Abstract
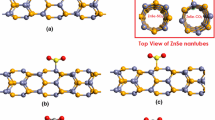
Using the density functional theory calculations, we investigated the electronic properties of the armchair (6, 6) and (8, 8) and zigzag (8, 0) stanene based nanotubes as promising sensing materials for SO3 molecules. We analyzed the structural and electronic properties of the adsorption system including the adsorption energies, band structures and projected density of states. We examined both molecular and dissociative adsorption of SO3 on the aforementioned nanotubes. Different orientation of the SO3 molecule towards the nanotube gives rise to the different adsorption configurations. The results suggest that the molecular adsorption of SO3 on the nanotubes is more energetically favorable than the dissociative adsorption, indicating that SO3 tends to be molecularly adsorbed on the buckled nanotubes. Besides, the adsorption of SO3 molecule on the (8, 8) nanotube is much more favorable in energy than the adsorption on the (6, 6) one, suggesting that (8, 8) stanene based nanotube can react with SO3 molecule more efficiently. The considerable adsorption energy values indicate that SO3 molecule chemisorbed on the stanene based nanotubes. This is well confirmed by the large overlaps between the PDOS spectra of the interacting atoms. Mulliken charge analysis reveals a noticeable charge transfer from the stanene based nanotube to the adsorbed gas molecule, suggesting that SO3 acts as a charge acceptor. The calculated band gaps for the armchair (6, 6) and (8, 8) nanotubes are 0.33 and 0.24 eV, respectively while that of zigzag (8, 0) is estimated to be 0.207 eV, which indicate the semiconductor characteristics of the mentioned nanotubes. By analyzing the gas sensing response, we found that the stanene based nanotube would be promising SO3 sensor device. Our obtained results thus provide a theoretical basis for future fabrications of highly efficient sensing materials.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The code, OPENMX, pseudoatomic basis functions, and pseudopotentials are available on a web site http://www.openmxsquare.org.
References
Abbasi, A., Sardroodi, J.J.: N-doped TiO2 anatase nanoparticles as a highly sensitive gas sensor for NO2 detection: insights from DFT computations. Environ. Sci. Nano 3, 1153–1164 (2016a)
Abbasi, A., Sardroodi, J.J.: Theoretical study of the adsorption of NOx on TiO2/MoS2 nanocomposites: a comparison between undoped and N-doped nanocomposites. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 6, 309–327 (2016b)
Abbasi, A., Sardroodi, J.J.: Modified N-doped TiO2 anatase nanoparticle as an ideal O3 gas sensor: Insights from density functional theory calculations. Comput. Theor. Chem. 1095, 15–28 (2016c)
Abbasi, A., Sardroodi, J.J.: Molecular design of O3 and NO2 sensor devices based on a novel heterostructured N-doped TiO2/ZnO nanocomposite: a van der Waals corrected DFT study. J Nanostruct. Chem. 7, 345–358 (2017a)
Abbasi, A., Sardroodi, J.J.: Prediction of a highly sensitive molecule sensor for SOx detection based on TiO2/MoS2 nanocomposites: a DFT study. J. Sulfur Chem. 38(1), 52–68 (2017b)
Abbasi, A., Sardroodi, J.J.: A novel strategy for SOx removal by N-doped TiO2/WSe2 nanocomposite as a highly efficient molecule sensor investigated by van der Waals corrected DFT. Comput. Theor. Chem. 1114, 8–19 (2017c)
Abbasi, A., Sardroodi, J.J.: An innovative gas sensor system designed from a sensitive nanostructured ZnO for the selective detection of SOx molecules: a density functional theory study. New J. Chem. 41, 12569–12580 (2017d)
Abbasi, A., Sardroodi, J.J.: Adsorption and dissociation of SO3 on N-doped TiO2 supported Au overlayers investigated by van der Waals corrected DFT. Surf. Sci. 663, 35–46 (2017e)
Abbasi, A., Sardroodi, J.J.: Investigation of the adsorption of ozone molecules on TiO2/WSe2 nanocomposites by DFT computations: applications to gas sensor devices. Appl. Surf. Sci. 436, 27–41 (2018a)
Abbasi, A., Sardroodi, J.J.: Adsorption of toxic SOx molecules on heterostructured TiO2/ZnO nanocomposites for gas sensing applications: a DFT study. Adsorption 24, 29–41 (2018b)
Abbasi, A., Sardroodi, J.J.: Density functional theory investigation of the interactions between the buckled stanene nanosheet and XO2 gases (X = N, S, C). Comput. Theor. Chem. 1125, 15–28 (2018c)
Abbasi, A., Sardroodi, J.J., Ebrahimzadeh, A.R., Yaghoobi, M.: Theoretical study of the structural and electronic properties of novel stanene-based buckled nanotubes and their adsorption behaviors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 435, 733–742 (2018d)
Bianco, E., Butler, S., Jiang, S., Restrepo, O.D., Windl, W., Joshua, E.: Stability and exfoliation of germanane: a germanium graphane analogue. ACS Nano 7, 4414–4421 (2013)
Castro Neto, A.H., Guinea, F., Peres, N.M.R., Novoselov, K.S., Geim, A.K.: The electronic properties of graphene. Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 109–162 (2009)
Chen, X., Tan, C., Yang, Q., Meng, R., Liang, Q., Cai, M., Zhang, S., Jiang, J.: Ab initio study of the adsorption of small molecules on stanene. J. Phys. Chem. C, 120(26), 13987–13994 (2016)
Fleming, S., Rohi, A.: GDIS: a visualization program for molecular and periodic systems. Z. Kristallograph. Crystal. Mater. 220, 580–584 (2005)
Grimme, S.: Semiempirical GGA-type density functional constructed with a long-range dispersion correction. J. Comput. Chem. 27(15), 1787–1799 (2006)
Hohenberg, P., Kohn, W.: Inhomogeneous electron gas. Phys. Rev. 136, B864 (1964)
Kaloni, T.P., Schwingenschlögl, U.: Stability of germanene under tensile strain. Phys. Lett. 583, 137–140 (2013)
Kohn, W., Sham, L.: Self-consistent equations including exchange and correlation effects. Phys. Rev. 140, A1133 (1965)
Koklj, A.: Computer graphics and graphical user interfaces as tools in simulations of matter at the atomic scale. Comput. Mater. Sci. 28, 155–168 (2003)
Lee, C., Wei, X., Kysar, J.W., Hone, J.: Measurement of the elastic properties and intrinsic strength of monolayer graphene. Science 321, 385–388 (2008)
Li, S.S., Zhang, C.W.: Tunable electronic structures and magnetic properties in two-dimensional stanene with hydrogenation. Mater. Chem. Phys. 173, 246–254 (2016)
Manjanath, A., Kumar, V., Singh, A.K.: Mechanical and electronic properties of pristine and Ni-doped Si, Ge, and Sn sheets. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 16, 1667–1671 (2014)
Modarresi, M., Kakoee, A., Mogulkoc, Y., Roknabadi, M.R.: Effect of external strain on electronic structure of stanene. Comput. Mater. Sci. 101, 164–167 (2015)
Momma, K., Izumi, F.: VESTA 3 for three-dimensional visualization of crystal, volumetric and morphology data. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 44, 1272–1276 (2011)
Neto, A.C., Guinea, F., Peres, N.M., Novoselov, K.S., Geim, A.K.: The electronic properties of graphene. Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 109 (2009)
Odom, T.W., Huang, J.-L., Kim, P., Lieber, C.M.: Atomic structure and electronic properties of single-walled carbon nanotubes. Nature 391, 62–64 (1998)
Ozaki, T.: Variationally optimized atomic orbitals for large-scale electronic structures. Phys. Rev. B 67, 155108 (2003)
Ozaki, T., Kino, H.: Variationally optimized basis orbitals for biological molecules. J. Chem. Phys. 121, 10879–10888 (2004a)
Ozaki, T., Kino, H.: Numerical atomic basis orbitals from H to Kr. Phys. Rev. B 69, 195113 (2004b)
Perdew, J.P., Burke, K., Ernzerhof, M.: Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 1396 (1981)
Schneider, W.F., Li, J., Hass, K.C.: Combined computational and experimental investigation of SOx adsorption on MgO. J. Phys. Chem. B 105, 6972–6979 (2001)
Schwierz, F.: Graphene transistors. Nat. Nanotechnol. 5, 487–496 (2010)
Tang, S., Cao, Z.: Adsorption of nitrogen oxides on graphene and graphene oxides: insights from density functional calculations. JCP 134, 044710 (2011)
Tang, S., Cao, Z.: Adsorption and dissociation of ammonia on graphene oxides: a first-principles study. J. Phys. Chem. C 116, 8778–8791 (2012)
Vogt, P., De Padova, P., Quaresima, C., Avila, J., Frantzeskakis, E., Asensio, M.C., Resta, A., Ealet, B., Le Lay, G.: Silicene: compelling experimental evidence for graphenelike two-dimensional silicon. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 155501 (2012)
Xu, Y., Yan, B., Zhang, H.-J., Wang, J., Xu, G., Tang, P., Duan, W., Zhang, S.-C.: Large-gap quantum spin Hall insulators in tin films. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 136804 (2013)
Zhang, X., Gui, Y., Dong, X.: Preparation and application of TiO2 nanotube array gas sensor for SF6-insulated equipment detection: a review. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 11, 302 (2016)
Zhang, X., Cui, H., Gui, Y., Tang, J.: Mechanism and application of carbon nanotube sensors in SF6 decomposed production detection: a review. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 12, 177 (2017)
Zhu, F.F., Chen, W.J., Xu, Y., Gao, C.L., Guan, D.D., Liu, C.H., Qian, D., Zhang, S.C., Jia, J.F.: Epitaxial growth of two-dimensional stanene. Nat. Mater. 14, 1020 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by Azarbaijan Shahid Madani University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abbasi, A., Jahanbin Sardroodi, J. Interaction of sulfur trioxide molecules with armchair and zigzag stanene-based nanotubes: electronic properties exploration by DFT calculations. Adsorption 24, 443–458 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-018-9954-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-018-9954-1