Abstract
Background
Phosphorylated AKT is highly expressed or overexpressed in chemoresistant tumor samples. However, the precise molecular mechanism involved in AKT phosphorylation-related chemoresistance in breast cancer is still elusive. The present research was designed to estimate the effect of AKT phosphorylation on cell viability and chemoresistance in breast cancer.
Methods
We utilized MCF-7 and MDA-MB468 human breast cancer cell lines and developed multidrug-resistant MCF-7/MDR and cisplatin-resistant MDA-MB-468 cells. Immunofluorescence analysis and Western blotting were employed to test the level of glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK3β), phosphorylated phosphatase and tension homologue (p-PTEN) and phosphorylated AKT (p-AKT) in MCF-7/MDR and MDA-MB468 cells. Xenograft assays in nude mice were performed with MCF-7/MDR cells to verify chemoresistance and the signaling pathway upstream of phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT.
Results
An increase in GSK3β, p-PTEN and p-AKT expression was strongly induced in MCF-7/MDR and cisplatin-resistant MDA-MB-468 cells, and augmented GSK3β phosphorylation and PTEN inactivation enhanced AKT signaling. The elevation in GSK3β, p-PTEN and p-AKT was associated with cell viability based on a CCK-8 assay. The results of in vivo and in vitro assays indicated that GSK3β knockdown with lentiviral shRNA (shRNA-GSK3β) promoted apoptosis and suppressed the migration of cisplatin-resistant MCF-7/MDR cells, while these effects were reversed by activating p-AKT with the PTEN inhibitor bpV(pic).
Conclusions
AKT phosphorylation mediated by GSK3β and PTEN were correlated with cell viability, migration and apoptosis, which may promote chemoresistance in breast cancer. Furthermore, GSK3β can regulate cell viability through the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and induce chemoresistance, serving as a valuable molecular strategy for breast cancer therapy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hong W, Dong E (2014) The past, present and future of breast cancer research in China. Cancer Lett 351(1):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2014.04.007
Fan L, Strasser-Weippl K, Li JJ, St Louis J, Finkelstein DM, Yu KD, Chen WQ, Shao ZM, Goss PE (2014) Breast cancer in China. Lancet Oncol 15(7):e279–e289. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70567-9
Ghebeh H, Al-Khaldi S, Olabi S, Al-Dhfyan A, Al-Mohanna F, Barnawi R, Tulbah A, Al-Tweigeri T, Ajarim D, Al-Alwan M (2014) Fascin is involved in the chemotherapeutic resistance of breast cancer cells predominantly via the PI3K/Akt pathway. Br J Cancer 111(8):1552–1561. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2014.453
O’Driscoll L, Clynes M (2006) Biomarkers and multiple drug resistance in breast cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 6(5):365–384
Luo J (2009) Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta (GSK3beta) in tumorigenesis and cancer chemotherapy. Cancer Lett 273(2):194–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2008.05.045
Grassilli E, Ianzano L, Bonomo S, Missaglia C, Cerrito MG, Giovannoni R, Masiero L, Lavitrano M (2014) GSK3A is redundant with GSK3B in modulating drug resistance and chemotherapy-induced necroptosis. PLoS ONE 9(7):e100947. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0100947
Hilliard TS, Gaisina IN, Muehlbauer AG, Gaisin AM, Gallier F, Burdette JE (2011) Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta inhibitors induce apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells and inhibit in vivo tumor growth. Anticancer Drugs 22(10):978–985. https://doi.org/10.1097/CAD.0b013e32834ac8fc
Pyko IV, Nakada M, Sabit H, Teng L, Furuyama N, Hayashi Y, Kawakami K, Minamoto T, Fedulau AS, Hamada J (2013) Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta inhibition sensitizes human glioblastoma cells to temozolomide by affecting O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase promoter methylation via c-Myc signaling. Carcinogenesis 34(10):2206–2217. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgt182
Wang G, Shi Y, Jiang X, Leak RK, Hu X, Wu Y, Pu H, Li WW, Tang B, Wang Y, Gao Y, Zheng P, Bennett MV, Chen J (2015) HDAC inhibition prevents white matter injury by modulating microglia/macrophage polarization through the GSK3beta/PTEN/Akt axis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112(9):2853–2858. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1501441112
Cohen P, Goedert M (2004) GSK3 inhibitors: development and therapeutic potential. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3(6):479–487. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd1415
Vazquez F, Matsuoka S, Sellers WR, Yanagida T, Ueda M, Devreotes PN (2006) Tumor suppressor PTEN acts through dynamic interaction with the plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(10):3633–3638. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0510570103
Farina AK, Bong YS, Feltes CM, Byers SW (2009) Post-transcriptional regulation of cadherin-11 expression by GSK-3 and beta-catenin in prostate and breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 4(3):e4797. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0004797
Ohigashi T, Mizuno R, Nakashima J, Marumo K, Murai M (2005) Inhibition of Wnt signaling downregulates Akt activity and induces chemosensitivity in PTEN-mutated prostate cancer cells. Prostate 62(1):61–68. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.20117
Corral-Vazquez C, Aguilar-Quesada R, Catalina P, Lucena-Aguilar G, Ligero G, Miranda B, Carrillo-Avila JA (2017) Cell lines authentication and mycoplasma detection as minimun quality control of cell lines in biobanking. Cell Tissue Banking 18(2):271–280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-017-9617-6
Domoto T, Pyko IV, Furuta T, Miyashita K, Uehara M, Shimasaki T, Nakada M, Minamoto T (2016) Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta is a pivotal mediator of cancer invasion and resistance to therapy. Cancer Sci 107(10):1363–1372. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13028
Grassilli E, Narloch R, Federzoni E, Ianzano L, Pisano F, Giovannoni R, Romano G, Masiero L, Leone BE, Bonin S, Donada M, Stanta G, Helin K, Lavitrano M (2013) Inhibition of GSK3B bypass drug resistance of p53-null colon carcinomas by enabling necroptosis in response to chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 19(14):3820–3831. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-3289
Kawazoe H, Bilim VN, Ugolkov AV, Yuuki K, Naito S, Nagaoka A, Kato T, Tomita Y (2012) GSK-3 inhibition in vitro and in vivo enhances antitumor effect of sorafenib in renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 423(3):490–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.05.147
Manning BD, Cantley LC (2007) AKT/PKB signaling: navigating downstream. Cell 129(7):1261–1274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.06.009
Li Y, Tsang CK, Wang S, Li XX, Yang Y, Fu L, Huang W, Li M, Wang HY, Zheng XF (2016) MAF1 suppresses AKT-mTOR signaling and liver cancer through activation of PTEN transcription. Hepatology 63(6):1928–1942. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.28507
Ning K, Miller LC, Laidlaw HA, Watterson KR, Gallagher J, Sutherland C, Ashford ML (2009) Leptin-dependent phosphorylation of PTEN mediates actin restructuring and activation of ATP-sensitive K+ channels. J Biol Chem 284(14):9331–9340. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M806774200
Ougolkov AV, Fernandez-Zapico ME, Savoy DN, Urrutia RA, Billadeau DD (2005) Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta participates in nuclear factor kappaB-mediated gene transcription and cell survival in pancreatic cancer cells. Can Res 65(6):2076–2081. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-3642
Wang Z, Smith KS, Murphy M, Piloto O, Somervaille TC, Cleary ML (2008) Glycogen synthase kinase 3 in MLL leukaemia maintenance and targeted therapy. Nature 455(7217):1205–1209. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07284
De Toni-Costes F, Despeaux M, Bertrand J, Bourogaa E, Ysebaert L, Payrastre B, Racaud-Sultan C (2010) A new alpha5beta1 integrin-dependent survival pathway through GSK3beta activation in leukemic cells. PLoS ONE 5(3):e9807. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0009807
Ougolkov AV, Fernandez-Zapico ME, Bilim VN, Smyrk TC, Chari ST, Billadeau DD (2006) Aberrant nuclear accumulation of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in human pancreatic cancer: association with kinase activity and tumor dedifferentiation. Clin Cancer Res 12(17):5074–5081. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0196
Naito S, Bilim V, Yuuki K, Ugolkov A, Motoyama T, Nagaoka A, Kato T, Tomita Y (2010) Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta: a prognostic marker and a potential therapeutic target in human bladder cancer. Clin Cancer Res 16(21):5124–5132. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-0275
Quintayo MA, Munro AF, Thomas J, Kunkler IH, Jack W, Kerr GR, Dixon JM, Chetty U, Bartlett JM (2012) GSK3beta and cyclin D1 expression predicts outcome in early breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat 136(1):161–168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-012-2229-8
Namba T, Kodama R, Moritomo S, Hoshino T, Mizushima T (2015) Zidovudine, an anti-viral drug, resensitizes gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells to gemcitabine by inhibition of the Akt-GSK3beta-Snail pathway. Cell Death Dis 6:e1795. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2015.172
Dey G, Bharti R, Dhanarajan G, Das S, Dey KK, Kumar BN, Sen R, Mandal M (2015) Marine lipopeptide Iturin A inhibits Akt mediated GSK3beta and FoxO3a signaling and triggers apoptosis in breast cancer. Sci Rep 5:10316. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep10316
Funding
This study was supported by the Chinese Natural Science Foundation (Grant 81471257), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province of China (Grant BK20161283), Jiangsu Province “Six Summit Talent” Foundation (2016-YY-061), and Nantong science and technology project (MS22016066) and sponsored by Qing Lan Project (to G.W.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors of this manuscript have no conflicts of interest to report.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors. All animal care and experimental protocols were carried out according to the Chinese Animal Management Rules of the Ministry of Health and were authorized by the Animal Ethics Committees of Nantong University research program protocol #NT-16-086. Original data used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10549_2019_5239_MOESM1_ESM.tif
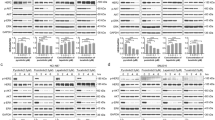
Supplemental Fig. 1 Expression level of p-AKT, p-PTEN and GSK3β in MDA-MB-468 cells and cisplatin-resistant MDA-MB-468 cells. Western blot analysis of p-AKT (A), p-PTEN (B) and GSK3β (C) in wild-type and cisplatin-resistant MDA-MB-468 cells. The relative band intensities were quantified using ImageJ software and are presented as the ratio of p-AKT, p-PTEN and GSK3β to β-actin, and finally normalized to control. The values are the mean ± SD (n = 3). Statistical significance was established with a two-tailed t-test; *p < 0.05, and **p< 0.01 versus wild-type cells. Supplementary material 1 (TIFF 234 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, C., Yuan, X., Jiang, Z. et al. Regulation of AKT phosphorylation by GSK3β and PTEN to control chemoresistance in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 176, 291–301 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-019-05239-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-019-05239-3