Abstract
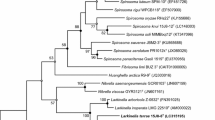
A Gram-stain negative, aerobic, salmon-pink, non-motile and rod-shaped bacterium, designated strain 15J11-1T, was isolated from a soil sample collected from the university garden in Nowongu, South Korea. The 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis showed that strain 15J11-1T is phylogenetically related to Runella slithyformis DSM 19594T and Runella palustris HMF3829T (96.9% and 95.4% sequence similarity, respectively). The major fatty acids of strain 15J11-1T were identified as iso-C15:0, iso-C17:0 3-OH, C16:1ω5c and summed feature 3 (C16:1ω7c and/or C16:1ω6c). The predominant respiratory quinone was identified as MK-7. The polar lipids were found to comprise of phosphatidylethanolamine, three unidentified aminolipids, five unidentified glycolipids, two unidentified aminoglycolipids, an unidentified phospholipid and an unidentified polar lipid. The G + C content in the genomic DNA of the strain 15J11-1T was determined to be 49.9 mol%. Based on the results of genotypic, phenotypic and chemotaxonomic analyses, strain 15J11-1T is concluded to represent a novel species of the genus Runella, for which the name Runella soli sp. nov. (type strain 15J11-1T = KCTC 52021T = NBRC 112817T) is proposed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman J et al (eds) (1995) Short protocols in molecular biology: a compendium of methods from current protocols in molecular biology, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York
Bernardet J F, Nakagawa Y, Holmes B & Subcommittee on the taxonomy of Flavobacterium and Cytophaga-like bacteria of the International Committee on Systematics of Prokaryotes (2002). Proposed minimal standards for describing new taxa of the family Flavobacteriaceae and emended description of the family. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52: 1049–1070
Breznak JA, Costilow RN (2007) Physicochemical factors in growth. In: Beveridge TJ, Breznak JA, Marzluf GA, Schmidt TM, Snyder LR (eds) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology, 3rd edn. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 309–329
Buck JD (1982) Nonstaining (KOH) method for determination of gram reactions of marine bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 44:992–993
Chelius MK, Henn JA, Triplett EW (2002) Runella zeae sp. nov., a novel gram-negative bacterium from the stems of surface-sterilized Zea mays. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:2061–2063
Chhetri G, Yang D, Choi J et al (2018a) Edaphorhabdus rosea gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Cytophagaceae isolated from soil in South Korea. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 111:2385. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-018-1127-4
Chhetri G, Yang D, Choi J et al (2018b) Flavobacterium edaphi sp. nov., isolated from soil from Jeju Island, Korea. Arch Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-018-1593-0
Collins MD, Jones D (1981) Distribution of isoprenoid quinone structural types in bacteria and their taxonomic implications. Microbiol Rev 45:316–354
Fautz E, Reichenbach H (1980) A simple test for flexirubin-type pigments. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 8:87–91
Felsenstein J (1985) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Hall T (1997) BioEdit. Biological sequence alignment editor for Win 95/98/NT/2 K/XP. Ibis Therapeutics, Carlsbad
Hiraishi A, Ueda Y, Ishihara J, Mori T (1996) Comparative lipoquinone analysis of influent sewage and activated sludge by highperformance liquid chromatography and photodiode array detection. J Gen Appl Microbiol 42:457–469
Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K, Yoon SH, Kim M, Na H, Park SC, Jeon YS, Lee JH et al (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbial 62:716–721
Kim H, Kang H, Joung Y, Joh K et al (2017) Runella palustris sp. nov., isolated from wetland freshwater. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:676–680
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rate of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Komagata K, Suzuki KI (1987) Lipid and cell-wall analysis in bacterial systematics. Methods Microbiol 19:161–205
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K et al (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874
Kuykendall LD, Roy MA, O’Neill JJ, Devine TE (1988) Fatty acids, antibiotic resistance and deoxyribonucleic acid homology groups of Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 38:358–361
Larkin JM, Williams PM (1978) Runella slithyformis gen. nov., sp. nov., a curved, nonflexible, pink bacterium. Int J Syst Bacteriol 28:32–36
Lu S, Lee JR, Ryu SH, Chung BS, Choe WS et al (2007) Runella defluvii sp. nov., isolated from a domestic wastewater treatment plant. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2600–2603
Minnikin DE, O’Donnell AG, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Athalye M et al (1984) An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoidquinones and polar lipids. J Microbiol Methods 2:233–241
Ryu SH, Nguyen TT, Park W, Kim CJ, Jeon CO (2006) Runella limosa sp. nov., isolated from activated sludge. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:2757–2760
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbour-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Smibert RM, Krieg NR (1994) Phenotypic characterization. In: Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Wood WA, Krieg NR (eds) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 607–654
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a research grant from Seoul Women’s University (2018) and the Project on Survey of Indigenous Species of Korea of the National Institute of Biological Resources (NIBR) under the Ministry of Environment (MOE) (NIBR201701206). We thank Prof Dr. Bernhard Schink (University of Konstanz, Konstanz, Germany) for the species name.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study does not describe any experimental work related to human.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chhetri, G., Kim, J., Kim, I. et al. Runella soli sp. nov., isolated from garden soil. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 112, 1245–1252 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-019-01257-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-019-01257-9