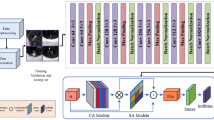
Abstract
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death. Since lung cancer appears as nodules in the early stage, detecting the pulmonary nodules in an early phase could enhance the treatment efficiency and improve the survival rate of patients. The development of computer-aided analysis technology has made it possible to automatically detect lung nodules in Computed Tomography (CT) screening. In this paper, we propose a novel detection network, TiCNet. It is attempted to embed a transformer module in the 3D Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) for pulmonary nodule detection on CT images. First, we integrate the transformer and CNN in an end-to-end structure to capture both the short- and long-range dependency to provide rich information on the characteristics of nodules. Second, we design the attention block and multi-scale skip pathways for improving the detection of small nodules. Last, we develop a two-head detector to guarantee high sensitivity and specificity. Experimental results on the LUNA16 dataset and PN9 dataset showed that our proposed TiCNet achieved superior performance compared with existing lung nodule detection methods. Moreover, the effectiveness of each module has been proven. The proposed TiCNet model is an effective tool for pulmonary nodule detection. Validation revealed that this model exhibited excellent performance, suggesting its potential usefulness to support lung cancer screening.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
The datasets analyzed during the current study are public and are available at https://luna16.grand-challenge.org/ and https://mmcheng.net/sanet/.
References
R. L. Siegel, K. D. Miller, N. S. Wagle, and A. Jemal, “Cancer statistics, 2023,” CA: a cancer journal for clinicians, vol. 73, no. 1, pp. 17–48, 2023.
J. Ferlay, I. Soerjomataram, R. Dikshit, S. Eser, C. Mathers, M. Rebelo, D. M. Parkin, D. Forman, and F. Bray, “Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in globocan 2012,” Int J Cancer, vol. 136, no. 5, pp. E359–E386, 2015.
D. J. Brenner and E. J. Hall, “Computed tomography–an increasing source of radiation exposure,” New England journal of medicine, vol. 357, no. 22, pp. 2277–2284, 2007.
S. G. Armato III, G. McLennan, L. Bidaut, M. F. McNitt-Gray, C. R. Meyer, A. P. Reeves, B. Zhao, D. R. Aberle, C. I. Henschke, E. A. Hoffman, et al., “The lung image database consortium (lidc) and image database resource initiative (idri): a completed reference database of lung nodules on ct scans,” Medical physics, vol. 38, no. 2, pp. 915–931, 2011.
S. Singh, D. S. Gierada, P. Pinsky, C. Sanders, N. Fineberg, Y. Sun, D. Lynch, and H. Nath, “Reader variability in identifying pulmonary nodules on chest radiographs from the national lung screening trial,” Journal of thoracic imaging, vol. 27, no. 4, p. 249, 2012.
I. R. S. Valente, P. C. Cortez, E. C. Neto, J. M. Soares, V. H. C. de Albuquerque, and J. M. R. Tavares, “Automatic 3d pulmonary nodule detection in ct images: a survey,” Computer methods and programs in biomedicine, vol. 124, pp. 91–107, 2016.
K. He, X. Zhang, S. Ren, and J. Sun, “Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition,” IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence, vol. 37, no. 9, pp. 1904–1916, 2015.
S. Ren, K. He, R. Girshick, and J. Sun, “Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks,” Advances in neural information processing systems, vol. 28, 2015.
T.-Y. Lin, P. Dollár, R. Girshick, K. He, B. Hariharan, and S. Belongie, “Feature pyramid networks for object detection,” in Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 2117–2125, 2017.
N. Sharma, L. M. Aggarwal, et al., “Automated medical image segmentation techniques,” Journal of medical physics, vol. 35, no. 1, p. 3, 2010.
R. A. Rensink, “The dynamic representation of scenes,” Visual cognition, vol. 7, no. 1-3, pp. 17–42, 2000.
A. Vaswani, N. Shazeer, N. Parmar, J. Uszkoreit, L. Jones, A. N. Gomez, Ł. Kaiser, and I. Polosukhin, “Attention is all you need,” Advances in neural information processing systems, vol. 30, 2017.
A. Dosovitskiy, L. Beyer, A. Kolesnikov, D. Weissenborn, X. Zhai, T. Unterthiner, M. Dehghani, M. Minderer, G. Heigold, S. Gelly, et al., “An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929, 2020.
T. Messay, R. C. Hardie, and S. K. Rogers, “A new computationally efficient cad system for pulmonary nodule detection in ct imagery,” Medical image analysis, vol. 14, no. 3, pp. 390–406, 2010.
C. Jacobs, E. M. Van Rikxoort, T. Twellmann, E. T. Scholten, P. A. De Jong, J.-M. Kuhnigk, M. Oudkerk, H. J. De Koning, M. Prokop, C. Schaefer-Prokop, et al., “Automatic detection of subsolid pulmonary nodules in thoracic computed tomography images,” Medical image analysis, vol. 18, no. 2, pp. 374–384, 2014.
E. Lopez Torres, E. Fiorina, F. Pennazio, C. Peroni, M. Saletta, N. Camarlinghi, M. Fantacci, and P. Cerello, “Large scale validation of the m5l lung cad on heterogeneous ct datasets,” Medical physics, vol. 42, no. 4, pp. 1477–1489, 2015.
H. Law and J. Deng, “Cornernet: Detecting objects as paired keypoints,” in Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp. 734–750, 2018.
X. Lu, B. Li, Y. Yue, Q. Li, and J. Yan, “Grid r-cnn,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7363–7372, 2019.
X. Zhou, J. Zhuo, and P. Krahenbuhl, “Bottom-up object detection by grouping extreme and center points,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 850–859, 2019.
L. Huang, Y. Yang, Y. Deng, and Y. Yu, “Densebox: Unifying landmark localization with end to end object detection,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1509.04874, 2015.
J. Wang, K. Chen, S. Yang, C. C. Loy, and D. Lin, “Region proposal by guided anchoring,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2965–2974, 2019.
J. Hu, L. Shen, and G. Sun, “Squeeze-and-excitation networks,” in Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 7132–7141, 2018.
L. Gong, S. Jiang, Z. Yang, G. Zhang, and L. Wang, “Automated pulmonary nodule detection in ct images using 3d deep squeeze-and-excitation networks,” International journal of computer assisted radiology and surgery, vol. 14, pp. 1969–1979, 2019.
Y. Li and Y. Fan, “Deepseed: 3d squeeze-and-excitation encoder-decoder convolutional neural networks for pulmonary nodule detection,” in 2020 IEEE 17th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), pp. 1866–1869, IEEE, 2020.
Q. Wang, B. Wu, P. Zhu, P. Li, W. Zuo, and Q. Hu, “Eca-net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 11534–11542, 2020.
Z. Guo, L. Zhao, J. Yuan, and H. Yu, “Msanet: Multiscale aggregation network integrating spatial and channel information for lung nodule detection,” IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, vol. 26, no. 6, pp. 2547–2558, 2021.
S. Woo, J. Park, J.-Y. Lee, and I. S. Kweon, “Cbam: Convolutional block attention module,” in Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp. 3–19, 2018.
L. Sun, Z. Wang, H. Pu, G. Yuan, L. Guo, T. Pu, and Z. Peng, “Attention-embedded complementary-stream cnn for false positive reduction in pulmonary nodule detection,” Computers in Biology and Medicine, vol. 133, p. 104357, 2021.
C. Wen, M. Hong, X. Yang, and J. Jia, “Pulmonary nodule detection based on convolutional block attention module,” in 2019 Chinese Control Conference (CCC), pp. 8583–8587, IEEE, 2019.
N. Carion, F. Massa, G. Synnaeve, N. Usunier, A. Kirillov, and S. Zagoruyko, “End-to-end object detection with transformers,” in Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23–28, 2020, Proceedings, Part I 16, pp. 213–229, Springer, 2020.
X. Zhu, W. Su, L. Lu, B. Li, X. Wang, and J. Dai, “Deformable detr: Deformable transformers for end-to-end object detection,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.04159, 2020.
I. Misra, R. Girdhar, and A. Joulin, “An end-to-end transformer model for 3d object detection,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2906–2917, 2021.
Z. Dai, B. Cai, Y. Lin, and J. Chen, “Up-detr: Unsupervised pre-training for object detection with transformers,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 1601–1610, 2021.
J. Chen, Y. Lu, Q. Yu, X. Luo, E. Adeli, Y. Wang, L. Lu, A. L. Yuille, and Y. Zhou, “Transunet: Transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2102.04306, 2021.
W. Wang, C. Chen, M. Ding, H. Yu, S. Zha, and J. Li, “Transbts: Multimodal brain tumor segmentation using transformer,” in Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2021: 24th International Conference, Strasbourg, France, September 27–October 1, 2021, Proceedings, Part I 24, pp. 109–119, Springer, 2021.
H. Jiang, P. Zhang, C. Che, B. Jin, et al., “Rdfnet: A fast caries detection method incorporating transformer mechanism,” Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, vol. 2021, 2021.
X. Ma, G. Luo, W. Wang, and K. Wang, “Transformer network for significant stenosis detection in ccta of coronary arteries,” in Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2021: 24th International Conference, Strasbourg, France, September 27–October 1, 2021, Proceedings, Part VI 24, pp. 516–525, Springer, 2021.
H. Li, L. Chen, H. Han, and S. Kevin Zhou, “Satr: Slice attention with transformer for universal lesion detection,” in Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2022: 25th International Conference, Singapore, September 18–22, 2022, Proceedings, Part III, pp. 163–174, Springer, 2022.
A. A. A. Setio, F. Ciompi, G. Litjens, P. Gerke, C. Jacobs, S. J. Van Riel, M. M. W. Wille, M. Naqibullah, C. I. Sánchez, and B. Van Ginneken, “Pulmonary nodule detection in ct images: false positive reduction using multi-view convolutional networks,” IEEE transactions on medical imaging, vol. 35, no. 5, pp. 1160–1169, 2016.
J. Mei, M.-M. Cheng, G. Xu, L.-R. Wan, and H. Zhang, “Sanet: A slice-aware network for pulmonary nodule detection,” IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence, vol. 44, no. 8, pp. 4374–4387, 2021.
W. Zhu, C. Liu, W. Fan, and X. Xie, “Deeplung: Deep 3d dual path nets for automated pulmonary nodule detection and classification,” in 2018 IEEE winter conference on applications of computer vision (WACV), pp. 673–681, IEEE, 2018.
H. Tang, C. Zhang, and X. Xie, “Nodulenet: Decoupled false positive reduction for pulmonary nodule detection and segmentation,” in Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2019: 22nd International Conference, Shenzhen, China, October 13–17, 2019, Proceedings, Part VI 22, pp. 266–274, Springer, 2019.
T. Song, J. Chen, X. Luo, Y. Huang, X. Liu, N. Huang, Y. Chen, Z. Ye, H. Sheng, S. Zhang, et al., “Cpm-net: A 3d center-points matching network for pulmonary nodule detection in ct scans,” in International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, pp. 550–559, Springer, 2020.
X. Luo, T. Song, G. Wang, J. Chen, Y. Chen, K. Li, D. N. Metaxas, and S. Zhang, “Scpm-net: An anchor-free 3d lung nodule detection network using sphere representation and center points matching,” Medical Image Analysis, vol. 75, p. 102287, 2022.
I. W. Harsono, S. Liawatimena, and T. W. Cenggoro, “Lung nodule detection and classification from thorax ct-scan using retinanet with transfer learning,” Journal of King Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences, vol. 34, no. 3, pp. 567–577, 2022.
Funding
This research was partly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 61901234.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ling Ma and Gen Li conceived the presented idea and wrote the manuscript. Gen Li performed most of the experiments. Xingyu Feng and Qiliang Fan verified the analytical methods. Lizhi Liu supervised the project. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
This study proposed a new machine-learning method for the detection of lung nodules on CT images. The CT images used in this study are from the public LUNA16 database and PN9 database. We have gotten permission by accepting their licenses.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, L., Li, G., Feng, X. et al. TiCNet: Transformer in Convolutional Neural Network for Pulmonary Nodule Detection on CT Images. J Digit Imaging. Inform. med. 37, 196–208 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-023-00904-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-023-00904-y