Abstract
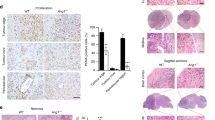
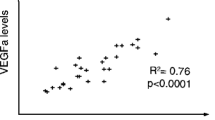
We have established a pair of animal models (J3T-1 and J3T-2) with different invasive and angiogenic phenotypes, and demonstrated that annexin A2 is expressed at higher levels in J3T-1 than J3T-2 cells. The function of annexin A2 in relation to angiogenesis and invasion was investigated using these models. Stable silencing or overexpression of annexin A2 in J3T-1 and J3T-2 cells (J3T-1shA and J3T-2A cells) was established and used. Thirty human glioblastoma samples were evaluated for expression of annexin A2, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF). Immunohistochemical and quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction analyses revealed higher expression of annexin A2, VEGF and PDGF in J3T-1 and J3T-2A cells. Cultured J3T-1 and J3T-2A cells exhibited higher adhesive ability to endothelial cells. Histopathological analysis of animal brain tumors revealed that J3T-1 and J3T-2A tumors displayed marked angiogenesis and invasion along the neovasculature, whereas J3T-2 and J3T-1shA tumors exhibited diffuse, infiltrative invasion without angiogenesis. Positive expression of annexin A2 was observed in tumor cells surrounding dilated vessels in 25/30 human glioblastoma specimens. Our results reveal that the phenotype of glioma invasion is closely related to angiogenesis. We identify annexin A2 as a factor regulating angiogenesis and invasion of malignant gliomas.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ et al (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352(10):987–996
Onishi M, Ichikawa T, Kurozumi K, Date I (2011) Angiogenesis and invasion in glioma. Brain Tumor Pathol 28(1):13–24
Inoue S, Ichikawa T, Kurozumi K et al (2012) Novel animal glioma models that separately exhibit two different invasive and angiogenic phenotypes of human glioblastomas. World Neurosurg 78(6):670–682
Maruo T, Ichikawa T, Kanzaki H et al (2013) Proteomics-based analysis of invasion-related proteins in malignant gliomas. Neuropathology 33(3):264–275
Tatenhorst L, Rescher U, Gerke V, Paulus W (2006) Knockdown of annexin 2 decreases migration of human glioma cells in vitro. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 32(3):271–277
Onishi M, Ichikawa T, Kurozumi K et al (2013) Bimodal anti-glioma mechanisms of cilengitide demonstrated by novel invasive glioma models. Neuropathology 33(2):162–174
Godiksen S, Selzer-Plon J, Pedersen ED et al (2008) Hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor-1 has a complex subcellular itinerary. Biochem J 413(2):251–259
Nakamori S, Okamoto H, Kusama T et al (1997) Increased endothelial cell retraction and tumor cell invasion by soluble factors derived from pancreatic cancer cells. Ann Surg Oncol 4(4):361–368
Ichikawa T, Tamiya T, Adachi Y et al (2000) In vivo efficacy and toxicity of 5-fluorocytosine/cytosine deaminase gene therapy for malignant gliomas mediated by adenovirus. Cancer Gene Ther 7(1):74–82
Moss SE, Morgan RO (2004) The annexins. Genome Biol 5(4):219
Emoto K, Sawada H, Yamada Y et al (2001) Annexin II overexpression is correlated with poor prognosis in human gastric carcinoma. Anticancer Res 21(2B):1339–1345
Duncan R, Carpenter B, Main LC, Telfer C, Murray GI (2008) Characterisation and protein expression profiling of annexins in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 98(2):426–433
Esposito I, Penzel R, Chaib-Harrireche M et al (2006) Tenascin C and annexin II expression in the process of pancreatic carcinogenesis. J Pathol 208(5):673–685
Sharma MR, Koltowski L, Ownbey RT, Tuszynski GP, Sharma MC (2006) Angiogenesis-associated protein annexin II in breast cancer: selective expression in invasive breast cancer and contribution to tumor invasion and progression. Exp Mol Pathol 81(2):146–156
Zimmermann U, Woenckhaus C, Pietschmann S et al (2004) Expression of annexin II in conventional renal cell carcinoma is correlated with Fuhrman grade and clinical outcome. Virchows Arch 445(4):368–374
Syed SP, Martin AM, Haupt HM, Arenas-Elliot CP, Brooks JJ (2007) Angiostatin receptor annexin II in vascular tumors including angiosarcoma. Hum Pathol 38(3):508–513
Reeves SA, Chavez-Kappel C, Davis R, Rosenblum M, Israel MA (1992) Developmental regulation of annexin II (Lipocortin 2) in human brain and expression in high grade glioma. Cancer Res 52(24):6871–6876
Roseman BJ, Bollen A, Hsu J, Lamborn K, Israel MA (1994) Annexin II marks astrocytic brain tumors of high histologic grade. Oncol Res 6(12):561–567
Iwadate Y, Sakaida T, Hiwasa T et al (2004) Molecular classification and survival prediction in human gliomas based on proteome analysis. Cancer Res 64(7):2496–2501
Rescher U, Gerke V (2004) Annexins–unique membrane binding proteins with diverse functions. J Cell Sci 117(Pt 13):2631–2639
Sharma MC, Sharma M (2007) The role of annexin II in angiogenesis and tumor progression: a potential therapeutic target. Curr Pharm Des 13(35):3568–3575
Tressler RJ, Updyke TV, Yeatman T, Nicolson GL (1993) Extracellular annexin II is associated with divalent cation-dependent tumor cell-endothelial cell adhesion of metastatic RAW117 large-cell lymphoma cells. J Cell Biochem 53(3):265–276
Jung Y, Wang J, Song J et al (2007) Annexin II expressed by osteoblasts and endothelial cells regulates stem cell adhesion, homing, and engraftment following transplantation. Blood 110(1):82–90
Bao H, Jiang M, Zhu M, Sheng F, Ruan J, Ruan C (2009) Overexpression of Annexin II affects the proliferation, apoptosis, invasion and production of proangiogenic factors in multiple myeloma. Int J Hematol 90(2):177–185
Zhao SH, Pan DY, Zhang Y, Wu JH, Liu X, Xu Y (2010) Annexin A2 promotes choroidal neovascularization by increasing vascular endothelial growth factor expression in a rat model of argon laser coagulation-induced choroidal neovascularization. Chin Med J (Engl) 123(6):713–721
Zagzag D, Amirnovin R, Greco MA et al (2000) Vascular apoptosis and involution in gliomas precede neovascularization: a novel concept for glioma growth and angiogenesis. Lab Invest 80(6):837–849
de Groot JF, Fuller G, Kumar AJ et al (2010) Tumor invasion after treatment of glioblastoma with bevacizumab: radiographic and pathologic correlation in humans and mice. Neuro Oncol 12(3):233–242
Sun H, Guo D, Su Y, Yu D, Wang Q et al (2014) Hyperplasia of pericytes is one of the main characteristics of microvascular architecture in malignant glioma. PLoS One 9(12):e114246
Kesavan K, Ratliff J, Johnson EW et al (2010) Annexin A2 is a molecular target for TM601, a peptide with tumor-targeting and anti-angiogenic effects. J Biol Chem 285(7):4366–4374
Acknowledgments
We thank M. Arao, A. Ishikawa and N. Uemori for their technical assistance. The following medical students also contributed to the animal experiments: T. Mifune, S. Murai, M. Matsueda, H. Matsumoto and Y. Yoshida. This study was supported by Grants-in-aid for Scientific Research from the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to T.I. (No. 19591675; No. 22591611) and K.K. (No. 20890133; No. 21791364).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Onishi, M., Ichikawa, T., Kurozumi, K. et al. Annexin A2 regulates angiogenesis and invasion phenotypes of malignant glioma. Brain Tumor Pathol 32, 184–194 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10014-015-0216-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10014-015-0216-6