Abstract
Purpose
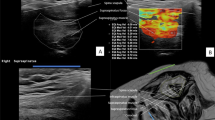
The gray-level histogram of ultrasound is a promising tool for scanning the hypoechogenic appearance of supraspinatus tendinopathy, and the aim of this study was to test the hypothesis that the gray-level value of the supraspinatus tendon in the painful shoulder has a lower value on B-mode images even though in different ultrasound devices.
Methods
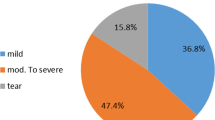
Sixty-seven patients who had unilateral shoulder pain with rotator cuff tendinopathy underwent bilateral shoulder ultrasonography, and we compared the mean gray-level values of painful shoulders and contralateral shoulders without any pain in each patient using two ultrasound devices. The echogenicity ratio (symptomatic/asymptomatic side) of two ultrasound devices was compared.
Results
A significant difference existed between the symptomatic shoulder and contralateral asymptomatic shoulder (p < 0.001) on the mean gray-level value measurements of each device. The symptomatic-to-asymptomatic tendon echogenicity ratio of device A was 0.919 ± 0.090 in the transverse plane and 0.937 ± 0.081 in the longitudinal plane, and the echogenicity ratio of device B was 0.899 ± 0.113 in the transverse plane and 0.940 ± 0.113 in the longitudinal plane.
Conclusions
The decline of the mean gray-level value and the echogenicity ratio of the supraspinatus tendon in the painful shoulder may be utilized as a useful sonographic reference of unilateral rotator cuff lesions.
Level of evidence
Diagnostic level III.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guerini H, Fermand M, Godefroy D, et al. US appearance of partial-thickness supraspinatus tendon tears: application of the String theory. Pictorial essay. J Ultrasound. 2012;15:7–15.
Finnoff JT, Smith J, Peck ER. Ultrasonography of the shoulder. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2010;21:481–507.
Smith TO, Back T, Toms AP, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound for rotator cuff tear in adult: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Radiol. 2011;66:1036–48.
Maeda K, Utsu M, Kihaile PE. Quantificaion of sonographic echogenicity with grey-level hostogram width: a clinical tissue characterization. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1998;24:225–34.
Ito T, Ishihara K, Deura I, et al. Tissue characterizarion of uterine myometrium using the ultrasound gray-level histogram width. J Med Ultrasonics. 2007;34:189–92.
Maeda K, Ulsu M, Yamamoto N, et al. Echoeniciy of fetal lung and liver quantified by the grey-level histogram width. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1999;25:201–8.
Serizawa M, Maeda K. Noninvasive fetal lung maturity prediction based on ultrasonic gray-level histogram width. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2010;36:1998–2003.
Yang X, Tridandapani S, Beitler JJ, et al. Ultrasound histogram assessment of parotid gland injury following head-and neck radiotherapy: a feasibility study. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2012;38:1514–21.
Lee CH, Choi JW, Kim KA, et al. Usefulness of standard deviation on the histogram of ultrasound as a quantitative value for hepatic parenchymal echo texture; preliminary study. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2006;32:1817–26.
Al-Took S, Watkin K, Tulandi T, et al. Ovarian stromal echogenicity in women with clomiphene citrate-sensitive and clomiphene citrate-resistant polycystic ovary syndrome. Fertil Steril. 1999;71:952–4.
Pillan S, Verrips A, van Alfen N, et al. Quantitative skeletal muscle ultrasound: diagnostic value in childhood neuromuscular disease. Neuromuscul Disord. 2007;17:509–16.
Maffulli N, Wong J, Almekinders LC. Types and epidemiology of tendinopathy. Clin Sports Med. 2003;22:675–92.
Robinson P. Sonography of common tendon injuries. AJR. 2009;193:607–18.
Collinger JL, Gagnon D, Jacobson J, et al. Reliability of quantitative ultrasound measures of the biceps and supraspinatus tendon. Acad Radiol. 2009;16:1424–32.
Yu TY, Tsai WC, Cheng JW, et al. The effects of aging on quantitative sonographic features of rotator cuff tendons. J Clin Ultrasound. 2012;40:471–8.
Huang SW, Wang WT. Quantitative diagnostic method for biceps long head tendinitis by using ultrasound. Sci World J. 2013;948323:7.
Chang KV, Chen WS, Wang TG, et al. Quantitative ultrasound facilitates the exploration of morphological association of the long head biceps tendon with supraspinatus tendon full thickness tear. PLoS One. 2014;11:e113803.
Tsai YH, Huang K, Shen SH, et al. Quantification of sonographic echogenicity by the gray-level histogram in patients with supraspinatus tendinopathy. J Med Ultrasonics. 2014;41:343–9.
Rutten MJ, Maresch BJ, Jager GJ, et al. Ultrasound of the rotator cuff with MRI and anatomic correlation. Eur J Radiol. 2007;62:427–36.
Lewis JS, Raza SA, Pilcher J, et al. The prevalence of neovascularity in patients clinically diagnosed with rotator cuff tendinopathy. BMC Musculoskel Disord. 2009;10:163.
Bianchi S, Martinoli C. Ultrasound of the musculoskeletal system. New York: Spinger; 2007.
Mochizuki T, Sugaya H, Uomizu M, et al. Humeral insertion of the supraspinatus and infraspinatus. New anatomical findings regarding the footprint of the rotator cuff. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90:962–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no financial or other relations that could lead to a conflict of interest.
Ethical statement
This retrospective study was approved by the Ethics Committee and institutional review board of Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (97-1302B).
About this article
Cite this article
Hsu, JC., Chen, PH., Huang, KC. et al. Efficiency of quantitative echogenicity for investigating supraspinatus tendinopathy by the gray-level histogram of two ultrasound devices. J Med Ultrasonics 44, 297–303 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-017-0777-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-017-0777-6