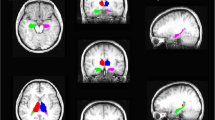
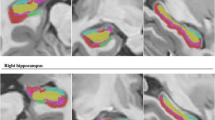
Abstract
Objective
To develop a decision-making tool to evaluate and compare the performance of neuroimaging markers with clinical findings and the significance of attributes for presurgical lateralization of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy (mTLE).
Methods
Thirty-five unilateral mTLE patients who qualified as candidates for surgical resection were studied. Seizure semiology, ictal EEG, ictal epileptogenic zone, interictal–irritative zone, and MRI findings were used as clinical markers. Hippocampal T1 volumetry and FLAIR intensity, DTI estimated; mean diffusivity (MD) in the hippocampus and fractional anisotropy (FA) in posteroinferior cingulum and crus of fornix, and the output of logistic regression method on volumetrics of the hippocampus, amygdala, and thalamus were adopted as neuroimaging markers. The self-organizing map (SOM) method was applied to markers to provide predictive methods for mTLE lateralization.
Results
The SOM clustered all clinical attributes correctly with 100% accuracy and sensitivity for both the left and right mTLE. Among the clinical markers, seizure semiology and interictal-irrelative zone are the most sensitive attribute for the left-mTLE group lateralization. The accuracy achieved by applying the SOM method to the neuroimaging attributes was 94%, while the sensitivity was achieved 90% for left and 100% for right mTLE. SOM evidence indicated that the hippocampal volume is the most sensitive attribute for the prediction of the laterality in left-mTLE groups.
Conclusion
The proposed SOM method showed that neuroimaging markers may not replace with clinical findings. Nevertheless, multimodal neuroimaging can play an effective role in preoperative lateralization to reduce the costs and risks of surgical resection.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Engel J (2001) Mesial temporal lobe epilepsy: what have we learned? Neuroscientist 7:340–352. https://doi.org/10.1177/107385840100700410
Téllez-Zenteno JF, Hernández-Ronquillo L (2012) A review of the epidemiology of temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res Treat. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/630853
Rubinger L, Chan C, D’Arco F, Moineddin R, Muthaffar O, Rutka JT, Snead OC, Lou SM, Widjaja E (2016) Change in presurgical diagnostic imaging evaluation affects subsequent pediatric epilepsy surgery outcome. Epilepsia 57:32–40. https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.13229
Akhondi-Asl A, Jafari-Khouzani K, Elisevich K, Soltanian-Zadeh H (2011) Hippocampal volumetry for lateralization of temporal lobe epilepsy: automated versus manual methods. Neuroimage 54:S218–S226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.03.066
Lopez-Acevedo M, Martinez-Lopez M, Favila R, Roldan-Valadez E (2012) Secondary MRI-findings, conventional volumetric and spectroscopic measurements between negative- and positive-patients with mesial temporal sclerosis: a multivariate discriminant analysis. Swiss Med Wkly. https://doi.org/10.4414/smw.2012.13549
Schiller Y, Cascino GD, Sharbrough FW (1998) Chronic intracranial EEG monitoring for localizing the epileptogenic zone: an electroclinical correlation. Epilepsia 39:1302–1308. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1157.1998.tb01328.x
Jafari-Khouzani K, Elisevich K, Wasade VS, Soltanian-Zadeh H (2018) Contribution of quantitative amygdalar MR FLAIR signal analysis for lateralization of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neuroimaging 28:666–675. https://doi.org/10.1111/jon.12549
Nazem-Zadeh M-R, Davoodi-Bojd E, Soltanian-Zadeh H (2010) Level set fiber bundle segmentation using spherical harmonic coefficients. Comput Med Imaging Graph 34:192–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compmedimag.2009.09.003
Mahmoudi F, Elisevich K, Bagher-Ebadian H, Nazem-Zadeh MR, Davoodi-Bojd E, Schwalb JM, Kaur M, Soltanian-Zadeh H (2018) Correction: data mining MR image features of select structures for lateralization of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. PLoS ONE 13(8):e0199137. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0199137
Nazem-Zadeh MR, Elisevich K, Air EL, Schwalb JM, Divine G, Kaur M, Wasade VS, Mahmoudi F, Shokri S, Bagher-Ebadian H, Soltanian-Zadeh H (2016) DTI-based response-driven modeling of mTLE laterality. NeuroImage Clin 11:694–706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2015.10.015
Nazem-Zadeh MR, Elisevich KV, Schwalb JM, Bagher-Ebadian H, Mahmoudi F, Soltanian-Zadeh H (2014) Lateralization of temporal lobe epilepsy by multimodal multinomial hippocampal response-driven models. J Neurol Sci 347:107–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2014.09.029
Hufnagel A, Weber J, Marks S, Ludwig T, De Greiff A, Leonhardt G, Widmann G, Stolke D, Forsting M (2003) Brain diffusion after single seizures. Epilepsia 44:54–63. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1528-1157.2003.07802.x
Parekh MB, Carney PR, Sepulveda H, Norman W, King M, Mareci TH (2010) Early MR diffusion and relaxation changes in the parahippocampal gyrus precede the onset of spontaneous seizures in an animal model of chronic limbic epilepsy. Exp Neurol 224:258–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2010.03.031
Wall CJ, Kendall EJ, Obenaus A (2000) Rapid alterations in diffusion-weighted images with anatomic correlates in a rodent model of status epilepticus. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1841–1852
Ahmadi ME, Hagler DJ, McDonald CR, Tecoma ES, Iragui VJ, Dale AM, Halgren E (2009) Side matters: diffusion tensor imaging tractography in left and right temporal lobe epilepsy. Am J Neuroradiol 30:1740–1747. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A1650
Focke NK, Yogarajah M, Bonelli SB, Bartlett PA, Symms MR, Duncan JS (2008) Voxel-based diffusion tensor imaging in patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy and hippocampal sclerosis. Neuroimage 40:728–737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.12.031
Yoo SY, Chang K-H, Song IC, Han MH, Kwon BJ, Lee SH, Yu IK, Chun C-K (2002) Apparent diffusion coefficient value of the hippocampus in patients with hippocampal sclerosis and in healthy volunteers. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23(809–12):12006282
Gabrieli JDE, Ghosh SS, Whitfield-Gabrieli S (2015) Prediction as a humanitarian and pragmatic contribution from human cognitive neuroscience. Neuron 85:11–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2014.10.047
Lee JS, Lee DS, Kim SK, Lee SK, Chung JK, Lee MC, Park KS (2000) Localization of epileptogenic zones in F-18 FDG brain PET of patients with temporal lobe epilepsy using artificial neural network. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 19:347–355. https://doi.org/10.1109/42.848185
Sahebzamani G, Saffar M, Soltanian-Zadeh H (2019) Machine learning based analysis of structural MRI for epilepsy diagnosis. In: 2019 4th international conference on pattern recognition and image analysis (IPRIA). IEEE, pp 58–63
Mahmoudi F, Elisevich K, Bagher-Ebadian H, Nazem-Zadeh MR, Davoodi-Bojd E, Schwalb JM, Kaur M, Soltanian-Zadeh H (2018) Data mining MR image features of select structures for lateralization of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. PLoS ONE 13:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0199137
Beheshti I, Sone D, Maikusa N, Kimura Y, Shigemoto Y, Sato N, Matsuda H (2020) Pattern analysis of glucose metabolic brain data for lateralization of MRI-negative temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 167:106474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2020.106474
Beheshti I, Sone D, Maikusa N, Kimura Y, Shigemoto Y, Sato N, Matsuda H (2020) FLAIR-wise machine-learning classification and lateralization of mri-negative 18F-FDG PET-positive temporal lobe epilepsy. Front Neurol 11:1–9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2020.580713
Amiri S, Mehvari-Habibabadi J, Mohammadi-Mobarakeh N, Hashemi-Fesharaki SS, Mirbagheri MM, Elisevich K, Nazem-Zadeh M-R (2020) Graph theory application with functional connectivity to distinguish left from right temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 167:106449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2020.106449
Fallahi A, Pooyan M, Lotfi N, Baniasad F, Tapak L, Mohammadi-Mobarakeh N, Hashemi-Fesharaki SS, Mehvari-Habibabadi J, Ay MR, Nazem-Zadeh M-R (2020) Dynamic functional connectivity in temporal lobe epilepsy: a graph theoretical and machine learning approach. Neurol Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-020-04759-x
Yang Z, Choupan J, Reutens D, Hocking J (2015) Lateralization of temporal lobe epilepsy based on resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging and machine learning. Front Neurol 6:1–9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2015.00184
Su L, An J, Ma Q, Qiu S, Hu D (2015) Influence of resting-state network on lateralization of functional connectivity in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Am J Neuroradiol 36:1479–1487. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A4346
Nazem-Zadeh M-R, Schwalb JM, Elisevich KV, Bagher-Ebadian H, Hamidian H, Akhondi-Asl A-R, Jafari-Khouzani K, Soltanian-Zadeh H (2014) Lateralization of temporal lobe epilepsy using a novel uncertainty analysis of MR diffusion in hippocampus, cingulum, and fornix, and hippocampal volume and FLAIR intensity. J Neurol Sci 342:152–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2014.05.019
Nazem-Zadeh M-R, Bowyer SM, Moran JE, Davoodi-Bojd E, Zillgitt A, Weiland BJ, Bagher-Ebadian H, Mahmoudi F, Elisevich K, Soltanian-Zadeh H (2016) MEG coherence and DTI connectivity in mTLE. Brain Topogr 29:598–622. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-016-0488-0
Jamali-Dinan S-S, Soltanian-Zadeh H, Bowyer SM, Almohri H, Dehghani H, Elisevich K, Nazem-Zadeh M-R (2020) A combination of particle swarm optimization and minkowski weighted k-means clustering: application in lateralization of temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain Topogr 33:519–532. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-020-00770-9
Kamiya K, Amemiya S, Suzuki Y, Kunii N, Kawai K, Mori H, Kunimatsu A, Saito N, Aoki S, Ohtomo K (2016) Machine learning of dti structural brain connectomes for lateralization of temporal lobe epilepsy. Magn Reson Med Sci 15:121–129. https://doi.org/10.2463/mrms.2015-0027
Wu T, Chen D, Chen Q, Zhang R, Zhang W, Li Y, Zhang L, Liu H, Wan S, Jiang T, Zhang J (2018) Automatic lateralization of temporal lobe epilepsy based on MEG network features using support vector machines. Complexity. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/4325096
Wong CYO, Gannon J, Bong J, Wong CO, Saha GB (2007) Computer-assisted lateralization of unilateral temporal lobe epilepsy using Z-score parametric F-18 FDG PET images. BMC Nucl Med 7:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2385-7-5
Pustina D, Avants B, Sperling M, Gorniak R, He X, Doucet G, Barnett P, Mintzer S, Sharan A, Tracy J (2015) Predicting the laterality of temporal lobe epilepsy from PET, MRI, and DTI: a multimodal study: Predicting temporal lobe epilepsy laterality. NeuroImage Clin 9:20–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2015.07.010
Ercan K, Gunbey HP, Bilir E, Zan E, Arslan H (2016) Comparative lateralizing ability of multimodality MRI in temporal lobe epilepsy. Dis Markers. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/5923243
Cantor-Rivera D, Khan AR, Goubran M, Mirsattari SM, Peters TM (2015) Detection of temporal lobe epilepsy using support vector machines in multi-parametric quantitative MR imaging. Comput Med Imaging Graph 41:14–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compmedimag.2014.07.002
Ma K, Zhang X, Zhang H, Yan X, Gao A, Song C, Wang S, Lian Y, Cheng J (2020) Mean apparent propagator-MRI: a new diffusion model which improves temporal lobe epilepsy lateralization. Eur J Radiol 126:108914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.108914
Kohonen T (2001) Self-organizing maps. Springer, Berlin
Li T, Sun G, Yang C, Liang K, Ma S, Huang L (2018) Using self-organizing map for coastal water quality classification: towards a better understanding of patterns and processes. Sci Total Environ 628–629:1446–1459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.02.163
Speight VL, Mounce SR, Boxall JB (2019) Identification of the causes of drinking water discolouration from machine learning analysis of historical datasets. Environ Sci Water Res Technol 5:747–755. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ew00733k
Krasznai E, Boda P, Csercsa A, Ficsór M, Várbíró G (2016) Use of self-organizing maps in modelling the distribution patterns of gammarids (Crustacea: Amphipoda). Ecol Inf 31:39–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoinf.2015.11.007
Dayhoff JE (1990) Neural network architectures: an introduction. Van Nostrand Reinhold Co., New York
Chen DG, Ware DM (1999) A neural network model for forecasting fish stock recruitment. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 56:2385–2396. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjfas-56-12-2385
Astel A, Tsakovski S, Barbieri P, Simeonov V (2007) Comparison of self-organizing maps classification approach with cluster and principal components analysis for large environmental data sets. Water Res 41:4566–4578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.06.030
Kohonen T (1998) The self-organizing map. Neurocomputing 21:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-2312(98)00030-7
Nazem-Zadeh M-R, Chapman CH, Lawrence TL, Tsien CI, Cao Y (2012) Radiation therapy effects on white matter fiber tracts of the limbic circuit. Med Phys 39:5603–5613. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.4745560
Jenkinson M, Bannister P, Brady M, Smith S (2002) Improved optimization for the robust and accurate linear registration and motion correction of brain images. Neuroimage 17:825–841
Jafari-Khouzani K, Elisevich K, Patel S, Smith B, Soltanian-Zadeh H (2010) FLAIR signal and texture analysis for lateralizing mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Neuroimage 49:1559–1571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.08.064
Ki SJ, Kang J-H, Lee SW, Lee YS, Cho KH, An K-G, Kim JH (2011) Advancing assessment and design of stormwater monitoring programs using a self-organizing map: characterization of trace metal concentration profiles in stormwater runoff. Water Res 45:4183–4197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.05.021
Tobiszewski M, Tsakovski S, Simeonov V, Namieśnik J (2012) Chlorinated solvents in a petrochemical wastewater treatment plant: an assessment of their removal using self-organising maps. Chemosphere 87:962–968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.01.057
Davies DL, Bouldin DW (1979) A Cluster Separation Measure. IEEE Trans Anal Mach Intell PAMI-1. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.1979.4766909
Céréghino R, Park Y-S (2009) Review of the Self-Organizing Map (SOM) approach in water resources: commentary. Environ Model Softw 24:945–947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2009.01.008
Vesanto J, Alhoniemi E (2000) Clustering of the self-organizing map. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 11:586–600. https://doi.org/10.1109/72.846731
Park Y-S, Céréghino R, Compin A, Lek S (2003) Applications of artificial neural networks for patterning and predicting aquatic insect species richness in running waters. Ecol Model 160:265–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3800(02)00258-2
Tsai W-P, Huang S-P, Cheng S-T, Shao K-T, Chang F-J (2017) A data-mining framework for exploring the multi-relation between fish species and water quality through self-organizing map. Sci Total Environ 579:474–483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.11.071
Vesanto J, Himberg J, Alhoniemi E, Parhankangas J (1999) Self-organizing map in Matlab: the SOM toolbox. In: MATLAB digital signal processing conference. pp 35–40
Nazem-Zadeh MR, Bowyer SM, Moran JE, Davoodi-Bojd E, Zillgitt A, Bagher-Ebadian H, Mahmoudi F, Elisevich KV, Soltanian-Zadeh H (2016) Application of DTI connectivity in lateralization of mTLE. In: 2016 38th annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society (EMBC). IEEE, pp 5525–5528
Mahmoudi F, Elisevich K, Bagher-ebadian H, Nazem-zadeh R, Davoodi-bojd E, Schwalb JM, Kaur M, Soltanian-zadeh H (2018) Data mining MR image features of select structures for lateralization of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. PLoS ONE 13(8):1–19
Baghdadi G, Amiri M (2020) Detection of static, dynamic, and no tactile friction based on non- linear dynamics of EEG signals : a preliminary study. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 142:1–37
Serles W, Caramanos Z, Lindinger G, Pataraia E, Baumgartner C (2000) Combining ictal surface-electroencephalography and seizure semiology improves patient lateralization in temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 41:1567–1573. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1499-1654.2000.001567.x
Elwan S, Alexopoulos A, Silveira DC, Kotagal P (2018) Lateralizing and localizing value of seizure semiology: comparison with scalp EEG, MRI and PET in patients successfully treated with resective epilepsy surgery. Seizure 61:203–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seizure.2018.08.026
Kerr WT, Nguyen ST, Cho AY, Lau EP, Silverman DH, Douglas PK, Reddy NM, Anderson A, Bramen J, Salamon N, Stern JM, Cohen MS (2013) Computer-aided diagnosis and localization of lateralized temporal lobe epilepsy using interictal FDG-PET. Front Neurol 4:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2013.00031
García-Fiñana M, Denby CE, Keller SS, Wieshmann UC, Roberts N (2006) Degree of hippocampal atrophy is related to side of seizure onset in temporal lobe epilepsy. Am J Neuroradiol 27:1046–1052
Verhoeven T, Coito A, Plomp G, Thomschewski A, Pittau F, Trinka E, Wiest R, Schaller K, Michel C, Seeck M, Dambre J, Vulliemoz S, Van Mierlo P (2018) NeuroImage : clinical automated diagnosis of temporal lobe epilepsy in the absence of interictal spikes. NeuroImage Clin 17:10–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2017.09.021
Mahmoudi F, Bagher-Ebadian H, Nazem-Zadeh MR, Elisevich K V., Schwalb JM, Air EL, Soltanian-Zadeh H (2015) A multistructural imaging marker for non-invasive lateralization of temporal lobe epilepsy. Proceedings international symposium on biomedical imaging, pp, 482–485. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ISBI.2015.7163916
Acknowledgements
We must acknowledge the contribution of the Iranian National Brain Mapping Lab (NBML), and their staffs for MRI data acquisition throughout conducting this project.
Funding
This work was partially funded and supported by Iran’s National Elites Foundation, National Institute for Medical Research Development (Grant No. 971683), and Cognitive Sciences and Technologies Council (Grant No. 6431), between 2017 and 2019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or the national research committee as well as with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fallahi, A., Pooyan, M., Habibabadi, J.M. et al. Comparison of multimodal findings on epileptogenic side in temporal lobe epilepsy using self-organizing maps. Magn Reson Mater Phy 35, 249–266 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-021-00948-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-021-00948-7