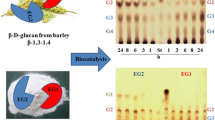
Abstract
An endoglucanase that is able to degrade both crystalline and amorphous cellulose was purified from the culture filtrates of the brown-rot fungus Fomitopsis pinicola grown on cellulose. An apparent molecular weight of the purified enzyme was ∼32 kDa by SDS-PAGE analysis. The enzyme was purified 11-fold with a specific activity of 944 U/mg protein against CMC. The partial amino acid sequences of the purified endoglucanase had high homology with endo-β-1,4-glucanase of glycosyl hydrolase family 5 from other fungi. The K m and K cat values for CMC were 12 mg CMC/ml and 670/s, respectively. The purified EG hydrolyzed both cellotetraose (G4) and cellopentaose (G5), but did not degrade either cellobiose (G2) or cellotriose (G3).


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berghem LE, Pettersson LG (1973) The mechanism of enzymatic cellulose degradation. Purification of a cellulolytic enzyme from Trichoderma viride active on highly ordered cellulose. Eur J Biochem 37:21–30
Cohen R, Suzuki M, Hammel KE (2005) Processive endoglucanase active in crystalline cellulose hydrolysis by the brown rot basidiomycete Gloeophyllum trabeum. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:2412–2417
Dewey D, Ryu Y, Mandels M (1980) Cellulases: biosynthesis and applications. Enzyme Microb Technol 2:91–101
Gilad R, Rabinovich L, Yaron S, Bayer EA, Lamed R, Gilbert HJ, Shoham Y (2003) CelI, a noncellulosomal family 9 enzyme from Clostridium thermocellum, is a processive endoglucanase that degrades crystalline cellulose. J Bacteriol 185:391–398
Herr D, Baumer F, Dellweg H (1978) Purification and properties of an extracellular endo-1,4-β-glucanase from Lenzites trabea. Arch Microbiol 117:287–292
Highley TL (1975) Properties of cellulases of two brown-rot and two white-rot fungi. Wood Fiber 6:275–281
Kerem Z, Jensen KA, Hammel KE (1999) Biodegradative mechanism of the brown rot basidiomycete Gleophyllum trabeum: evidence for an extracellular hydroquinone-driven fenton reaction. FEBS Lett 446:49–54
Mansfield SD, Saddler JN, Gubitz GM (1998) Characterization of endoglucanases from the brown rot fungi Gloeophyllum sepiarium and Gloeophyllum trabeum. Enzyme Microb Technol 23:133–140
Ritschkoff AC (1996) Decay mechanisms of brown-rot fungi. VTT Publications 268, Espoo
Schmidhalter DR, Canevascini G (1993) Purification and characterization of two cellobiohydrolases from the brown rot fungus Coniophora puteana (Schum ex Fr.) Krst. Arch Biochem Biophys 300:551–558
Shevchenko A, Wilm M, Vorm O, Mann M (1996) Mass spectrometric sequencing of proteins silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. Anal Chem 68:850–858
Valášková V, Baldrian P (2006) Degradation of cellulose and hemicellulose by the brown rot fungus Piptoporus betulinus—production of extracellular enzymes and characterization of the major cellulases. Microbiology 152:3613–3622
Wood TM, McCrae SI, Bhat KM (1989) The mechanism of fungal cellulase action. Synergism between enzyme components of Penicillium pinophilum cellulase in solubilizing hydrogen bond-ordered cellulose. Biochem J 260:37–43
Woodward J (1991) Synergism in cellulose systems. Bioresour Technol 36:67–75
Yamanobe T, Mitsuishi Y, Yagisawa M (1988) Purification and some properties of a microcrystalline cellulose-hydrolyzing enzyme (Avicelase II) from fungal strain Y-94. Agric Biol Chem 52:2493–2524
Yoon J-J, Kim Y-K (2005) Degradation of crystalline cellulose by the brown-rot basidiomycete Fomitopsis palustris. J Microbiol 43:487–492
Yoon J-J, Cha C-J , Kim Y-S, Son D-W, Kim Y-K (2007) The brown-rot basidiomycete Fomitopsis palustris has the endo-glucanases capable of degrading microcrystalline cellulose. J Microbiol Biotechnol 17:800–805
Acknowledgements
This study was carried out with the support of Forest Science & Technology Projects (Project No. S210707L010110) provided by the Korea Forest Service. The authors would like to thank Miss N.-M. Kim for her support and technical help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoon, JJ., Cha, CJ., Kim, YS. et al. Degradation of cellulose by the major endoglucanase produced from the brown-rot fungus Fomitopsis pinicola . Biotechnol Lett 30, 1373–1378 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-008-9715-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-008-9715-4