Abstract
Introduction
Chest radiography (CXR) is commonly performed in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), particularly for the diagnosis of pulmonary disease. However, other structures are visible on CXR, abnormalities of which may contribute to morbidity and early mortality. This study was undertaken to evaluate the extent of CXR abnormalities in RA patients.
Methods
Consecutive out-patients meeting the 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria for RA were included. The most recent CXR was assessed by two independent reviewers. Abnormalities identified were recorded and compared to the formal CXR report. Predictors of abnormalities on CXR were assessed using chi-squared tests. SPSS 18.0 was used for statistical analysis.
Results
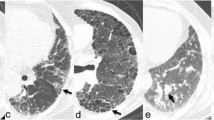
One hundred and ninety-eight patients were included. Mean age was 62 years (range 18–90). One hundred and nine (55.1%) were current or ex-smokers. One hundred and fifty-six (79%) patients were seropositive and 123 (62.1%) had joint erosions. A recent CXR was available in 163 (82%) cases. Abnormalities were identified in 129 (79.1%). Ninety-seven (60%) had bony abnormalities. Seventy-one (43.6%) had pulmonary abnormalities; old tuberculosis in 34 (20.9%), hyperinflation in 24 (14.7%), interstitial changes in 20 (13.3%), nodules in 4 (2.4%), consolidation in 2 (1.2%), and pneumothorax in 1 (0.6%). Cardiomegaly was identified in 37 (22.7%) and aortic calcification in 24 (14.7%). Age (p = 0.001), male gender (p = 0.01), and seropositivity (p = 0.04) were significantly associated with lung abnormalities. Cardiomegaly was associated with hypertension (p = 0.012) and ischaemic heart disease (p = 0.018).
Conclusion
Abnormalities were identified in 79% of chest radiographs in RA patients. Sixty-six percent of these were not reported. Clinicians need to be aware of the need to check for abnormalities.
Key Points • RA patients have a high prevalence of CXR abnormalities. • Many of these are of clinical significance. • Age, being male, and seropositivity were associated with lung abnormalities. |

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brooks PM (2006) The burden of musculoskeletal disease--a global perspective. Clin Rheumatol 25(6):778–781. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-006-0240-3
Conway R, Carey JJ (2016) Methotrexate and lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Panminerva Med. https://doi.org/10.23736/S0031-0808.16.03260-2
Sokka T, Abelson B, Pincus T (2008) Mortality in rheumatoid arthritis: 2008 update. Clin Exp Rheumatol 26(5 Suppl 51):S35–S61
Wasko MC, Dasgupta A, Hubert H, Fries JF, Ward MM (2013) Propensity-adjusted association of methotrexate with overall survival in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 65(2):334–342. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.37723
Lacaille D, Avina-Zubieta JA, Sayre EC, Abrahamowicz M (2017) Improvement in 5-year mortality in incident rheumatoid arthritis compared with the general population-closing the mortality gap. Ann Rheum Dis 76(6):1057–1063. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209562
de Vries-Bouwstra JK, Huizinga TW, Willems LN, van der Helm-van Mil AH (2012) Diagnostic value of performing chest x-rays in patients presenting with recent-onset arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 71(4):627–628. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200319
(2005) BTS recommendations for assessing risk and for managing Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection and disease in patients due to start anti-TNF-alpha treatment. Thorax. 60(10):800–805. https://doi.org/10.1136/thx.2005.046797
Ledingham J, Gullick N, Irving K, Gorodkin R, Aris M, Burke J, Gordon P, Christidis D, Galloway S, Hayes E, Jeffries A, Mercer S, Mooney J, van Leuven S, Galloway J, on behalf of the BSR and BHPR Standards, Guidelines and Audit Working Group (2017) BSR and BHPR guideline for the prescription and monitoring of non-biologic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs. Rheumatology (Oxford) 56(6):865–868. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kew479
Ropp A, Waite S, Reede D, Patel J (2015) Did I miss that: subtle and commonly missed findings on chest radiographs. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol 44(3):277–289. https://doi.org/10.1067/j.cpradiol.2014.09.003
Holland AE, Hill CJ, Glaspole I, Goh N, McDonald CF (2012) Predictors of benefit following pulmonary rehabilitation for interstitial lung disease. Respir Med 106(3):429–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2011.11.014
Combe B, Landewe R, Daien CI, Hua C, Aletaha D, Alvaro-Gracia JM et al (2017) 2016 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of early arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 76(6):948–959. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210602
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO 3rd et al (2010) 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann Rheum Dis 69(9):1580–1588. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2010.138461
Smolen JS, Landewe R, Breedveld FC, Buch M, Burmester G, Dougados M et al (2014) EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2013 update. Ann Rheum Dis 73(3):492–509. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204573
Simon TA, Thompson A, Gandhi KK, Hochberg MC, Suissa S (2015) Incidence of malignancy in adult patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis. Arthritis Res Ther 17:212. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-015-0728-9.
Gross RL, Schwartzman-Morris JS, Krathen M, Reed G, Chang H, Saunders KC, Fisher MC, Greenberg JD, Putterman C, Mease PJ, Gottlieb AB, Kremer JM, Broder A (2014) A comparison of the malignancy incidence among patients with psoriatic arthritis and patients with rheumatoid arthritis in a large US cohort. Arthritis Rheumatol 66(6):1472–1481. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.38385
Pinsky PF, Freedman M, Kvale P, Oken M, Caporaso N, Gohagan J (2006) Abnormalities on chest radiograph reported in subjects in a cancer screening trial. Chest. 130(3):688–693. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.130.3.688
Mader R, Verlaan JJ, Eshed I, Jacome BA, Puttini PS, Atzeni F, Buskila D, Reinshtein E, Novofastovski I, Fawaz A, Kurt V, Baraliakos X (2017) Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH): where we are now and where to go next. RMD Open 3(1):e000472. https://doi.org/10.1136/rmdopen-2017-000472
van der Heijde DM, van Leeuwen MA, van Riel PL, Koster AM, van 't Hof MA, van Rijswijk MH et al (1992) Biannual radiographic assessments of hands and feet in a three-year prospective follow-up of patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 35(1):26–34
Fuchs HA, Kaye JJ, Callahan LF, Nance EP, Pincus T (1989) Evidence of significant radiographic damage in rheumatoid arthritis within the first 2 years of disease. J Rheumatol 16(5):585–591
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and animal rights and informed consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goggins, M.R., Conway, R., Durcan, L.J. et al. High prevalence of abnormalities on chest radiography in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 38, 3375–3380 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-019-04717-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-019-04717-9