Abstract
Objective
To investigate cognitive dysfunction in adult patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc) who had no known clinical neurological manifestations and to relate it with other disease severity parameters.
Methods
In the present study, 20 SSc consecutive female patients, who met the 2013 American College of Rheumatology SSc criteria, were compared with 20 healthy age–, gender-, and educational status–matched volunteer hospital workers. Mean age and duration of illness were 41.8 ± 12.52 and 6.9 ± 5.4 years respectively. Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE), Wechsler Adult Intelligence scale (WAIS-III), and P300 component of event-related potentials (ERPs) were used to evaluate cognitive function in SS subjectively and objectively respectively.
Results
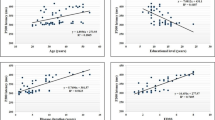
Sixty-five percent (13 out of 20) of SSc patients had MMSE score < 25, and cognitive impairment. Despite the lack of clinically apparent neurological manifestations, SSc patients had significantly low MMSE score, high Deterioration Index (DI), and prolonged P300 latency compared with that of the control group (P = 0.0001; 0.010 and 0.008 respectively). A significant positive association was found between (DI) and the Medsger severity vascular score (r = 0.518; P = 0.012).There were few differences between limited and diffuse SSc.
Conclusions
To our knowledge, few studies highlighted that subclinical cognitive impairment can occur in the course of SSc disease. Early diagnosis of cognitive impairment should be investigated either subjectively (using psychometrics tests as MMSE or WAIS-III) or objectively using P300 evoked related potentials. Medsger severity vascular score seems to be closely related to cognitive impairment.
Key points • Cognitive impairment can be associated with Medsger Vascular severity score and the duration of illness. • Further larger studies will be needed to estimate the effect of disease activity on cognitive function, to further delineate the differences between limited and diffuse SSc in this area, and to understand the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms causing cognitive impairment in patients with SSc. • To investigate impaired cognitive function in patients with SSc, even in the absence of clinically apparent neurological and vascular disease. |




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Simeoni S, Puccetti A, Tinazzi E, Tomelleri G, Corrocher R, Lunardi C (2008) Systemic sclerosis and superficial siderosis of the central nervous system: casuality or causality? Rheumatol Int 28(8):815–818. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-008-0523-x
Gamal RM, Abozaid HSM, Zidan M, Abdelmegid MAF, Abdel-Razek MR, Alsayed SA, Mourad AF, Azoz NMA, Mohram LA, Furst DE (2019) Study of MRI brain findings and carotid US features in systemic sclerosis patients, relationship with disease parameters. Arthritis Res Ther 21(1):95. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-019-1877-z
Zhong W, Cruickshanks KJ, Schubert CR, Acher CW, Carlsson CM, Klein BE, Klein R, Chappell RJ (2012) Carotid atherosclerosis and 10-year changes in cognitive function. Atherosclerosis 224(2):506–510
Silvestrini M, Gobbi B, Pasqualetti P, Bartolini M, Baruffaldi R, Lanciotti C, Cerqua R, Altamura C, Provinciali L, Vernieri F (2009) Carotid atherosclerosis and cognitive decline in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 30(8):1177–1183
Gatto NM, Henderson VW, St. John JA, McCleary C, Detrano R, Hodis HN, Mack WJ (2009) Subclinical atherosclerosis is weakly associated with lower cognitive function in healthy hyperhomocysteinemic adults without clinical cardiovascular disease. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 24(4):390–399
Gamal RM, Gamal WM, Ghandour AM, Abozaid HSM, Mohamed ME, Emad Y, Abdel Galeel A (2018) Study of the osteoprotegerin/receptor activator of nuclear factor-kB ligand system association with inflammation and atherosclerosis in systemic sclerosis. Immunol Investig 47(3):241–250
Khedr EM, El Fetoh NA, Herdan O, El-Hammady DH, Khalifa H, Gamal RM, Ali AM (2015) Clinical and subclinical neuropsychiatric abnormalities in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Egypt Rheumatol Rehabil 42(1):11
Khedr EM, Khedr T, Farweez HM, Abdella G, El Beih EA (2001) Multimodal electroneurophysiological studies of systemic lupus erythematosus. Neuropsychobiology 43(3):204–212
Monastero R, Bettini P, Del Zotto E, Cottini E, Tincani A, Balestrieri G, Cattaneo R, Camarda R, Vignolo LA, Padovani A (2001) Prevalence and pattern of cognitive impairment in systemic lupus erythematosus patients with and without overt neuropsychiatric manifestations. J Neurol Sci 184(1):33–39
Tomietto P, Annese V, D’agostini S, Venturini P, La Torre G, De Vita S, Ferraccioli G (2007) General and specific factors associated with severity of cognitive impairment in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Care Res 57(8):1461–1472
Bertinotti L, Mortilla M, Conforti ML, Colangelo N, Nacci F, Del Rosso A, Fonda C, Casale R, Matucci-Cerinic M, Pignone A (2006) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy reveals central neuroaxonal impairment in systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol 33(3):546–551
Amaral TN, Peres FA, Lapa AT, Marques-Neto JF, Appenzeller S (2013) Neurologic involvement in scleroderma: a systematic review. Semin Arthritis Rheum 43(3):335–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semarthrit.2013.05.002
Amaral TN, Peres FA, Lapa AT, Fritolli RB, del Rio AP, Marques-Neto JF, Appenzeller S (2015) FRI0488 prevalence and clinical significance of cognitive impairment in systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 74(Suppl 2):605–605. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-eular.1903
Groseanu L, Gudu T, Balanescu A, Bojinca V, Opris D, Saulescu I, Borangiu A, Constantinescu C, Predeteanu D, Berghea F, Negru MM, Vlad V, Abobului M, Ionescu R (2016) FRI0256 significance of cognitive impairment in systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 75(Suppl 2):526–527. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-eular.5190
El-Kehdy J, Abbas O, Rubeiz N (2012) A review of Parry-Romberg syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol 67(4):769–784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2012.01.019
Klimiec E, Klimkowicz-Mrowiec A (2016) Mild cognitive impairment as a single sign of brain hemiatrophy in patient with localized scleroderma and Parry-Romberg syndrome. Neurol Neurochir Pol 50(3):215–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pjnns.2016.02.002
Mattsson M, Bostrom C, Mihai C, Stocker J, Geyh S, Stummvoll G, Gard G, Moller B, Hesselstrand R, Sandqvist G, Draghicescu O, Gherghe AM, Voicu M, Distler O, Smolen JS, Stamm TA (2015) Personal factors in systemic sclerosis and their coverage by patient-reported outcome measures. A multicentre European qualitative study and literature review. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med 51(4):405–421
Suarez-Almazor ME, Kallen MA, Roundtree AK, Mayes M (2007) Disease and symptom burden in systemic sclerosis: a patient perspective. J Rheumatol 34(8):1718–1726
Khanna D, Furst DE, Wong WK, Tsevat J, Clements PJ, Park GS, Postlethwaite AE, Ahmed M, Ginsburg S, Hays RD (2007) Reliability, validity, and minimally important differences of the SF-6D in systemic sclerosis. Qual Life Res 16(6):1083–1092. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-007-9207-3
Khanna D, Distler O, Avouac J, Behrens F, Clements PJ, Denton C, Foeldvari I, Giannini E, Huscher D, Kowal-Bielecka O, Lovell D, Matucci-Cerinic M, Mayes M, Merkel PA, Nash P, Opitz CF, Pittrow D, Rubin L, Seibold JR, Steen V, Strand CV, Tugwell PS, Varga J, Zink A, Furst DE (2009) Measures of response in clinical trials of systemic sclerosis: the Combined Response Index for Systemic Sclerosis (CRISS) and Outcome Measures in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension related to Systemic Sclerosis (EPOSS). J Rheumatol 36(10):2356–2361. https://doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.090372
Kallen MA, Mayes MD, Kriseman YL, de Achaval SB, Cox VL, Suarez-Almazor ME (2010) The symptom burden index: development and initial findings from use with patients with systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol 37(8):1692–1698. https://doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.090504
Jewett LR, Hudson M, Haythornthwaite JA, Heinberg L, Wigley FM, Baron M, Thombs BD (2010) Development and validation of the brief-satisfaction with appearance scale for systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Care Res 62(12):1779–1786. https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.20307
Pauling JD, Frech TM, Domsic RT, Hudson M (2017) Patient participation in patient-reported outcome instrument development in systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 35 Suppl 106(4):184–192
Medsger TA Jr, Bombardieri S, Czirjak L, Scorza R, Della Rossa A, Bencivelli W (2003) Assessment of disease severity and prognosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 21(3 Suppl 29):S42–S46
Zigmond AS, Snaith RP (1983) The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatr Scand 67(6):361–370. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0447.1983.tb09716.x
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR (1975) “Mini-mental state”. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 12(3):189–198
Williams JM (1991) Memory assessment scales. Odessa, Psychological Assessment Resources 199 (1)
Polich J (1998) P300 clinical utility and control of variability. J Clin Neurophysiol 15(1):14–33
Chapman RM, Bragdon HR (1964) Evoked responses to numerical and non-numerical visual stimuli while problem solving. Nature 203(4950):1155
van den Hoogen F, Khanna D, Fransen J, Johnson SR, Baron M, Tyndall A, Matucci-Cerinic M, Naden RP, Medsger TA Jr, Carreira PE, Riemekasten G, Clements PJ, Denton CP, Distler O, Allanore Y, Furst DE, Gabrielli A, Mayes MD, van Laar JM, Seibold JR, Czirjak L, Steen VD, Inanc M, Kowal-Bielecka O, Muller-Ladner U, Valentini G, Veale DJ, Vonk MC, Walker UA, Chung L, Collier DH, Ellen Csuka M, Fessler BJ, Guiducci S, Herrick A, Hsu VM, Jimenez S, Kahaleh B, Merkel PA, Sierakowski S, Silver RM, Simms RW, Varga J, Pope JE (2013) 2013 classification criteria for systemic sclerosis: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Collaborative Initiative. Ann Rheum Dis 72(11):1747–1755. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204424
Khanna D, Lovell DJ, Giannini E, Clements PJ, Merkel PA, Seibold JR, Matucci-Cerinic M, Denton CP, Mayes MD, Steen VD, Varga J, Furst DE (2008) Development of a provisional core set of response measures for clinical trials of systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 67(5):703–709. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2007.078923
Kirwan JR, Tugwell PS (2011) Overview of the patient perspective at OMERACT 10--conceptualizing methods for developing patient-reported outcomes. J Rheumatol 38(8):1699–1701. https://doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.110388
Boers M, Kirwan JR, Wells G, Beaton D, Gossec L, d’Agostino MA, Conaghan PG, Bingham CO 3rd, Brooks P, Landewe R, March L, Simon LS, Singh JA, Strand V, Tugwell P (2014) Developing core outcome measurement sets for clinical trials: OMERACT filter 2.0. J Clin Epidemiol 67(7):745–753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2013.11.013
Giuliodori G, Fraticelli P, Bartolini M, Cagnetti C, Baruffaldi R, Rocchi MBL, Provinciali L, Gabrielli A, Silvestrini M (2009) Cognitive and cerebral hemodynamic impairment in scleroderma patients. Eur J Neurol 16(12):1285–1290
Yilmaz N, Mollahasanoglu A, Gurvit H, Can M, Tuncer N, Inanc N, Yavuz S (2012) Dysexecutive syndrome: a specific pattern of cognitive impairment in systemic sclerosis. Cogn Behav Neurol 25(2):57–62
Silvestrini M, Vernieri F, Pasqualetti P, Matteis M, Passarelli F, Troisi E, Caltagirone C (2000) Impaired cerebral vasoreactivity and risk of stroke in patients with asymptomatic carotid artery stenosis. Jama 283(16):2122–2127
Heron E, Fornes P, Rance A, Emmerich J, Bayle O, Fiessinger JN (1998) Brain involvement in scleroderma: two autopsy cases. Stroke 29(3):719–721
Kramer JH, Reed BR, Mungas D, Weiner MW, Chui HC (2002) Executive dysfunction in subcortical ischaemic vascular disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 72(2):217–220. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.72.2.217
Sakr BR, Rabea RE, Aboulfotooh AM, Kishk NA (2019) Neurosonological and cognitive screening for evaluation of systemic sclerosis patients. Clin Rheumatol 38(7):1905–1916. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-019-04468-7
Rodnan GP, Myerowitz RL, Justh GO (1980) Morphologic changes in the digital arteries of patients with progressive systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) and Raynaud phenomenon. Medicine 59(6):393–408. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005792-198011000-00001
Carvalho D, Savage CO, Black CM, Pearson JD (1996) IgG antiendothelial cell autoantibodies from scleroderma patients induce leukocyte adhesion to human vascular endothelial cells in vitro. Induction of adhesion molecule expression and involvement of endothelium-derived cytokines. J Clin Invest 97(1):111–119. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci118377
Schachna L, Wigley FM (2002) Targeting mediators of vascular injury in scleroderma. Curr Opin Rheumatol 14(6):686–693. https://doi.org/10.1097/00002281-200211000-00010
Burfeind KG, Murchison CF, Westaway SK, Simon MJ, Erten-Lyons D, Kaye JA, Quinn JF, Iliff JJ (2017) The effects of noncoding aquaporin-4 single-nucleotide polymorphisms on cognition and functional progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement 3(3):348–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trci.2017.05.001
Jarius S, Jacobi C, de Seze J, Zephir H, Paul F, Franciotta D, Rommer P, Mader S, Kleiter I, Reindl M, Akman-Demir G, Seifert-Held T, Kristoferitsch W, Melms A, Wandinger K-P, Wildemann B (2011) Frequency and syndrome specificity of antibodies to aquaporin-4 in neurological patients with rheumatic disorders. Mult Scler J 17(9):1067–1073. https://doi.org/10.1177/1352458511403958
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EK, NAF, and RMI contributed to study design, case recruitment, acquisition and interpretation of data, statistical analysis, writing of manuscript, multiple revisions, and approval of the manuscript. MHE and NMAA contributed to data acquisition, revision, and final approval of the version of the article to be published. DEF contributed to interpretation of data, statistical analysis, multiple revisions, and approval of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The Ethics Committee of Assiut University Hospitals approved study protocols, and each participant signed a written informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khedr, E.M., El Fetoh, N.A., Gamal, R.M. et al. Evaluation of cognitive function in systemic sclerosis patients: a pilot study. Clin Rheumatol 39, 1551–1559 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-019-04884-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-019-04884-9