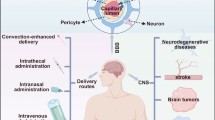
Abstract
The World Health Organization (WHO) has declared that neurodegenerative diseases will be the biggest health issues of the twenty-first century. Among these, Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases can be considered as the most acute incurable neurological diseases. Researchers are studying and developing a new treatment approach that uses nanotechnology to diagnosis and treatment neurodegenerative diseases. This treatment strategy will be used to regress neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is one of the most common forms of reduced brain function, which causes many devastating complications. Current neurodegenerative diseases treatment protocols only help to treat symptoms nevertheless with nanotechnology approaches, can regress nerve cells apoptosis, reduce inflammation, and improve brain drug delivery. In this paper, new nanotechnology methods such as nanobodies, nano-antibodies, and lipid nanoparticles have been investigated. Correspondingly blood-brain barrier drug delivery improvement methods have been suggested.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Noble W, Burns MP (2010) Challenges in neurodegeneration research. Front Psychiatr 1:7
Spuch C, Saida O, Navarro C (2012) Advances in the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders employing nanoparticles. Recent Patents Drug Deliv Formul 6(1):2–18
Abbasi-Oshaghi E, Mirzaei F, Mirzaei A (2018) Effects of ZnO nanoparticles on intestinal function and structure in normal/high fat diet-fed rats and Caco-2 cells. Nanomedicine. 13(21):2791–2816
Eftekhari A, Maleki Dizaj S, Sharifi S, Salatin S, Rahbar Saadat Y, Zununi Vahed S, Samiei M, Ardalan M, Rameshrad M, Ahmadian E, Cucchiarini M (2020) The use of nanomaterials in tissue engineering for cartilage regeneration; current approaches and future perspectives. Int J Mol Sci 21(2):536
Schmid G (2011) Nanoparticles: from theory to application. John Wiley & Sons
Caracciolo G, Vali H, Moore A, Mahmoudi M (2019) Challenges in molecular diagnostic research in cancer nanotechnology. Nano Today 27:6–10
Tierney T, Bodnár K, Rasmuson Å, Hudson S (2017) Carrier particle design for stabilization and isolation of drug nanoparticles. Int J Pharm 518(1-2):111–118
Amirrasouli H, Asefy Z, Taghikhani M (2011) Study of serum cystatin C as a reliable marker for metabolic syndrome. J Diab Metab Disord 10:6
Ley K (2003) The role of selectins in inflammation and disease. Trends Mol Med 9(6):263–268
Asefy Z, Mirinejad M, Amirrasooli H, Tagikhani M (2014) Assessing validity of serum cystatin C for predicting metabolic syndrome. Pak J Biol Sci 17(4):582–585
Ospelt C, Gay S (2010) TLRs and chronic inflammation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 42(4):495–505
Villapol S (2018) Roles of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma on brain and peripheral inflammation. Cell Mol Neurobiol 38(1):121–132
Clark AK, Gentry C, Bradbury EJ, McMahon SB, Malcangio M (2007) Role of spinal microglia in rat models of peripheral nerve injury and inflammation. Eur J Pain 11(2):223–230
Parisi V. (ed) (2003) Correlation between morphological and functional retinal impairment in patients affected by ocular hypertension, glaucoma, demyelinating optic neuritis and Alzheimer’s disease. Seminars in ophthalmology. Taylor & Francis
Šimić G, Babić Leko M, Wray S, Harrington C, Delalle I, Jovanov-Milošević N, Bažadona D, Buée L, de Silva R, di Giovanni G, Wischik C, Hof P (2016) Tau protein hyperphosphorylation and aggregation in Alzheimer’s disease and other tauopathies, and possible neuroprotective strategies. Biomolecules. 6(1):6
Enache TA, Oliveira-Brett AM (2017) Alzheimer’s disease amyloid beta peptides in vitro electrochemical oxidation. Bioelectrochemistry. 114:13–23
Stern Y (2012) Cognitive reserve in ageing and Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol 11(11):1006–1012
Readnower RD, Chavko M, Adeeb S, Conroy MD, Pauly JR, McCarron RM et al (2010) Increase in blood–brain barrier permeability, oxidative stress, and activated microglia in a rat model of blast-induced traumatic brain injury. J Neurosci Res 88(16):3530–3539
Denieffe S, Kelly RJ, McDonald C, Lyons A, Lynch MA (2013) Classical activation of microglia in CD200-deficient mice is a consequence of blood brain barrier permeability and infiltration of peripheral cells. Brain Behav Immun 34:86–97
Tang Y, Le W (2016) Differential roles of M1 and M2 microglia in neurodegenerative diseases. Mol Neurobiol 53(2):1181–1194
Matias D, Dubois LG, Pontes B, Rosário L, Ferrer VP, Balça-Silva J, Fonseca ACC, Macharia LW, Romão L, e Spohr TCLS, Chimelli L, Filho PN, Lopes MC, Abreu JG, Lima FRS, Moura-Neto V (2019) GBM-derived Wnt3a induces M2-like phenotype in microglial cells through Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Mol Neurobiol 56(2):1517–1530
Song M, Liu T, Shi C, Zhang X, Chen X (2016) Bioconjugated manganese dioxide nanoparticles enhance chemotherapy response by priming tumor-associated macrophages toward M1-like phenotype and attenuating tumor hypoxia. ACS Nano 10(1):633–647
Sushnitha M, Evangelopoulos M, Tasciotti E, Taraballi F (2020) Cell membrane-based biomimetic nanoparticles and the immune system: immunomodulatory interactions to therapeutic applications. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 8
Alkhalifa H, Alshebber E, Taurin S (2021) Regenerative nanomedicine applications for neurodegenerative diseases of central nervous system. Theory and Applications of Nonparenteral Nanomedicines: Elsevier, pp 259-87
Parodi A, Molinaro R, Sushnitha M, Evangelopoulos M, Martinez JO, Arrighetti N, Corbo C, Tasciotti E (2017) Bio-inspired engineering of cell-and virus-like nanoparticles for drug delivery. Biomaterials. 147:155–168
Cui W, Fu W, Lin Y, Zhang T (2021) Application of nanomaterials in neurodegenerative diseases. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther 16(1):83–94
Rai M, Yadav A, Gade A (2009) Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnol Adv 27(1):76–83
Kim JS, Kuk E, Yu KN, Kim J-H, Park SJ, Lee HJ, Kim SH, Park YK, Park YH, Hwang CY, Kim YK, Lee YS, Jeong DH, Cho MH (2007) Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 3(1):95–101
Sheikpranbabu S, Kalishwaralal K, Venkataraman D, Eom SH, Park J, Gurunathan S (2009) Silver nanoparticles inhibit VEGF-and IL-1β-induced vascular permeability via Src dependent pathway in porcine retinal endothelial cells. J Nanobiotechnol 7(1):8
Govindappa M, Hemashekhar B, Arthikala M-K, Rai VR, Ramachandra Y (2018) Characterization, antibacterial, antioxidant, antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory and antityrosinase activity of green synthesized silver nanoparticles using Calophyllum tomentosum leaves extract. Results Phys 9:400–408
AshaRani P (2009) Low Kah Mun G, Hande MP, Valiyaveettil S. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human cells. ACS Nano 3(2):279–290
Patel CB, Jyoti A. Promises of nanomaterials as antimicrobial agents: a review
Wilkinson L, White R, Chipman J (2011) Silver and nanoparticles of silver in wound dressings: a review of efficacy and safety. J Wound Care 20(11):543–549
Mandoli C, Pagliari F, Pagliari S, Forte G, Di Nardo P, Licoccia S et al (2010) Stem cell aligned growth induced by CeO2 nanoparticles in PLGA scaffolds with improved bioactivity for regenerative medicine. Adv Funct Mater 20(10):1617–1624
Adams CF, Pickard MR, Chari DM (2013) Magnetic nanoparticle mediated transfection of neural stem cell suspension cultures is enhanced by applied oscillating magnetic fields. Nanomedicine 9(6):737–741
Revets H, De Baetselier P, Muyldermans S (2005) Nanobodies as novel agents for cancer therapy. Expert Opin Biol Ther 5(1):111–124
Muyldermans S (2013) Nanobodies: natural single-domain antibodies. Annu Rev Biochem 82:775–797
Hassanzadeh-Ghassabeh G, Devoogdt N, De Pauw P, Vincke C, Muyldermans S (2013) Nanobodies and their potential applications. Nanomedicine. 8(6):1013–1026
Jovčevska I, Muyldermans S (2020) The therapeutic potential of nanobodies. BioDrugs. 34(1):11–26
Helma J, Cardoso MC, Muyldermans S, Leonhardt H (2015) Nanobodies and recombinant binders in cell biology. J Cell Biol 209(5):633–644
Muyldermans S (2020) Applications of nanobodies. Ann Rev Anim Biosci 9
Vincke C, Muyldermans S (2012) Introduction to heavy chain antibodies and derived Nanobodies. Single Domain Antibodies: Springer, p. 15-26
Gibbs WW (2005) Nanobodies. Sci Am 293(2):78–83
Deffar K, Shi H, Li L, Wang X, Zhu X (2009) Nanobodies-the new concept in antibody engineering. Afr J Biotechnol 8(12)
De Meyer T, Muyldermans S, Depicker A (2014) Nanobody-based products as research and diagnostic tools. Trends Biotechnol 32(5):263–270
Vaneycken I, D’huyvetter M, Hernot S, De Vos J, Xavier C, Devoogdt N et al (2011) Immuno-imaging using nanobodies. Curr Opin Biotechnol 22(6):877–881
Steeland S, Vandenbroucke RE, Libert C (2016) Nanobodies as therapeutics: big opportunities for small antibodies. Drug Discov Today 21(7):1076–1113
Alivisatos P (2004) The use of nanocrystals in biological detection. Nat Biotechnol 22(1):47–52
Gao L, Liu G, Ma J, Wang X, Zhou L, Li X (2012) Drug nanocrystals: in vivo performances. J Control Release 160(3):418–430
Naasani I (2005) Nanocrystals. Google Patents
De Jong WH, Borm PJ (2008) Drug delivery and nanoparticles: applications and hazards. Int J Nanomedicine 3(2):133–149
Cho K, Wang X, Nie S, Shin DM (2008) Therapeutic nanoparticles for drug delivery in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 14(5):1310–1316
Scott R Armstrong JH. Alzheimers Dis Res Grant Advis Board
Tehrani MD, Kim MO, Yoon J (2014) A novel electromagnetic actuation system for magnetic nanoparticle guidance in blood vessels. IEEE Trans Magn 50(7):1–12
Vio V, Jose Marchant M, Araya E, Kogan MJ (2017) Metal nanoparticles for the treatment and diagnosis of neurodegenerative brain diseases. Curr Pharm Des 23(13):1916–1926
Kassaee SM, Taghi Goodarzi M, Abbasi OE (2018) Antioxidant, antiglycation and anti-hyperlipidemic effects of Trigonella foenum and Cinnamon in type 2 diabetic rats. Jundishapur J Nat Pharm Prod 13(1)
Yadav N, Khatak S, Sara US (2013) Solid lipid nanoparticles-a review. Int J Appl Pharm 5(2):8–18
Shah R, Eldridge D, Palombo E, Harding I (2015) Lipid nanoparticles: production, characterization and stability. Springer
Weber S, Zimmer A, Pardeike J (2014) Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) and nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) for pulmonary application: a review of the state of the art. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 86(1):7–22
Naja G, Bouvrette P, Hrapovic S, Luong JH (2007) Raman-based detection of bacteria using silver nanoparticles conjugated with antibodies. Analyst. 132(7):679–686
Jazayeri MH, Amani H, Pourfatollah AA, Pazoki-Toroudi H, Sedighimoghaddam B (2016) Various methods of gold nanoparticles (GNPs) conjugation to antibodies. Sens Bio-sens Res 9:17–22
Gao H (2016) Progress and perspectives on targeting nanoparticles for brain drug delivery. Acta Pharm Sin B 6(4):268–286
Sarkar A, Fatima I, Mohammad Sajid Jamal Q, Sayeed U, Khan KA, Akhtar S et al (2017) Nanoparticles as a carrier system for drug delivery across blood brain barrier. Curr Drug Metab 18(2):129–137
Malhotra M, Prakash S (2011) Targeted drug delivery across blood-brain-barrier using cell penetrating peptides tagged nanoparticles. Curr Nanosci 7(1):81–93
Bhaskar S, Tian F, Stoeger T, Kreyling W, de la Fuente JM, Grazú V, Borm P, Estrada G, Ntziachristos V, Razansky D (2010) Multifunctional Nanocarriers for diagnostics, drug delivery and targeted treatment across blood-brain barrier: perspectives on tracking and neuroimaging. Part Fibr Toxicol 7(1):3
Fan Y, Chen M, Zhang J, Maincent P, Xia X, Wu W (2018) Updated progress of nanocarrier-based intranasal drug delivery systems for treatment of brain diseases. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst 35(5)
Hersh DS, Wadajkar AS, Roberts NB, Perez JG, Connolly NP, Frenkel V et al (2016) Evolving drug delivery strategies to overcome the blood brain barrier. Curr Pharm Des 22(9):1177–1193
Elsaesser A, Howard CV (2012) Toxicology of nanoparticles. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 64(2):129–137
Murugadoss S, Lison D, Godderis L, Van Den Brule S, Mast J, Brassinne F et al (2017) Toxicology of silica nanoparticles: an update. Arch Toxicol 91(9):2967–3010
Park MV, Neigh AM, Vermeulen JP, de la Fonteyne LJ, Verharen HW, Briedé JJ et al (2011) The effect of particle size on the cytotoxicity, inflammation, developmental toxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles. Biomaterials. 32(36):9810–9817
Petros RA, DeSimone JM (2010) Strategies in the design of nanoparticles for therapeutic applications. Nat Rev Drug Discov 9(8):615–627
Eftekhari A, Dizaj SM, Chodari L, Sunar S, Hasanzadeh A, Ahmadian E, Hasanzadeh M (2018) The promising future of nano-antioxidant therapy against environmental pollutants induced-toxicities. Biomed Pharmacother 103:1018–1027
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This research is involving no human participants and/or animals.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Informed consent
Authors declare their consent on this paper publication.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asefy, Z., Hoseinnejhad, S. & Ceferov, Z. Nanoparticles approaches in neurodegenerative diseases diagnosis and treatment. Neurol Sci 42, 2653–2660 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-021-05234-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-021-05234-x