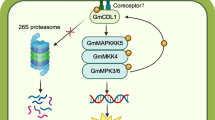
Abstract
We previously isolated the OsCBT gene, which encodes a calmodulin (CaM)-binding protein, from a rice expression library constructed from fungal elicitor-treated rice suspension cells. In order to understand the function of OsCBT in rice, we isolated and characterized a T-DNA insertion mutant allele named oscbt-1. The oscbt-1 mutant exhibits reduced levels of OsCBT transcripts and no significant morphological changes compared to wild-type plant although the growth of the mutant is stunted. However, oscbt-1 mutants showed significant resistance to two major rice pathogens. The growth of the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe grisea, as well as the bacterial pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae was significantly suppressed in oscbt-1 plants. Histochemical analysis indicated that the hypersensitive-response was induced in the oscbt-1 mutant in response to compatible strains of fungal pathogens. OsCBT expression was induced upon challenge with fungal elicitor. We also observed significant increase in the level of pathogenesis-related genes in the oscbt-1 mutant even under pathogen-free condition. Taken together, the results support an idea that OsCBT might act as a negative regulator on plant defense.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal, G.K., Jwa, N.S., and Rakwal, R. (2000)a. A novel rice (Oryza sativa L.) acidic PR1 gene highly responsive to cut, phytohormones, and protein phosphatase inhibitors. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 274, 157–165.
Agrawal, G.K., Rakwal, R., and Jwa, N.S. (2000)b. Rice (Oryza sativa L.) OsPR1b gene is phytohormonally regulated in close interaction with light signals. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 278, 290–298.
Ali, G.S., Reddy, V.S., Lindgren, P.B., Jakobek, J.L., and Reddy, A.S. (2003). Differential expression of genes encoding calmodulin-binding proteins in response to bacterial pathogens and inducers of defense responses. Plant Mol. Biol. 51, 803–815.
Belenghi, B., Acconcia, F., Trovato, M., Perazzolli, M., Bocedi, A., Polticelli, F., Ascenzi, P., and Delledonne, M. (2003). AtCYS1, a cystatin from Arabidopsis thaliana, suppresses hypersensitive cell death. Eur. J. Biochem. 270, 2593–2604.
Bouché, N., Scharlat, A., Snedden, W., Bouchez, D., and Fromm, H. (2002). A novel family of calmodulin-binding transcription activators in multicellular organisms. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 21851–21861.
Bouché, N., Yellin, A., Snedden, W.A., and Fromm, H. (2005). Plant-specific calmodulin-binding proteins. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 56, 435–466.
Büschges, R., Hollricher, K., Panstruga, R., Simons, G., Wolter, M., Frijters, A., van Daelen, R., van der Lee, T., Diergaarde, P., Groenendijk, J., et al. (1997). The barley Mlo gene: a novel control element of plant pathogen resistance. Cell 88, 695–705.
Cheong, Y.H., Moon, B.C., Kim, J.K., Kim, C.Y., Kim, M.C., Kim, I.H., Park, C.Y., Kim, J.C., Park, B.O., Koo, S.C., et al. (2003). BWMK1, a rice mitogen-activated protein kinase, locates in the nucleus and mediates pathogenesis-related gene expression by activation of a transcription factor. Plant Physiol. 132, 1961–1972.
Chisholm, S.T., Coaker, G., Day, B., and Staskawicz, B.J. (2006). Host-microbe interactions: shaping the evolution of the plant immune response. Cell 124, 803–814.
Choi, M.S., Kim, M.C., Yoo, J.H., Moon, B.C., Koo, S.C., Park, B.O., Lee, J.H., Koo, Y.D., Han, H.J., Lee, S.Y., et al. (2005). Isolation of a calmodulin-binding transcription factor from rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Biol. Chem. 28O, 40820–40831.
da Costa e Silva, O. (1994). CG-1, a parsley light-induced DNA-binding protein. Plant Mol. Biol. 25, 921–924.
Dangl, J.L., and Jones, J.D. (2001). Plant pathogens and integrated defence responses to infection. Nature 411, 826–833.
Dietrich, R.A., Richberg, M.H., Schmidt, R., Dean, C., and Dangl, J.L. (1997). A novel zinc finger protein is encoded by the Arabidopsis LSD1 gene and functions as a negative regulator of plant cell death. Cell 88, 685–694.
Diez-Navajas, A.M., Greif, C., Poutaraud, A., and Merdinoglu, D. (2007). Two simplified fluorescent staining techniques to observe infection structures of the oomycete Plasmopara viticola in grapevine leaf tissues. Micron 38, 680–683.
Eulgem, T. (2005). Regulation of the Arabidopsis defense transcriptome. Trends Plant Sci. 10, 71–78.
Finkler, A., Ashery-Padan, R., and Fromm, H. (2007). CAMTAs: calmodulin-binding transcription activators from plants to human. FEBS Lett. 581, 3893–3898.
Galon, Y., Nave, R., Boyce, J.M., Nachmias, D., Knight, M.R., and Fromm, H. (2008). Calmodulin-binding transcription activator (CAMTA) 3 mediates biotic defense responses in Arabidopsis. FEBS Lett. 582, 943–948.
Greenberg, J.T., and Yao, N. (2004). The role and regulation of programmed cell death in plant-pathogen interactions. Cell Microbiol. 6, 201–211.
Guimil, S., Chang, H.S., Zhu, T., Sesma, A., Osbourn, A., Roux, C., Ioannidis, V., Oakeley, E.J., Docquier, M., Descombes, P., et al. (2005). Comparative transcriptomics of rice reveals an ancient pattern of response to microbial colonization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 8066–8070.
Heil, M. (2002). Ecological costs of induced resistance. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 5, 345–350.
Heo, W.D., Lee, S.H., Kim, M.C., Kim, J.C., Chung, W.S., Chun, H.J., Lee, K.J., Park, C.Y., Park, H.C., Choi, J.Y., et al. (1999). Involvement of specific calmodulin isoforms in salicylic acid-independent activation of plant disease resistance responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 766–771.
Jeong, D.H., An, S., Kang, H.G., Moon, S., Han, J.J., Park, S., Lee, H.S., An, K., and An, G. (2002). T-DNA insertional mutagenesis for activation tagging in rice. Plant Physiol. 130, 1636–1644.
Jones, J.D., and Dangl, J.L. (2006). The plant immune system. Nature 444, 323–329.
Jung, Y.H., Lee, J.H., Agrawal, G.K., Rakwal, R., Kim, J.A., Shim, J.K., Lee, S.K., Jeon, J.S., Koh, H.J., Lee, Y.H., et al. (2005). The rice (Oryza sativa) blast lesion mimic mutant, blm, may confer resistance to blast pathogens by triggering multiple defense-associated signaling pathways. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 43, 397–406.
Kim, M.C., Panstruga, R., Elliott, C., Muller, J., Devoto, A., Yoon, H.W., Park, H.C., Cho, M.J., and Schulze-Lefert, P. (2002a). Calmodulin interacts with MLO protein to regulate defence against mildew in barley. Nature 416, 447–451.
Kim, M.C., Lee, S.H., Kim, J.K., Chun, H.J., Choi, M.S., Chung, W.S., Moon, B.C., Kang, C.H., Park, C.Y., Yoo, J.H., et al. (2002b). Mlo, a modulator of plant defense and cell death, is a novel calmodulin-binding protein. Isolation and characterization of a rice Mlo homologue. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 19304–19314.
Kim, C.Y., Koo, Y.D., Jin, J.B., Moon, B.C., Kang, C.H., Kim, S.T., Park, B.O., Lee, S.Y., Kim, M.L., Hwang, I., et al. (2003). Rice C2-domain proteins are induced and translocated to the plasma membrane in response to a fungal elicitor. Biochemistry 42, 11625–11633.
Kim, S.T., Kim, S.G., Hwang, D.H., Kang, S.Y., Kim, H.J., Lee, B.H., Lee, J.J., and Kang, K.Y. (2004). Proteomic analysis of pathogen-responsive proteins from rice leaves induced by rice blast fungus, Magnaporthe grisea. Proteomics 4, 3569–3578.
Kottapalli, K.R., Rakwal, R., Satoh, K., Shibato, J., Kottapalli, P., Iwahashi, H., and Kikuchi, S. (2007). Transcriptional profiling of indica rice cultivar IET8585 (Ajaya) infected with bacterial leaf blight pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv oryzae. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 45, 834–850.
Lee, S., Kim, J., Son, J.S., Nam, J., Jeong, D.H., Lee, K., Jang, S., Yoo, J., Lee, J., Lee, D.Y., et al. (2003). Systematic reverse genetic screening of T-DNA tagged genes in rice for functional genomic analyses: MADS-box genes as a test case. Plant Cell Physiol. 44, 1403–1411.
Lorrain, S., Vailleau, F., Balague, C., and Roby, D. (2003). Lesion mimic mutants: keys for deciphering cell death and defense pathways in plants? Trends Plant Sci. 8, 263–271.
Ma, W., and Berkowitz, G.A. (2007). The grateful dead: calcium and cell death in plant innate immunity. Cell Microbiol. 9, 2571–2585.
Maleck, K., Levine, A., Eulgem, T., Morgan, A., Schmid, J., Lawton, K.A., Dangl, J.L., and Dietrich, R.A. (2000). The transcriptome of Arabidopsis thaliana during systemic acquired resistance. Nat. Genet. 26, 403–410.
McGee, J.D., Hamer, J.E., and Hodges, T.K. (2001). Characterization of a PR-10 pathogenesis-related gene family induced in rice during infection with Magnaporthe grisea. Mol. Plant Microbe. Interact. 14, 877–886.
Park, C.Y., Lee, J.H., Yoo, J.H., Moon, B.C., Choi, M.S., Kang, Y.H., Lee, S.M., Kim, H.S., Kang, K.Y., Chung, W.S., et al. (2005). WRKY group IId transcription factors interact with calmodulin. FEBS Lett. 579, 1545–1550.
Reddy, A.S., Reddy, V.S., and Golovkin, M. (2000). A calmodulin binding protein from Arabidopsis is induced by ethylene and contains a DNA-binding motif. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 279, 762–769.
Snedden, W.A., and Fromm, H. (1998) Calmodulin, calmodulin-related proteins and plant responses to the environment. Trends Plant Sci. 5, 154–159.
Szymanski, D.B., Liao, B., and Zielinski, R.E. (1996). Calmodulin isoforms differentially enhance the binding of cauliflower nuclear proteins and recombinant TGA3 to a region derived from the Arabidopsis Cam-3 promoter. Plant Cell 8, 1069–1077.
Takabatake, R., Karita, E., Seo, S., Mitsuhara, I., Kuchitsu, K., and Ohashi, Y. (2007). Pathogen-induced calmodulin isoforms in basal resistance against bacterial and fungal pathogens in tobacco. Plant Cell Physiol. 48, 414–423.
Tao, Y., Xie, Z., Chen, W., Glazebrook, J., Chang, H.S., Han, B., Zhu, T., Zou, G., and Katagiri, F. (2003). Quantitative nature of Arabidopsis responses during compatible and incompatible interactions with the bacterial pathogen Pseudomonas syringae. Plant Cell 15, 317–330.
Veronese, P., Ruiz, M.T., Coca, M.A., Hernandez-Lopez, A., Lee, H., Ibeas, J.I., Damsz, B., Pardo, J.M., Hasegawa, P.M., Bressan, R.A., et al. (2003). In defense against pathogens. Both plant sentinels and foot soldiers need to know the enemy. Plant Physiol. 131, 1580–1590.
White, P.J., and Broadley, M.R. (2003). Calcium in plants. Ann. Bot. (Lond). 92, 487–511.
Yang, T., and Poovaiah, B.W. (2000). An early ethylene up-regulated gene encoding a calmodulin-binding protein involved in plant senescence and death. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 38467–38473.
Yang, T., and Poovaiah, B.W. (2002). A calmodulin-binding/CGCG box DNA-binding protein family involved in multiple signaling pathways in plants. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 45049–45058.
Yang, T., and Poovaiah, B.W. (2003). Calcium/calmodulin-mediated signal network in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 8, 505–512.
Yin, Z., Chen, J., Zeng, L., Goh, M., Leung, H., Khush, G.S., and Wang, G.L. (2000). Characterizing rice lesion mimic mutants and identifying a mutant with broad-spectrum resistance to rice blast and bacterial blight. Mol. Plant Microbe. Interact. 13, 869–876.
Yoo, J.H., Park, C.Y., Kim, J.C., Heo, W.D., Cheong, M.S., Park, H.C., Kim, M.C., Moon, B.C., Choi, M.S., Kang, Y.H., et al. (2005). Direct interaction of a divergent CaM isoform and the transcription factor, MYB2, enhances salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. J. Biol. Chem. 28O, 3697–3706.
Yu, I.C., Parker, J., and Bent, A.F. (1998). Gene-for-gene disease resistance without the hypersensitive response in Arabidopsis dnd1 mutant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 7819–7824.
Zegzouti, H., Jones, B., Frasse, P., Marty, C., Maitre, B., Latch, A., Pech, J.C., and Bouzayen, M. (1999). Ethylene-regulated gene expression in tomato fruit: characterization of novel ethylene-responsive and ripening-related genes isolated by differential display. Plant J. 18, 589–600.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Koo, S.C., Choi, M.S., Chun, H.J. et al. The calmodulin-binding transcription factor OsCBT suppresses defense responses to pathogens in rice. Mol Cells 27, 563–570 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-009-0081-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-009-0081-4