Abstract
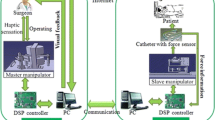
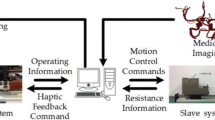
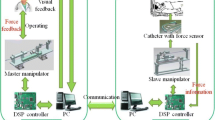
Vascular interventional surgery has its advantages compared to traditional operation. Master-slave robotic technology can further improve the operation accuracy, efficiency and safety of this complicated and high risk surgery. However, on-line acquisition of operating force information of catheter and guidewire remains to be a significant obstacle on the path to enhancing robotic surgery safety. Thus, a novel slave manipulator is proposed in this paper to realize on-line sensing of guidewire torsional operating torque and axial operation force during robotic assisted operations. A strain sensor is specially designed to detect the small scale torsional operation torque with low rotational frequency. Additionally, the axial operating force is detected via a load cell, which is incorporated into a sliding mechanism to eliminate the influence of friction. For validation, calibration and performance evaluation experiments are conducted. The results indicate that the proposed operation torque and force detection device is effective. Thus, it can provide the foundation for enabling accurate haptic feedback to the surgeon to improve surgical safety.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Back, R. Karim, Y. Noh, K. Rhod, K. Althoefer, H. Liu, Tension sensing for a linear actuated catheter robot. Intelligent robotics and applications. ICIRA 2015. Lecture notes in computer science, 9245 (Springer, Cham, 2015), pp. 472–482
L. Cercenelli, B. Bortolani, E. Marcelli, CathROB: A highly compact and versatile remote catheter navigation system. Applied Bionics and Biomechanics 2017(8), 1–13 (2017)
J. Dankelman, J.J. van den Dobbelsteen, P. Breedveld, in Proceedings of 2011 International Conference on Instrumentation Control and Automation. Current technology on minimally invasive surgery and interventional techniques (IEEE Press, Bandung, 2011), pp. 12–15
T. Datino, A. Arenal, P.M. Ruiz-Hernández, M. Pelliza, J. Hernández-Hernández, E. González-Torrecilla, F. Atienza, P. Ávila, F. Fernández-Avilés, Arrhythmia ablation using the amigo robotic remote catheter system versus manual ablation: One year follow-up results. Int. J. Cardiol. 202, 877–878 (2015)
R.A. Dello, G. Fassini, S. Conti, M. Casella, A.D. Monaco, E. Russo, S. Riva, M. Moltrasio, F. Tundo, G.D. Martino, G. Gallinghouse, L.D. Biase, A. Natale, C. Tondo, Analysis of catheter contact force during atrial fibrillation ablation using the robotic navigation system: Results from a randomized study. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 46(2), 97–103 (2016)
D. Filgueiras-Rama, A. Estrada, J. Shachar, S. Castrejón, D. Doiny, M. Ortega, E. Gang, J.L. Merino, Remote magnetic navigation for accurate, real-time catheter positioning and ablation in cardiac electrophysiology procedures. Journal of Visualized Experiments Jove. 74(74), e3658–e3658 (2013)
D. Gelman, A.C. Skanes, M.A. Tavallaei, M. Drangova, Design and evaluation of a catheter contact-force controller for cardiac ablation therapy. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 63(11), 2301–2307 (2016)
J. Guo, G. Shuxiang, Design and characteristics evaluation of a novel VR-based robot-assisted catheterization training system with force feedback for vascular interventional surgery. Microsyst. Technol. 23, 1–10 (2016)
J. Guo, S. Guo, N. Xiao, X. Ma, S. Yoshida, T. Tamiya, M. Kawanishi, A novel robotic catheter system with force and visual feedback for vascular interventional surgery. International Journal of Mechatronics and Automation. 2(1), 15–24 (2012)
J. Guo, S. Guo, L. Shao, P. Wang, Q. Gao, Design and performance evaluation of a novel robotic catheter system for vascular interventional surgery. Microsystem Technology. 22(9), 1–10 (2015)
J. Guo, S. Guo, Y. Yu, Design and characteristics evaluation of a novel teleoperated robotic catheterization system with force feedback for vascular interventional surgery. Biomed. Microdevices 18(5), 76 (2016)
F. Kiemeneij, M.S. Patterson, G. Amoroso, G. Laarman, T. Slagboom, Use of the Stereotaxis Niobe® magnetic navigation system for percutaneous coronary intervention: Results from 350 consecutive patients. Journal of Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions. 71(4), 510–516 (2008)
X. Liu, G. Xu, R. Zhang, Endovascular management for stroke (People’s medical publishing house, Beijing, 2006), pp. 134–136
Y. Song, S. Guo, X. Yin, L. Zhang, Y. Wang, H. Hirata, H. Ishihara, Design and performance evaluation of a haptic interface based on MR fluids for endovascular tele-surgery. Microsystem Technologies, 1–10 (2017)
Y. Thakur, J.S. Bax, D.W. Holdsworth, M. Drangova, Design and performance evaluation of a remote catheter navigation system. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 56(7), 1901–1908 (2009a)
Y. Thakur, D.W. Holdsworth, M. Drangova, Characterization of catheter dynamics during percutaneous transluminal catheter procedures. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 56(8), 2140–2143 (2009b)
V. Vitiello, K.W. Kwok, G. Yang, Introduction to robot-assisted minimally invasive surgery (MIS). Medical Robotics: Minimally Invasive Surgery 2(1–4), 1–40 (2012)
Y. Wang, S. Guo, B. Gao, Vascular Elastcity determined mass-spring model for virtual reality simulators. International Journal of Mechatronics and Automation. 5(1), 1–10 (2015)
Y. Wang, S. Guo, T. Tamiya, H. Hirata, H. Ishihara, X. Yin, A virtual-reality simulator and force sensation combined catheter operation training system and its preliminary evaluation. International Journal of Medical Robotics and Computer Assisted Surgery. 13, e1769 (2016)
N. Xiao, J. Guo, S. Guo, T. Tamiya, A robotic catheter system with real-time force feedback and monitor. Australasian Physical & Engineering Sciences in Medicine 35(3), 283–289 (2012)
X. Yin, S. Guo, H. Hirata, H. Ishihara, Design and experimental evaluation of a Teleoperated haptic robot assisted catheter operating system. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 27(1), 3–16 (2014)
X. Yin, S. Guo, N. Xiao, T. Tamiya, H. Hirata, H. Ishihara, Safety operation consciousness realization of a MR fluids-based novel haptic Interface for teleoperated catheter minimally invasive Neuro surgery. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics. 21(2), 1043–1054 (2015)
L. Zhang, S. Guo, H. Yu, Y. Song, Performance evaluation of a strain-gauge force sensor for a haptic robot-assisted catheter operating system. Microsyst. Technol. 5, 1–10 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This research is partly supported by the National High Tech. Research and Development Program of China (No.2015AA043202), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (61375094, 61503028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Guo, S., Xiao, N. et al. Operating force information on-line acquisition of a novel slave manipulator for vascular interventional surgery. Biomed Microdevices 20, 33 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-018-0275-7
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-018-0275-7