modification by menopausal status. Cancer Causes Control 20, 1985–1996 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-009-9393-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-009-9393-0