Abstract
Objective
The authors describe their experience in treating 22 children with a single brain arteriovenous malformation (bAVM) using a dedicated LINAC stereotactic radiosurgery unit.
Methods
The findings of 22 consecutive patients ≤ 18 years of age who underwent radiosurgery for a single bAVM and with at least 24 months of follow-up, or earlier proven obliteration,were reviewed. The median age at radiosurgery was 13.8 years,with a hemorrhagic presentation in 86%. Median bAVM-volume was 1.8 ml, with a median prescribed marginal dose of 19.0 Gy.
Results
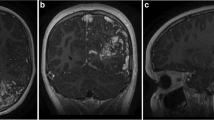
The crude complete obliteration-rate was 68% (n = 15) after a median follow-up of 24 months. The actuarial obliteration- rate was 45 % after two years and 64 % after three years. Patients with a radiosurgery-based AVM score ≤ 1 more frequently had an excellent outcome than patients with a bAVM score > 1 (71% vs. 20%, P = 0.12), as well as an increased obliteration rate (P = 0.03) One patient died from a bAVM-related hemorrhage 27 months after radiosurgery, representing a postradiosurgery hemorrhage rate of 1.3%/year for the complete followup interval. Overall outcome was good to excellent in 68% (n = 15). Radiation-induced changes on MR imaging were seen in 36% (n = 8) after a median interval of 12.5 months, resulting in deterioration of pre-existing neurological symptoms in one patient.
Conclusions
Radiosurgery is a relatively effective, minimally invasive treatment for small bAVMs in children. The rebleeding rate is low, provided that known predilection places for bleeding had been endovascularly eliminated.Our overall results compare unfavourably to recent pediatric microsurgical series, although comparison between series remains imprecise. Nevertheless, when treatment is indicated in a child with a bAVM that is amenable to both microsurgery or radiosurgery, microsurgery should carefully be advocated over radiosurgery, because of its immediate risk reduction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Shahi R, Warlow CP (2006) Interventions for treating brain arteriovenous malformations in adults. Cochrane Database Syst RevCD003436
Altschuler EM, Lunsford LD, Coffey RJ, Bissonette DJ, Flickinger JC (1989) Gamma knife radiosurgery for intracranial arteriovenous malformations in childhood and adolescence. Pediatr Neurosci 15:53–61
Amendola BE, Wolf A, Coy SR, DePrima S, Amendola MA (2000) Radiosurgery for intracranial arteriovenous malformations in children. J Radiosurg 3:159–164
Bristol RE, Albuquerque FC, Spetzler RF, Rekate HL, McDougall CG, Zabramski JM (2006) Surgical management of arteriovenous malformations in children. J Neurosurg 105:88–93
Cohen-Gadol AA, Pollock BE (2006) Radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations in children. J Neurosurg 104:388–391
Deorah S, Lynch CF, Sibenaller ZA, Ryken TC (2006) Trends in brain cancer incidence and survival in the United States: Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program, 1973 to 2001. Neurosurg Focus 20:E1
Friedman WA, Bova FJ, Bollampally S, Bradshaw P (2003) Analysis of factors predictive of success or complications in arteriovenous malformation radiosurgery. Neurosurgery 52:296–307
Fullerton HJ, Achrol AS, Johnston SC, McCulloch CE, Higashida RT, Lawton MT, Sidney S, Young WL (2005) Longterm hemorrhage risk in children versus adults with brain arteriovenous malformations. Stroke 36:2099–2104
Fuss M, Salter BJ, Caron JL, Vollmer DG, Herman TS (2005) Intensitymodulated radiosurgery for childhood arteriovenous malformations. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 147:1141–1150
Ganz JC, Reda WA, Abdelkarim K, Hafez A (2005) A simple method for predicting imaging-based complications following gamma knife surgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 102(Suppl):4–7
Gauvrit JY, Oppenheim C, Nataf F, Naggara O, Trystram D, Munier T, Fredy D, Pruvo JP, Roux FX, Leclerc X, Meder JF (2006) Three-dimensional dynamic magnetic resonance angiography for the evaluation of radiosurgically treated cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Eur Radiol 16:583–591
Gerszten PC, Adelson PD, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD (1996) Seizure outcome in children treated for arteriovenous malformations using gamma knife radiosurgery. Pediatr Neurosurg 24:139–144
Heffez DS, Osterdock RJ, Alderete L, Grutsch J (1998) The effect of incomplete patient follow-up on the reported results of AVM radiosurgery. Surg Neurol 49:373–381
Hoh BL, Ogilvy CS, Butler WE, Loeffler JS, Putman CM, Chapman PH (2000) Multimodality treatment of nongalenic arteriovenous malformations in pediatric patients. Neurosurgery 47:346–357
Izawa M, Hayashi M, Chernov M, Nakaya K, Ochiai T, Murata N, Takasu Y, Kubo O, Hori T, Takakura K (2005) Long-term complications after gamma knife surgery for arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 102(Suppl):34–37
Kim LJ, Albuquerque FC, Spetzler RF, McDougall CG (2006) Postembolization neurological deficits in cerebral arteriovenous malformations: stratification by arteriovenous malformation grade. Neurosurgery 59:53–59
Kondziolka D, Humphreys RP, Hoffman HJ, Hendrick EB, Drake JM (1992) Arteriovenous malformations of the brain in children: a forty year experience. Can J Neurol Sci 19:40–45
Levy EI, Niranjan A, Thompson TP, Scarrow AM, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD (2000) Radiosurgery for childhood intracranial arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 47:834–841
Lindqvist M, Karlsson B, Guo WY, Kihlstrom L, Lippitz B, Yamamoto M (2000) Angiographic long-term followup data for arteriovenous malformations previously proven to be obliterated after gamma knife radiosurgery. Neurosurgery 46:803–808
Loeffler JS, Rossitch E Jr, Siddon R, Moore MR, Rockoff MA, Alexander E III (1990) Role of stereotactic radiosurgery with a linear accelerator in treatment of intracranial arteriovenous malformations and tumors in children. Pediatrics 85:774–782
Maity A, Shu HK, Tan JE, Ruffer J, Sutton LN, Tochner Z, Lustig R (2004) Treatment of pediatric intracranial arteriovenous malformations with linear-accelerator-based stereotactic radiosurgery: the University of Pennsylvania experience. Pediatr Neurosurg 40:207–214
Maruyama K, Kawahara N, Shin M, Tago M, Kishimoto J, Kurita H, Kawamoto S, Morita A, Kirino T (2005) The risk of hemorrhage after radiosurgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations. N Engl J Med 352:146–153
McIver JI, Pollock BE (2004) Radiation- induced tumor after stereotactic radiosurgery and whole brain radiotherapy: case report and literature review. J Neurooncol 66:301–305
Meisel HJ, Mansmann U, Alvarez H, Rodesch G, Brock M, Lasjaunias P (2002) Effect of partial targeted Nbutyl- cyano-acrylate embolization in brain AVM. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 144:879–887
Nataf F, Schlienger M, Lefkopoulos D, Merienne L, Ghossoub M, Foulquier JN, Deniaud-Alexandre E, Mammar H, Meder JF, Turak B, Huart J, Touboul E, Roux FX (2003) Radiosurgery of cerebral arteriovenous malformations in children: a series of 57 cases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 57:184–195
Nicolato A, Foroni R, Seghedoni A, Martines V, Lupidi F, Zampieri P, Sandri MF, Ricci U, Mazza C, Beltramello A, Gerosa M, Bricolo A (2005) Leksell gamma knife radiosurgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations in pediatric patients. Childs Nerv Syst 21:301–307
Nicolato A, Gerosa M, Ferraresi P, Piovan E, Pasoli A, Perini S, Mazza C (1997) Stereotactic radiosurgery for the treatment of arteriovenous malformations in childhood. J Neurosurg Sci 41:359–371
Nicolato A, Lupidi F, Sandri MF, Foroni R, Zampieri P, Mazza C, Maluta S, Beltramello A, Gerosa M (2006) Gamma Knife radiosurgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations in children/ adolescents and adults. Part I: Differences in epidemiologic, morphologic, and clinical characteristics, permanent complications, and bleeding in the latency period. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 64:904–913
Nicolato A, Lupidi F, Sandri MF, Foroni R, Zampieri P, Mazza C, Pasqualin A, Beltramello A, Gerosa M (2006) Gamma Knife radiosurgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations in children/adolescents and adults. Part II: Differences in obliteration rates, treatment-obliteration intervals, and prognostic factors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 64:914–921
Petereit D, Mehta M, Turski P, Levin A, Strother C, Mistretta C, Mackie R, Gehring M, Kubsad S, Kinsella T (1993) Treatment of arteriovenous malformations with stereotactic radiosurgery employing both magnetic resonance angiography and standard angiography as a database. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 25:309–313
Pollock BE, Flickinger JC (2002) A proposed radiosurgery-based grading system for arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 96:79–85
Reyns N, Blond S, Gauvrit JY, Touzet G, Coche B, Pruvo JP, Dhellemmes P (2007) Role of radiosurgery in the management of cerebral arteriovenous malformations in the pediatric age group: data from a 100-patient series. Neurosurgery 60:268–276
Riva D, Pantaleoni C, Devoti M, Lindquist C, Steiner L, Giorgi C (1997) Radiosurgery for cerebral AVMs in children and adolescents: the neurobehavioral outcome. J Neurosurg 86:207–210
Rodriguez-Arias C, Martinez R, Rey G, Bravo G (2000) Recurrence in a different location of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation in a child after radiosurgery. Childs Nerv Syst 16:363–365
Sedzimir CB, Robinson J (1973) Intracranial hemorrhage in children and adolescents. J Neurosurg 38:269–281
Shin M, Kawahara N, Maruyama K, Tago M, Ueki K, Kirino T (2005) Risk of hemorrhage from an arteriovenous malformation confirmed to have been obliterated on angiography after stereotactic radiosurgery. J Neurosurg 102:842–846
Shin M, Kawamoto S, Kurita H, Tago M, Sasaki T, Morita A, Ueki K, Kirino T (2002) Retrospective analysis of a 10- year experience of stereotactic radio surgery for arteriovenous malformations in children and adolescents. J Neurosurg 97:779–784
Smyth MD, Sneed PK, Ciricillo SF, Edwards MS, Wara WM, Larson DA, Lawton MT, Gutin PH, McDermott MW (2002) Stereotactic radiosurgery for pediatric intracranial arteriovenous malformations: the University of California at San Francisco experience. J Neurosurg 97:48–55
Spetzler RF, Martin NA (1986) A proposed grading system for arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 65:476–483
Tanaka T, Kobayashi T, Kida Y, Oyama H, Niwa M (1996) Comparison between adult and pediatric arteriovenous malformations treated by Gamma Knife radiosurgery. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 66(Suppl 1):288–295
Voges J, Treuer H, Lehrke R, Kocher M, Staar S, Muller RP, Sturm V (1997) Risk analysis of LINAC radiosurgery in patients with arteriovenous malformation (AVM). Acta Neurochir Suppl 68:118–123
Yamamoto M, Jimbo M, Ide M, Tanaka N, Lindquist C, Steiner L (1992) Longterm follow-up of radiosurgically treated arteriovenous malformations in children: report of nine cases. Surg Neurol 38:95–100
Zabel-du Bois A, Milker-Zabel S, Huber P, Schlegel W, Debus J (2006) Stereotactic linac-based radiosurgery in the treatment of cerebral arteriovenous malformations located deep, involving corpus callosum, motor cortex, or brainstem. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 64:1044–1048
Zabel-du Bois A, Milker-Zabel S, Huber P, Schlegel W, Debus J (2006) Pediatric cerebral arteriovenous malformations: the role of stereotactic linac-based radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 65:1206–1211
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This manuscript was presented at the 56th Annual Meeting of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons, Chicago, IL, October 2006.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buis, D.R., Dirven, C.M.F., Lagerwaard, F.J. et al. Radiosurgery of brain arteriovenous malformations in children. J Neurol 255, 551–560 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-008-0739-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-008-0739-4