Abstract
Purpose
Diabetic neuropathy is a common and disabling disorder, and there are currently no proven effective disease-modifying treatments. Physical activity and dietary interventions in patients with diabetes and diabetic neuropathy have multiple beneficial effects and are generally low risk, which makes lifestyle interventions an attractive treatment option. We reviewed the literature on the effects of physical activity and dietary interventions on length-dependent peripheral neuropathy and cardiac autonomic neuropathy in diabetes.
Methods
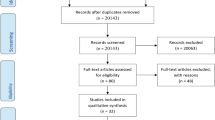
The electronic database PubMed was systematically searched for original human and mouse model studies examining the effect of either dietary or physical activity interventions in subjects with diabetes, prediabetes, or metabolic syndrome.
Results
Twenty studies are included in this review. Fourteen studies were human studies and six were in mice. Studies were generally small with few controlled trials, and there are no widely agreed upon outcome measures.
Conclusions
Recent research indicates that dietary interventions are effective in modifying diabetic neuropathy in animal models, and there are promising data that they may also ameliorate diabetic neuropathy in humans. It has been known for some time that lifestyle interventions can prevent the development of diabetic neuropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus subjects. However, there is emerging evidence that lifestyle interventions are effective in individuals with established diabetic neuropathy. In addition to the observed clinical value of lifestyle interventions, there is emerging evidence of effects on biochemical pathways that improve muscle function and affect other organ systems, including the peripheral nerve. However, data from randomized controlled trials are needed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cho NH, Shaw JE, Karuranga S, Huang Y, da Rocha Fernandes JD, Ohlrogge AW, Malanda B (2018) IDF diabetes atlas: global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 138:271–281
Dyck PJ, Kratz KM, Karnes JL, Litchy WJ, Klein R, Pach JM, Wilson DM, O’Brien PC, Melton LJ III, Service FJ (1993) The prevalence by staged severity of various types of diabetic neuropathy, retinopathy, and nephropathy in a population-based cohort: the Rochester Diabetic Neuropathy Study. Neurology 43:817–824
Dyck PJB, Dyck PJ (1999) Diabetic polyneuropathy. In: Dyck PJ, Thomas PK (eds) Diabetic neuropathy. W.B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia, pp 255–278
Albers JW, Herman WH, Pop-Busui R, Martin CL, Cleary P, Waberski B (2007) Subclinical neuropathy among Diabetes Control and Complications Trial participants without diagnosable neuropathy at trial completion: possible predictors of incident neuropathy? Diabetes Care 30:2613–2618
Zilliox L, Peltier AC, Wren PA, Anderson A, Smith AG, Singleton JR, Feldman EL, Alexander NB, Russell JW (2011) Assessing autonomic dysfunction in early diabetic neuropathy: the Survey of Autonomic Symptoms. Neurology 76:1099–1105
Costa LA, Canani LH, Lisbôa HR, Tres GS, Gross JL (2004) Aggregation of features of the metabolic syndrome is associated with increased prevalence of chronic complications in type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med 21:252–255
Smith AG, Rose K, Singleton JR (2008) Idiopathic neuropathy patients are at high risk for metabolic syndrome. J Neurol Sci 273:25–28
Smith AG, Singleton JR (2013) Obesity and hyperlipidemia are risk factors for early diabetic neuropathy. J Diabetes Complications 27:436–442
Bergström B, Lilja B, Osterlin S, Sundkvist G (1990) Autonomic neuropathy in non-insulin dependent (type II) diabetes mellitus. Possible influence of obesity. J Intern Med 227:57–63
Emdin M, Gastaldelli A, Muscelli E, Macerata A, Natali A, Camastra S, Ferrannini E (2001) Hyperinsulinemia and autonomic nervous system dysfunction in obesity: effects of weight loss. Circulation 103:513–519
Peterson HR, Rothschild M, Weinberg CR, Fell RD, McLeish KR, Pfeifer MA (1988) Body fat and the activity of the autonomic nervous system. N Engl J Med 318:1077–1083
Sumner CJ, Sheth S, Griffin JW, Cornblath DR, Polydefkis M (2003) The spectrum of neuropathy in diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance. Neurology 60:108–111
Polydefkis M, Hauer P, Sheth S, Sirdofsky M, Griffin JW, McArthur JC (2004) The time course of epidermal nerve fibre regeneration: studies in normal controls and in people with diabetes, with and without neuropathy. Brain 127:1606–1615
Smith AG, Howard JR, Kroll R, Ramachandran P, Hauer P, Singleton JR, McArthur J (2005) The reliability of skin biopsy with measurement of intraepidermal nerve fiber density. J Neurol Sci 228:65–69
Lauria G, Hsieh ST, Johansson O, Kennedy WR, Leger JM, Mellgren SI, Nolano M, Merkies IS, Polydefkis M, Smith AG, Sommer C, Valls-Sole J, European Federation of Neurological Societies, Peripheral Nerve Society (2010) European Federation of Neurological Societies/Peripheral Nerve Society guideline on the use of skin biopsy in the diagnosis of small fiber neuropathy. Report of a joint task force of the European Federation of Neurological Societies and the Peripheral Nerve Society. Eur J Neurol 17:903–912 (e944–909)
Knowler WC, Barrett-Connor E, Fowler SE, Hamman RF, Lachin JM, Walker EA, Nathan DM (2002) Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N Engl J Med 346:393–403
Ametov AS, Barinov A, Dyck PJ, Hermann R, Kozlova N, Litchy WJ, Low PA, Nehrdich D, Novosadova M, O’Brien PC, Reljanovic M, Samigullin R, Schuette K, Strokov I, Tritschler HJ, Wessel K, Yakhno N, Ziegler D (2003) The sensory symptoms of diabetic polyneuropathy are improved with alpha-lipoic acid: the SYDNEY trial. Diabetes Care 26:770–776
Ziegler D, Ametov A, Barinov A, Dyck PJ, Gurieva I, Low PA, Munzel U, Yakhno N, Raz I, Novosadova M, Maus J, Samigullin R (2006) Oral treatment with alpha-lipoic acid improves symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy: the SYDNEY 2 trial. Diabetes Care 29:2365–2370
Ziegler D, Low PA, Freeman R, Tritschler H, Vinik AI (2016) Predictors of improvement and progression of diabetic polyneuropathy following treatment with alpha-lipoic acid for 4 years in the NATHAN 1 trial. J Diabetes Complications 30:350–356
Ziegler D, Low PA, Litchy WJ, Boulton AJ, Vinik AI, Freeman R, Samigullin R, Tritschler H, Munzel U, Maus J, Schutte K, Dyck PJ (2011) Efficacy and safety of antioxidant treatment with alpha-lipoic acid over 4 years in diabetic polyneuropathy: the NATHAN 1 trial. Diabetes Care 34:2054–2060
Chandrasekaran KCC, Sagi AR, Russell JW (2016) A nicotinamide adenine nucleotide (NAD+) precursor is a potential therapy for diabetic neuropathy (abstract). In: ICNMD 2016: abstract book for the 14th International Congress on Neuromuscular Diseases, July 5–9, 2016 Toronto, Canada. J Neuromuscul Dis 3:S86
Trammell SA, Weidemann BJ, Chadda A, Yorek MS, Holmes A, Coppey LJ, Obrosov A, Kardon RH, Yorek MA, Brenner C (2016) Nicotinamide riboside opposes type 2 diabetes and neuropathy in mice. Sci Rep 6:26933. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep26933.:26933
Liu D, Gharavi R, Pitta M, Gleichmann M, Mattson MP (2009) Nicotinamide prevents NAD+ depletion and protects neurons against excitotoxicity and cerebral ischemia: NAD+ consumption by SIRT1 may endanger energetically compromised neurons. Neuromolecular Med 11:28–42
Min SW, Sohn PD, Cho SH, Swanson RA, Gan L (2013) Sirtuins in neurodegenerative diseases: an update on potential mechanisms. Front Aging Neurosci 5:53
Stevens MJ, Li F, Drel VR, Abatan OI, Kim H, Burnett D, Larkin D, Obrosova IG (2007) Nicotinamide reverses neurological and neurovascular deficits in streptozotocin diabetic rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 320:458–464
Canto C, Houtkooper RH, Pirinen E, Youn DY, Oosterveer MH, Cen Y, Fernandez-Marcos PJ, Yamamoto H, Andreux PA, Cettour-Rose P, Gademann K, Rinsch C, Schoonjans K, Sauve AA, Auwerx J (2012) The NAD(+) precursor nicotinamide riboside enhances oxidative metabolism and protects against high-fat diet-induced obesity. Cell Metab 15:838–847
Avinash Rao S, Priyanka S, Chen C, Chandrasekaran K, Russell JW (2015) Administration of either nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) or over expression of SIRT1 prevents and treats peripheral neuropathy in type 1 and type 2 diabetic mouse models (abstract). In: 3rd International Conference and Exhibition on Neurology and Therapeutics. J Neurol Neurophysiol 6:3
Zilliox LA, Chadrasekaran K, Kwan JY, Russell JW (2016) Diabetes and cognitive impairment. Curr Diabet Rep 16:87
Russell JW, Chandrasekaran K, Choi J, Chen H (2013) Nicotinamide adenine nucleotide (NAD+) regulation of sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) in the treatment of diabetic neuropathy (abstract). Ann Neurol p S95
Yoshino J, Mills KF, Yoon MJ, Imai S (2011) Nicotinamide mononucleotide, a key NAD(+) intermediate, treats the pathophysiology of diet- and age-induced diabetes in mice. Cell Metab 14:528–536
Kobilo T, Guerrieri D, Zhang Y, Collica SC, Becker KG, van Praag H (2014) AMPK agonist AICAR improves cognition and motor coordination in young and aged mice. Learn Mem 21:119–126
Cooper MA, Menta BW, Perez-Sanchez C, Jack MM, Khan ZW, Ryals JM, Winter M, Wright DE (2018) A ketogenic diet reduces metabolic syndrome-induced allodynia and promotes peripheral nerve growth in mice. Exp Neurol 306:149–157
Coppey L, Davidson E, Shevalye H, Torres ME, Yorek MA (2018) Effect of dietary oils on peripheral neuropathy-related endpoints in dietary obese rats. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes 11:117–127
Hinder LM, O’Brien PD, Hayes JM, Backus C, Solway AP, Sims-Robinson C, Feldman EL (2017) Dietary reversal of neuropathy in a murine model of prediabetes and metabolic syndrome. Dis Model Mech 10:717–725
Lewis EJH, Perkins BA, Lovblom LE, Bazinet RP, Wolever TMS, Bril V (2017) Effect of omega-3 supplementation on neuropathy in type 1 diabetes: a 12-month pilot trial. Neurology 88:2294–2301
Lewis EJ, Perkins BA, Lovblom LE, Bazinet RP, Wolever TM, Bril V (2017) Using in vivo corneal confocal microscopy to identify diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy risk profiles in patients with type 1 diabetes. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care 5:e000251
Pritchard N, Edwards K, Russell AW, Perkins BA, Malik RA, Efron N (2015) Corneal confocal microscopy predicts 4-year incident peripheral neuropathy in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 38:671–675
Groover AL, Ryals JM, Guilford BL, Wilson NM, Christianson JA, Wright DE (2013) Exercise-mediated improvements in painful neuropathy associated with prediabetes in mice. Pain 154:2658–2667
Simone DA, Nolano M, Johnson T, Wendelschafer-Crabb G, Kennedy WR (1998) Intradermal injection of capsaicin in humans produces degeneration and subsequent reinnervation of epidermal nerve fibers: correlation with sensory function. J Neurosci 18:8947–8959
Singleton JR, Marcus RL, Lessard MK, Jackson JE, Smith AG (2015) Supervised exercise improves cutaneous reinnervation capacity in metabolic syndrome patients. Ann Neurol 77:146–153
Singleton JR, Smith AG, Russell JW, Feldman EL (2003) Microvascular complications of impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetes 52:2867–2876
Orchard TJ, Temprosa M, Goldberg R, Haffner S, Ratner R, Marcovina S, Fowler S, Group DPPR (2005) The effect of metformin and intensive lifestyle intervention on the metabolic syndrome: the Diabetes Prevention Program randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 142:611–619
Balducci S, Iacobellis G, Parisi L, Di Biase N, Calandriello E, Leonetti F, Fallucca F (2006) Exercise training can modify the natural history of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J Diabetes Complications 20:216–223
Singleton JR, Marcus RL, Jackson JE, Lessard K, Graham TE, Smith AG (2014) Exercise increases cutaneous nerve density in diabetic patients without neuropathy. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 1:844–849
Smith AG, Russell JW, Feldman EL, Goldstein J, Peltier A, Smith S, Hamwi J, Pollari D, Bixby B, Howard J, Singleton JR (2006) Lifestyle intervention for prediabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Care 29:1294–1299
Kluding PM, Pasnoor M, Singh R, Jernigan S, Farmer K, Rucker J, Sharma NK, Wright DE (2012) The effect of exercise on neuropathic symptoms, nerve function, and cutaneous innervation in people with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J Diabetes Complications 26:424–429
Müller-Stich BP, Fischer L, Kenngott HG, Gondan M, Senft J, Clemens G, Nickel F, Fleming T, Nawroth PP, Büchler MW (2013) Gastric bypass leads to improvement of diabetic neuropathy independent of glucose normalization—results of a prospective cohort study (DiaSurg 1 study). Ann Surg 258:760–765 (discussion 765–766)
Dixit S, Maiya A, Shastry B (2014) Effect of aerobic exercise on quality of life in population with diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes: a single blind, randomized controlled trial. Qual Life Res 23:1629–1640
Handsaker JC, Brown SJ, Bowling FL, Cooper G, Maganaris CN, Boulton AJ, Reeves ND (2014) Contributory factors to unsteadiness during walking up and down stairs in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Diabetes Care 37:3047–3053
Handsaker JC, Brown SJ, Bowling FL, Maganaris CN, Boulton AJ, Reeves ND (2016) Resistance exercise training increases lower limb speed of strength generation during stair ascent and descent in people with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Diabet Med 33:97–104
Morrison S, Colberg SR, Parson HK, Vinik AI (2014) Exercise improves gait, reaction time and postural stability in older adults with type 2 diabetes and neuropathy. J Diabetes Complications 28:715–722
Mueller MJ, Tuttle LJ, Lemaster JW, Strube MJ, McGill JB, Hastings MK, Sinacore DR (2013) Weight-bearing versus nonweight-bearing exercise for persons with diabetes and peripheral neuropathy: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 94:829–838
Taveggia G, Villafane JH, Vavassori F, Lecchi C, Borboni A, Negrini S (2014) Multimodal treatment of distal sensorimotor polyneuropathy in diabetic patients: a randomized clinical trial. J Manip Physiol Ther 37:242–252
Astrup AS, Tarnow L, Rossing P, Hansen BV, Hilsted J, Parving HH (2006) Cardiac autonomic neuropathy predicts cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in type 1 diabetic patients with diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Care 29:334–339
Spallone V, Ziegler D, Freeman R, Bernardi L, Frontoni S, Pop-Busui R, Stevens M, Kempler P, Hilsted J, Tesfaye S, Low P, Valensi P (2011) Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in diabetes: clinical impact, assessment, diagnosis, and management. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 27:639–653
Grisé KN, Olver TD, McDonald MW, Dey A, Jiang M, Lacefield JC, Shoemaker JK, Noble EG, Melling CW (2016) High intensity aerobic exercise training improves deficits of cardiovascular autonomic function in a rat model of type 1 diabetes mellitus with moderate hyperglycemia. J Diabetes Res 2016:8164518
Voulgari C, Pagoni S, Vinik A, Poirier P (2013) Exercise improves cardiac autonomic function in obesity and diabetes. Metabolism 62:609–621
Facchini M, Malfatto G, Sala L, Silvestri G, Fontana P, Lafortuna C, Sartorio A (2003) Changes of autonomic cardiac profile after a 3-week integrated body weight reduction program in severely obese patients. J Endocrinol Invest 26:138–142
Figueroa A, Baynard T, Fernhall B, Carhart R, Kanaley JA (2007) Endurance training improves post-exercise cardiac autonomic modulation in obese women with and without type 2 diabetes. Eur J Appl Physiol 100:437–444
Ito H, Ohshima A, Tsuzuki M, Ohto N, Yanagawa M, Maruyama T, Kaji Y, Kanaya S, Nishioka K (2001) Effects of increased physical activity and mild calorie restriction on heart rate variability in obese women. Jpn Heart J 42:459–469
The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group (1998) The effect of intensive diabetes therapy on measures of autonomic nervous system function in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT). Diabetologia 41:416–423
Pop-Busui R, Low PA, Waberski BH, Martin CL, Albers JW, Feldman EL, Sommer C, Cleary PA, Lachin JM, Herman WH (2009) Effects of prior intensive insulin therapy on cardiac autonomic nervous system function in type 1 diabetes mellitus: the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications study (DCCT/EDIC). Circulation 119:2886–2893
UKPDS (1998) Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Lancet 352:837–853
Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, Neil HA, Matthews DR (2008) Long-term follow-up after tight control of blood pressure in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 359:1565–1576
Gaede P, Vedel P, Larsen N, Jensen GV, Parving HH, Pedersen O (2003) Multifactorial intervention and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 348:383–393
Pop-Busui R, Boulton AJ, Feldman EL, Bril V, Freeman R, Malik RA, Sosenko JM, Ziegler D (2017) Diabetic neuropathy: a position statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 40:136–154
Bhagyalakshmi S, Nagaraja H, Anupama B, Ramesh B, Prabha A, Niranjan M, Shreedhara A (2007) Effect of supervised integrated exercise on heart rate variability in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Kardiol Pol 65:363–368 (discussion 369)
Goit RK, Pant BN, Shrewastwa MK (2018) Moderate intensity exercise improves heart rate variability in obese adults with type 2 diabetes. Indian Heart J 70:486–491
Vanninen E, Uusitupa M, Länsimies E, Siitonen O, Laitinen J (1993) Effect of metabolic control on autonomic function in obese patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med 10:66–73
Zoppini G, Cacciatori V, Gemma ML, Moghetti P, Targher G, Zamboni C, Thomaseth K, Bellavere F, Muggeo M (2007) Effect of moderate aerobic exercise on sympatho-vagal balance in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabet Med 24:370–376
American Diabetes Association (2018) 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of medical care in diabetes—2018. Diabetes Care 41:S13–S27
Howorka K, Pumprla J, Haber P, Koller-Strametz J, Mondrzyk J, Schabmann A (1997) Effects of physical training on heart rate variability in diabetic patients with various degrees of cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy. Cardiovasc Res 34:206–214
Pagkalos M, Koutlianos N, Kouidi E, Pagkalos E, Mandroukas K, Deligiannis A (2008) Heart rate variability modifications following exercise training in type 2 diabetic patients with definite cardiac autonomic neuropathy. Br J Sports Med 42:47–54
Villafaina S, Collado-Mateo D, Fuentes JP, Merellano-Navarro E, Gusi N (2017) Physical exercise improves heart rate variability in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review. Curr Diab Rep 17:110
Burr JF, Shephard RJ, Riddell MC (2012) Physical activity in type 1 diabetes mellitus: assessing risks for physical activity clearance and prescription. Can Fam Physician 58:533–535
Vadstrup ES, Frølich A, Perrild H, Borg E, Røder M (2011) Health-related quality of life and self-related health in patients with type 2 diabetes: effects of group-based rehabilitation versus individual counselling. Health Qual Life Outcomes 9:110
Gibbons CH, Freeman R (2010) Treatment-induced diabetic neuropathy: a reversible painful autonomic neuropathy. Ann Neurol 67:534–541
Colberg SR, Sigal RJ, Fernhall B, Regensteiner JG, Blissmer BJ, Rubin RR, Chasan-Taber L, Albright AL, Braun B, American College of Sports Medicine, American Diabetes Association (2010) Exercise and type 2 diabetes: the American College of Sports Medicine and the American Diabetes Association: joint position statement executive summary. Diabetes Care 33:2692–2696
Colberg SR, Vinik AI (2014) Exercising with peripheral or autonomic neuropathy: what health care providers and diabetic patients need to know. Physiol Sports Med 42:15–23
Colberg SR, Swain DP, Vinik AI (2003) Use of heart rate reserve and rating of perceived exertion to prescribe exercise intensity in diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Diabetes Care 26:986–990
Acknowledgements
Supported in part by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National Institutes of Health 1R01DK107007-01A1, the Office of Research Development, Department of Veterans Affairs (Biomedical and Laboratory Research Service and Rehabilitation Research and Development, 101RX001030), the Diabetes Action Research and Education Foundation, and the Baltimore GRECC (JWR), 1K2RX001651 (LAZ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zilliox, L.A., Russell, J.W. Physical activity and dietary interventions in diabetic neuropathy: a systematic review. Clin Auton Res 29, 443–455 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10286-019-00607-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10286-019-00607-x