Abstract
Although brain arteriovenous malformations (bAVMs) account for a very small proportion of cerebral pathologies in the pediatric population, they are the cause of roughly 50% of spontaneous intracranial hemorrhages. Pediatric bAVMs tend to rupture more frequently and seem to have higher recurrence rates than bAVMs in adults. Thus, the management of pediatric bAVMs is particularly challenging. In general, the treatment options are conservative treatment, microsurgery, endovascular therapy (EVT), gamma knife radiosurgery (GKRS), proton-beam stereotactic radiosurgery (PSRS), or a combination of the above. In order to identify the best approach to deep-seated pediatric bAVMs, we performed a systematic review, according to the PRISMA guidelines. None of the options seem to offer a clear advantage over the others when used alone. Microsurgery provides the highest obliteration rate, but has higher incidence of neurological complications. EVT may play a role when used as adjuvant therapy, but as a stand-alone therapy, the efficacy is low and the long-term side effects of radiation from the multiple sessions required in deep-seated pediatric bAVMs are still unknown. GKRS has a low risk of complication, but the obliteration rates still leave much to be desired. Finally, PSRS offers promising results with a more accurate radiation that avoids the surrounding tissue, but data is limited due to its recent introduction. Overall, a multi-modal approach, or even an active surveillance, might be the most suitable when facing deep-seated bAVM, considering the difficulty of their management and the high risk of complications in the pediatric population.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Capitanio JF, Panni P, Gallotti AL, Gigliotti CR, Scomazzoni F, Acerno S, Del Vecchio A, Mortini P (2018) Radiosurgical treatment of arteriovenous malformations in a retrospective study group of 33 children: the importance of radiobiological scores. Childs Nerv Syst 35:301–308. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-018-4008-2
Horgan MA, Florman J, Spetzler RF (2006) Surgical treatment of arteriovenous malformations in children. In: Alexander MJ, Spetzler RF (eds) Pediatric Neurovascular Disease: Surgical, Endovascular and Medical Management. Thieme, New York
El-Ghanem M, Kass-Hout T, Kass-Hout O, Alderazi YJ, Amuluru K, Al-Mufti F, Prestigiacomo CJ, Gandhi CD (2016) Arteriovenous malformations in the pediatric population: review of the existing literature. Interventional Neurology 5(3–4):218–225. https://doi.org/10.1159/000447605
Smith ER, Butler WE, Ogilvy CS (2002) Surgical approaches to vascu-lar anomalies of the child’s brain. Curr Opin Neurol 15:165–171
Ding D, Starke RM, Kano H, Mathieu D, Huang PP, Feliciano C, Sheehan JP (2017) International multicenter cohort study of pediatric brain arteriovenous malformations. Part 1: predictors of hemorrhagic presentation. J Neurosurg Pediatr 19(2):127–135. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.9.PEDS16283
Sanchez-Mejia RO, Chennupati SK, Gupta N, Fullerton H, Young WL, Lawton MT (2006) Superior outcomes in children compared with adults after microsurgical resection of brain arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 105(2 Suppl):82–87
Thiex R, Williams A, Smith E, Scott RM, Orbach DB (2010) The use of onyx for embolization of central nervous system arteriovenous lesions in pediatric patients. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31(1):112–120. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A1786
Cenzato M, Boccardi E, Beghi E, Vajkoczy P, Szikora I, Motti E, Regli L, Raabe A, Eliava S, Gruber A, Meling TR, Niemela M, Pasqualin A, Golanov A, Karlsson B, Kemeny A, Liscak R, Lippitz B, Radatz M, La Camera A, Chapot R, Islak C, Spelle L, Debernardi A, Agostoni E, Revay M, Morgan MK (2017) European consensus conference on unruptured brain AVMs treatment (supported by EANS, ESMINT, EGKS, and SINCH). Acta Neurochir 159(6):1059–1064. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-017-3154-8
Gross BA, Storey A, Orbach DB, Scott RM, Smith ER (2015) Microsurgical treatment of arteriovenous malformations in pediatric patients: the Boston Children’s Hospital experience. J Neurosurg Pediatr 15(1):71–77. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.9.PEDS146
Nair AP, Kumar R, Mehrotra A, Srivastava AK, Sahu RN, Nair P (2012) Clinical, radiological profile and outcome in pediatric Spetzler–Martin grades I–III arteriovenous malformations. Childs Nerv Syst 28(4):593–598. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-011-1668-6
Soltanolkotabi M, Schoeneman SE, Alden TD, Hurley MC, Ansari SA, DiPatri AJ Jr, Tomita T, Shaibani A (2013) Onyx embolization of intracranial arteriovenous malformations in pediatric patients. J Neurosurg Pediatr 11(4):431–437. https://doi.org/10.3171/2013.1
Berenstein A, Ortiz R, Niimi Y, Elijovich L, Fifi J, Madrid M, Ghatan S, Molofsky W (2010) Endovascular management of arteriovenous malformations and other intracranial arterio-venous shunts in neonates, infants, and children. Childs Nerv Syst 26:1345–1358
Kano H, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Yang HC, Flannery TJ, Niranjan A, Novotny J Jr, Lunsford LD (2012) Stereotactic radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations, part 4: management of basal ganglia and thalamus arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 116(1):33–43
Hanakita S, Koga T, Shin M, Igaki H, Saito N (2015) The long-term outcomes of radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations in pediatric and adolescent populations. J Neurosurg Pediatr 16(2):222–231. https://doi.org/10.3171/2015.1.PEDS14407
Yen CP, Monteith SJ, Nguyen JH, Rainey J, Schlesinger DJ, Sheehan JP (2010) Gamma knife surgery for arteriovenous malformations in children. J Neurosurg Pediatr 6:426–434
Starke RM, Ding D, Kano H, Mathieu D, Huang PP, Feliciano C, Rodriguez-Mercado R, Almodovar L, Grills IS, Silva D, Abbassy M, Missios S, Kondziolka D, Barnett GH, Dade Lunsford L, Sheehan JP (2016) International multicenter cohort study of pediatric brain arteriovenous malformations. Part 2: outcomes after stereotactic radiosurgery. J Neurosurg Pediatr 2017 Feb 19(2):136–148. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.9.PEDS16284
Ding D, Yen CP, Starke RM, Xu Z, Sheehan JP (2014) Radiosurgery for ruptured intracranial arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 121(2):470–481. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.2.jns131605
Pan DH, Kuo YH, Guo WY, Chung WY, Wu HM, Liu KD, Chang YC, Wang LW, Wong TT (2008) Gamma knife surgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations in children: a 13-year experience. J Neurosurg Pediatr 1(4):296–304. https://doi.org/10.3171/ped/2008/1/4/296
Potts MB, Sheth SA, Louie J, Smyth MD, Sneed PK, McDermott MW, Lawton MT, Young WL, Hetts SW, Fullerton HJ, Gupta N (2014) Stereotactic radiosurgery at a low marginal dose for the treatment of pediatric arteriovenous malformations: obliteration, complications, and functional outcomes. J Neurosurg Pediatr 14(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.3.PEDS13381
Potts MB, Young WL, Lawton MT (2013) Deep arteriovenous malformations in the basal ganglia, thalamus, and insula. Neurosurgery 73(3):417–429. https://doi.org/10.1227/neu.0000000000000004
Walcott BP, Hattangadi-Gluth JA, Stapleton CJ, Ogilvy CS, Chapman PH, Loeffler JP (2014) Proton beam stereotactic radiosurgery for pediatric cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 74(4):367–373; discussion 374. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0000000000000294
Shtaya A, Millar J, Sparrow O (2017) Multimodality management and outcomes of brain arterio-venous malformations (AVMs) in children: personal experience and review of the literature, with specific emphasis on age at first AVM bleed. Childs Nerv Syst 33(4):573–581. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-017-3383-4
Dorfer C, Czech T, Bavinzski G, Kitz K, Mert A, Knosp E, Gruber A (2010) Multimodality treatment of cerebral AVMs in children: a single-centre 20 years experience. Childs Nerv Syst 26:681–687. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-009-1039-8
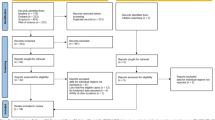
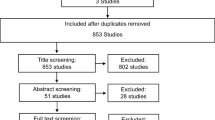
Moher D, Shamseer L, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M et al (2015) Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst Rev 4:1
Mohr JP, Parides MK, Stapf C, Moquete E, Moy CS, Overbey JR, Al-Shahi Salman R, Vicaut E, Young WL, Houdart E, Cordonnier C, Stefani MA, Hartmann A, von Kummer R, Biondi A, Berkefeld J, Klijn CJ, Harkness K, Libman R, Barreau X, Moskowitz AJ, International ARUBA Investigators (2014) Medical management with or without interventional therapy for unruptured brain arteriovenous malformations (ARUBA): a multicentre, nonblinded, randomised trial. Lancet 383(9917):614–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62302-8. Epub 2013 Nov 20
Meling TR, Proust F, Gruber A, Niemela M, Regli L, Roche P-H, Vajkoczy P (2014) On apples, oranges, and ARUBA. Acta Neurochir 156(9):1775–1779. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-014-2140-7
Akin ED, Perkins E, Ross IB (2003) Surgical handling characteristics of an ethylene vinyl alcohol copolymer compared with N-butyl cyanoacrylate used for embolization of vessels in an arteriovenous malformation resection model in swine. J Neurosurg 98:366–370
Blauwblomme T, Bourgeois M, Meyer P, Puget S, Di Rocco F, Boddaert N, Zerah M, Brunelle F, Rose CS, Naggara O (2014) Long-term outcome of 106 consecutive pediatric ruptured brain arteriovenous malformations after combined treatment. Stroke 45(6):1664–1671. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.004292
Kleinerman RA (2006) Cancer risks following diagnostic and therapeutic radiation exposure in children. Pediatr Radiol 36(Suppl 2):121–125
Zheng T, Wang QJ, Liu YQ, Cui XB, Gao YY, Lai LF, Su SX, Zhang X, Li XF, He XY, Duan CZ (2013) Clinical features and endovascular treatment of intracranial arteriovenous malformations in pediatric patients. Childs Nerv Syst 30:647–653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-013-2277-3
Orbach DB, Stamoulis C, Strauss KJ, Manchester J, Smith ER, Scott RM, Lin N (2014) Neurointerventions in children: radiation exposure and its import. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 35(4):650–656. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A3758
Bruno CA, Meyers PM (2013) Endovascular management of arteriovenous malformations of the brain. Interv Neurol 1:109–123
Huang PP, Kamiryo T, Nelson PK (2001) De novo aneurysm formation after stereotactic radiosurgery of a residual arteriovenous malformation: case report. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22(7):1346–1348
Nicolato A, Longhi M, Tommasi N, Ricciardi GK, Spinelli R, Foroni RI, Zivelonghi E, Zironi S, Dall’Oglio S, Beltramello A, Meglio M (2015) Leksell gamma knife for pediatric and adolescent cerebral arteriovenous malformations: results of 100 cases followed up for at least 36 months. J Neurosurg Pediatr 16(6):736–747. https://doi.org/10.3171/2015.4.PEDS158
Galván De la Cruz OO, Ballesteros-Zebadúa P, Moreno-Jiménez S, Celis MA, García-Garduño OA (2015) Stereotactic radiosurgery for pediatric patients with intracranial arteriovenous malformations: variables that may affect obliteration time and probability. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 129:62–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2014.11.019
Hasegawa H, Hanakita S, Shin M, Kawashima M, Takahashi W, Ishikawa O, Koizumi S, Nakatomi H, Saito N (2018) Comparison of the long-term efficacy and safety of gamma knife radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations in pediatric and adult patients. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 58:231–239
Buis DR, Dirven CMF, Lagerwaard FJ, Mandl ES, Lycklama A, Nijeholt GJ, Eshghi DS, Van Den Berg R, Baayen JC, Meijer OW, Slotman BJ, Vandertop WP (2008) Radiosurgery of brain arteriovenous malformations in children. J Neurol 255:551–560
Morgenstern PF, Hoffman CE, Kocharian G, Singh R, Stieg PE, Souweidane MM (2016) Postoperative imaging for detection of recurrent arteriovenous malformations in children. JNS Pediatr. 17(2):134–140. https://doi.org/10.3171/2015.6.PEDS14708
Jimenez JE, Gersey ZC, Wagner J, Snelling B, Ambekar S, Peterson EC (2017) Role of follow-up imaging after resection of brain arteriovenous malformations in pediatric patients: a systematic review of the literature. JNS Pediatr 19(2):149–156. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.9.PEDS16235
Darsaut TE, Guzman R, Marcellus ML, Edwards MS, Tian L, Do HM, Chang SD, Levy RP, Adler JR, Marks MP, Steinberg GK (2011) Management of pediatric intracranial arteriovenous malformations: experience with multimodality therapy. Neurosurgery 69(3):540–556; discussion 556. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0b013e3182181c00
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approved
Not applicable as no new patients were involved in this research.
Informed consent
Not applicable as no new patients were involved in this research.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meling, T.R., Patet, G. What is the best therapeutic approach to a pediatric patient with a deep-seated brain AVM?. Neurosurg Rev 42, 409–416 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-019-01101-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-019-01101-8